Summary
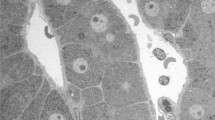
The parasinusoidal cells of the liver (Ito cells) were demonstrated light microscopically in autopsy specimens fixed in formalin and stained with Oil red O after dichromate treatment. The method allows examination of large samples containing numerous acini.
Quantitative assessment showed a zonal gradient with 6.3 and 7.7 parasinusoidal cells per 62.5 × 103 µm2 in zone 1 and 3, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aterman K (1986) The parasinusoidal cells of the liver: A historical account. Histochem J 18:299–305
Bronfenmajer S, Schaffner F, Popper H (1966) Fat-storing cells (lipocytes) in human liver. Arch Pathol 22:447–453
De Leeuw AM, McCarthy SP, Geerts A, Knook DL (1984) Purified rat liver fat-storing cells in culture divide and contain collagen. Hepatology 4:392–403
Giampieri MP, Jezequel AM, Orlandi F (1981) The lipocytes in normal human liver. A quantitative study. Digestion 22:165–169
Horn T, Lyon H, Christoffersen P (1986a) The “Blood-Hepatocyt Barrier”. A light microscopical transmission- and scanning electron microscopic study. Liver 6:233–245
Horn T, Junge J, Christoffersen P (1986b) Activation of the lipocytes in zone 3 and correlation to degree of collagen formation in the Disse space. J Hepatol 3:333–340
Lillie RD, Fullmer HM (1976) Histopathologic technic and practical histochemistry, 4th Ed. Mc-Graw-Hill Inc New York pp 682–765
Mak KM, Leo MA, Liber CS (1984) Alcoholic liver injury in baboons. Transformation of lipocytes to transitional cells. Gastroenterology 87:188–200
McGee JOD, Patrick RS (1972) The role of perisinusoidal cells in hepatic fibrogenesis. An electron microscopic study of acute carbon tetrachloride liver injury. Lab Invest 26:429–440
Minato Y, Hasumura Y, Takeuchi J (1983) The role of fatstoring cells in Disse space fibrogenesis in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 3:559–566
Okanoue T, Burbige EJ, French SW (1982) The role of the Ito cell in perivenular and centrolobular fibrosis in alcoholic hepatitis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 107:459–463
Wake K (1980) Perisinusoidal stellate cells (fat-storing cells, interstitial cells, lipocytes), their related structures in and around the liver sinusoids, and vitamin A-storing cells in extrahepatic organs. In: Bourne GH, Danielli JF, Jeon KWT (eds) International Review of Cytology. Academic Press, New York London, Vol 66, pp 303–353
Wake K, Motonatsu K, Senoo H, Masuda A, Adachi E (1986) Improved Kupffer's gold chloride method for demonstrating the stellate cells (vitamin A-storing cells) in the liver and extrahepatic organs of vertebrae. Stain Technology 61:193–200
Yokoi Y, Namihisa T, Kuroda H, Komatsu J, Miyazaki A, Watanabe S, Usui K (1984) Immunocytochemical detection of desmin in fat-storing cells (Ito-cells). Hepatology 4:709–714
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horn, T., Junge, J., Nielsen, O. et al. Light microscopical demonstration and zonal distribution of parasinusoidal cells (Ito cells) in normal human liver. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 413, 147–149 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749676
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749676