Summary
-
1.
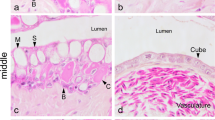
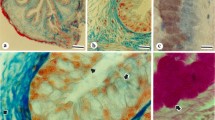
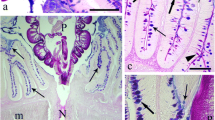
The structure of mucus in the oesophagus of the sea-water adapted eel, consists of a framework of fibers decreasing in density and thickness from the anterior to the posterior oesophagus.
-
2.
With seawater in the lumen the mucus layer supports, in vitro, about 45% of the lumen to serosa gradient of sodium ion activity along the whole oesophagus. It supports different chloride ion activity gradients: about 80% in the anterior and about 45% in the middle and posterior oesophagus. These results are confirmed by X-ray micro-analysis.
-
3.
Experiments without lumen-to-serosa gradients demonstrate a linked sodium and chloride active absorption appearing in the middle oesophagus and increasing towards the posterior oesophagus.
-
4.
Na+−K+-ATPase is cytochemically demon-strated but could not be inhibited by ouabaïn during in vitro experiments, due to its particular localization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SW :
-
seawater
- FW :
-
freshwater
- SEM :
-
scanning electron microscope
- TEM :
-
transmission electron microscope
- ISM :
-
ion-selective microelectrode
References
Allen A, Pain RH, Robson TR (1976) Model for the structure of the gastric mucous gel. Nature 264:88–89
Allen A, Flemström G, Garner A, Silen W, Turnberg LA (1984) Mechanisms of mucosal protection in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Raven Press, New York
Armstrong W McD, Garcia-Diaz JF (1980) Ion-selective micro-electrodes: theory and technique. Federation Proc 39:2851–2859
Bert P (1871) Sur les phénomènes et les causes de la mort des animaux d'eau douce que l'on plonge dans l'eau de mer. CR Acad Sci Paris 75:382–385, 464–467
Clamp JR, Cooper B, Creeth M, Ene D, Barrett J, Gouth M (1983) The presence of polysaccharides in normal human gastric mucus. Biochem J 215:421–423
Ernst SA (1972) Transport adenosine triphosphatase cytochemistry. 1. Biochemical characterization of a cytochemical medium for the ultrastructural localization of ouabaïne-sensitive, potassium-dependent phosphatase activity in the avian salt gland. J Histochem Cytochem 20:13–22
Engelhardt W von, Rechkemmer G (1983) Absorption of inorganic ions and short-chain fatty acids in the colon of mammals. In: Gilles-Baillien M, Gilles R (eds) Intestinal Transport. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 26–45
Fauconneau B, Saglio P (1984) Protein-bound and free amino acid content in the skin mucus of the European eelAnguilla anguilla (L.). Comp Biochem Physiol 77B:513–516
Field M, Karnaky KJ, Smith PL, Bolton JE, Kinter WB (1978) Ion transport across the isolated intestinal mucosa of the winter flounder,Pseudopleuronectes americanus. I. Functional and structural properties of cellular and paracellular pathways for Na and Cl. J Membrane Biol 41:265–293
Flood PR (1981) On the ultrastructure of mucus. Biomed Res 2:49–53
Flood PR, Fiala-Medioni A (1981) Ultrastructure and histochemistry of the food trapping mucous film in benthic filter-feeders (Ascidians). Acta Zool 62:53–65
Frizzell RA, Field M, Schultz SG (1979) Sodium-coupled chloride transport by epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol 236:F1-F8
Garner A, Flemström G, Allen A, Heylings JR McQueen S (1984) Gastric mucosal protective mechanisms: roles of epithelial bicarbonate and mucus secretions. Scand J Gastroenterol 19:79–86
Gilles-Baillien M (1983) Several compartments involved in intestinal transport. In: Gilles-Baillien M, Gilles R (eds) Intestinal transport. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 103–119
Humbert W, Kirsch R, Meister MF (1984) Scanning electron microscopic study of the oesophageal mucous layer in the eel,Anguilla anguilla, L. J Fish Biol 25:117–122
Jehl B, Bauer B, Dörge A, Rick K (1981) The use of propane/isopentane mixtures for rapid freezing of biological specimens. J Microsc 123:307–309
Kirsch R, Guinier D, Meens R (1975) L'équilibre hydrique de l'anguille européenne (Anguilla anguilla L.). Etude du rôle de l'oesophage dans l'utilisation de l'eau de boisson et étude de la perméabilité osmotique branchiale. J Physiol (Paris) 70:605–626
Kirsch R (1978) Role of the oesophagus in osmoregulation in teleost fishes. In: Jorgensen CB, Skadhauge E (eds) Osmotic and volume regulation. Alfred Benzon Symposium XI, Munskgaard. Academic Press, New York, pp 138–154
Kirsch R, Meister MF (1982) Progressive processing of ingested water in the gut of sea-water teleosts. J Exp Biol 98:67–81
Kirsch R, Humbert W, Rodeau JL (1984) Control of the blood osmolarity in fishes, with references to the functional anatomy of the gut. In: Pequeux A, Gilles R, Bolis A (eds) Osmo-regulation in estuarine and marine animals. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 67–92
Kirsch R, Humbert W, Simonneaux V (1985) The gut as an osmoregulatory organ: comparative aspects and special references to fishes. In: Gilles R, Gilles-Baillien M (eds) Transport processes, Iono- and osmoregulation. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 265–277
Kirschner LB (1978) External charged layer and Na+ regulation. In: Jorgensen CB, Skadhauge E (eds) Osmotic and volume regulation. Alfred Benzon symposium XI, Munskgaard. Academic Press, New York, pp 310–321
Laurent P, Kirsch R (1975) Modifications structurales de l'oesophage liées à l'osmorégulation chez l'anguille. CR Acad Sci Paris 280:2227–2229
Lee CO (1981) Determination of selectivity coefficients of ion-selective microelectrodes. In: Sykova E, Hnick P, Vyklicky L (eds) Ion-selective microelectrodes and their use in excitable tissues. Plenum Press, New York, pp 47–52
Lemoine AM, Olivereau M (1973a) Variations de la teneur en acide N-acetyl-neuraminique de la branchie de l'anguille au cours des changements de salinité. CR Soc Biol 167:411–416
Lemoine AM, Olivereau M (1973b) Variations de la teneur en acide N-acetyl-neuraminique de l'intestin de l'anguille, au cours des changements de salinité. CR Soc Biol 167:644–649
Marriott C (1983) The effects of drugs on the structure and secretion of mucus. Pharm Int Dec 1983:320–323
Marshall WS (1978) On the involvement of mucous secretion in teleost osmoregulation. Can J Zool 56:1088–1091
Meier PC, Lanter F, Ammann D, Steiner RA, Simon W (1982) Applicability of available ion-selective liquid-membrane microelectrodes to intracellular ion-activity measurements. Pflügers Arch 393:23–30
Meister MF, Humbert W, Kirsch R, Vivien-Roëls B (1983) Structure and ultrastructure of the oesophagus in sea-water and fresh-water teleosts (Pisces). Zoomorphology 102:33–51
Nonnotte G (1983) Fonctions de la peau des téléotéens: étude expérimentale des échanges respiratoires et des échanges ioniques. Thèse, Strasbourg
Olivereau M, Lemoine AM (1972) Effects des variations de la salinité externe sur la teneur en acide N-acetyl-neuraminique (ANAN) de la peau chez l'Anguille. J Comp Physiol 79:411–422
Parmelee JT, Renfro JL (1983) Esophageal desalination of sea-water in flounder: role of active sodium transport. Am J Physiol 245:R888–R893
Parson R (1959) Handbook of electrochemical constants. Butterworths, London
Pärt P, Lock RAC (1983) Diffusion of calcium, cadmium and mercury in a mucous solution from rainbow trout. Comp Biochem Physiol 76C:259–263
Portier P, Duval M (1922) Variations de la pression osmotique du sang de l'anguille essuyée en fonction des modifications de la salinité du milieu exterieur. CR Acad Sci Paris 175:1100–1105
Robinson RA, Stokes RH (1959) Electrolyte solutions. Butter-worths, London
Sakata T, Engelhardt von W (1981) Luminal mucin in the large intestine of mice, rats and guinea pigs. Cell Tissue Res 219:629–635
Shelhamer JH, Marom Z, Logun C, Kaliner M (1984) Human respiratory mucous glycoproteins. Exp Lung Res 7:149–162
Shephard KL (1981) The influence of mucus on the diffusion of water across fish epidermis. Physiol Zool 54:224–229
Shephard KL (1982) The influence of mucus on the diffusion of ions across the oesophagus of fish. Physiol Zool 55:23–34
Shephard KL (1984a) Diffusion of chloride ions in the mucus of the oesophagus ofEnophrys bison, a marine teleost fish. Pflügers Arch 402:207–210
Shephard KL (1984b) The influence of mucus on the diffusion of the chloride ions across the oesophagus of the minnow (Phoxinus phoxinus L.). J Physiol 346:449–460
Shiau YF, Fernandez P, Jackson MJ, McMonagle S (1985) Mechanisms maintaining a low-pH microclimate in the intestine. Am J Physiol 248:G608–G617
Singh B, Thakur R (1975) A histochemical study on the respiratory epithelia of an eel fish,Amphipnous cuchia. Acta Hist 54:161–167
Skadhauge E (1974) Coupling of transmural flows of NaCl and water in the intestine of the eel (Anguilla anguilla). J Exp Biol 60:535–546
Schlichter LC (1982) Unstirred mucous layers: ion exchange properties and effect on ion regulation inLymnea stagnalis. J Exp Biol 98:363–372
Stith BJ (1984) Biochemical examination ofRana pipiens epithelial mucus. J Comp Physiol B 155:89–96
Thomas RC (1978) Ion-Sensitive Intracellular Microelectrodes. Academic Press, London New York San Fransisco
Yamamoto M, Hirano T (1978) Morphological changes in the oesophageal epithelium of the eel,Anguilla japonica during adaptation to sea water. Cell Tissue Res 192:25–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simonneaux, V., Barra, J.A., Humbert, W. et al. The role of mucus in ion absorption by the oesophagus of the sea-water eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). J Comp Physiol B 157, 187–199 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692363
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692363