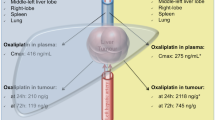
Summary
To enable the treatment of hepatic metastasis with higher, theoretically more effective, doses of systemically toxic anticancer drugs, an isolated liver perfusion (ILP) technique was developed in WAG/Ola rats. First, in a toxicity study the maximally tolerated dose (MTD) of mitomycin C (MMC) was determined for a 25-min ILP and for hepatic artery infusion (HAI) after the administration of a bolus dose. The MTD in the ILP setting (4.8 mg/kg) was 4 times that using HAI (1.2 mg/kg). Subsequently, in a rat colorectal hepatic-metastasis model, concentrations of MMC in tumour, liver, plasma and perfusate were measured during a 25-min ILP to investigate the expected pharmacokinetic advantage of ILP. The mean plasma level determined after ILP (1.2 as well as 4.8 mg/kg MMC) was significantly lower (P<0.001) than that obtained following HAI. This may explain both the absence of severe systemic toxicity and the higher MTD in ILP-treated groups. No significant difference in mean tumour and liver tissue concentrations of MMC were found when the groups treated with 1.2 mg/kg drug via HAI vs ILP were compared. The mean MMC concentration in tumour tissue was significantly higher (almost 5 times;P<0.05) in rats treated by ILP with the MTD (4.8 mg/kg) than in those treated via HAI with the MTD (1.2 mg/kg). ILP of MMC can be safely performed using a dose 4 times higher than the MTD in the HAI setting, leading to an almost 5-fold concentration of MMC in hepatic metastasis. ILP of MMC may therefore represent a promising therapy for metastasis confined to the liver.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HAI:
-
hepatic artery infusion
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- ILP:
-
isolated liver perfusion
- MMC:
-
mitomycin C
- MTD:
-
maximally tolerated dose
References
Ackerman NB (1974) The blood supply of experimental liver metatasis: IV. Changes in vascularity with increasing tumor growth. Surgery 75:589
Brauw LM de, Velde CJH van de, Tjaden UR, Bruijn EA de, Bele AVRJ, Hermans J, Zwaveling A (1988) In vivo isolated liver perfusion technique in a rat hepatic metastasis model: 5-fluorouracil concentrations in tumor tissue. J Surg Res 44:137
Bruijn EA de, Slee PHThJ, Kuppen PJK, Hoeven RA van der, Tjaden UR, Oosterom AT van, Velde CJH van de, Brauw LM de, Tanke HJ, regional chemotherapy: MMC and fluoropyrimidines. Contr Oncol 29:43
Crooke ST, Bradner WT (1976) Mitomycin C: a review. Cancer Treat Rev 3:121
Doll DC, Weiss RB, Issell BF (1985) Mitomycin: ten years after approval for marketing. J Clin Oncol 3:276
Drewinko B, Patchin M, Yang L (1981) Differential killing of twenty anti-tumor drugs on proliferating and non-proliferating human tumor cells. Cancer Res 41:2328
Ensminger WD, Gyves JW (1984) Regional cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Treat Rep 68:101
Frei E III, Canellos GP (1980) Dose: a critical factor in cancer chemotherapy. Am J Med 69:584
Griswold DP Jr., Trader MW, Frei E III, Peters WP, Wolpert MK, Laster WR Jr (1987) Response of drug sensitive and resistant L1210 leukemia cells to high dose chemotherapy. Cancer Res 47:2323
Gunstream SR, Seidenfeld JJ, Sibonya RE, McMahon LJ (1983) Mitomycin-associated lung disease. Cancer Treat Rep 67:301
Kerpel-Fronius S, Verweij J, Stuurman MM, Kanyár B, Lelieveld P, Pinedo HM (1988) Pharmacokinetics and toxicity of mitomycin C in rodents given alone, in combination or after induction of microsomal drug metabolism. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 22:104
Lazarus HM, Gottfried MR, Herzig RH, Phillips GL, Weiner RS, Sama GP, Fay J, Wolff SN, Sudilovsky O, Gale RP, Herzig GP (1982) Venoocclusive of the liver after high dose mitomycin C therapy and autologous bone marrow transplantation. Cancer 49:1789
Levillian R, Cluzan R (1973) Cardiac toxicity of anti-mitotic drugs. Proceedings, 3rd Meeting of the European Association for Cancer Research, b, p 100
Liu K, Mittelman A, Sproul EE, Elias EG (1971) Renal toxicity in man treated with MMC. Cancer 28:1314
Marquet RL, Westbroek DL, Jeekel J (1984) Interferon treatment of a transplantable rat colon carcinoma. Int J Cancer 38:689
Orwoll ES, Kiessling PJ, Patterson JR (1978) Interstitial pneumonia from MMC. Ann Intern Med 89:352
Philips FS, Schwartz HS, Sternberg SS (1960) Pharmacology of mitomycin C, toxicity and pathologi effects. Cancer Res 20:1354
Ridge JA, Collin C, Bading JR (1988) Increased Adriamycin levels in hepatic implants of rabbit Vx-2 carcinoma from regional infusion. Cancer Res 48:4584
Sigurdson ER, Ridge JA, Kemeny N, Daly JM (1986) Tumor and liver drug uptake following hepatic artery and portal vein infusion. J Clin Oncol 5:1836
Slee PHThJ, Bruijn EA, Leeflang P, Kuppen PJK, Berg L van den, Oosterom AT van (1986) Variations in exposure to mitomycin C in an in vitro colony-forming assay. Br J Cancer 54:951
Tjaden UR, Bruijn EA de, Hoeven RAM van der, Jol C, Greet J van der, Lingeman H (1987) Automated analysis of MMC in body fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography with on-line sample pretreatment. J Chromatogr 420:53
Verweij J (1986) Studies on the toxicology of MMC. Thesis, Free University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Verweij J, Zanten T van, Souren T, Goldwig R, Pinedo HM (1987) Prospective study on the dose relationship of mitomycin C induced interstitial pneumonitis. Cancer 60:756
Wilson JKV, Byron HL, Marks ME, Brattain DE, Willey JE, Brattain MG (1984) Mitomycin C resistance in a human colon carcinoma cell line associated with cell surface protein alterations. Cancer Res 44:5880
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grant IKW 88-07 from the Dutch Cancer Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marinelli, A., Pons, D.H.A., Vreeken, J.A.C. et al. High mitomycin C concentration in tumour tissue can be achieved by isolated liver perfusion in rats. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 28, 109–114 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689698
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689698