Abstract
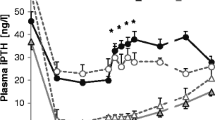
To further characterize the mechanisms by which 25(OH)vitamin D3 (25(OH)D3) and 1.25(OH)2 vitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3) suppress the phosphaturic action of parathyroid hormone (PTH) we have studied the effects of cycloheximide (cyclohex), a protein synthesis inhibitor, on the interaction between PTH and vitamin D metabolites in parathyroidectomized (PTX) rats, both in vivo and in vitro experiments. In clearance studies PTX PTH-infused rats were pretreated with cyclohex 2 h before the administration of vitamin D. In control, PTX PTH-infused rats not pretreated with cyclohex, the administration of 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 was associated with a fall in fractional excretion of phosphate (CP/CIN) from 0.30±0.05 to 0.16±0.02 and from 0.31±0.05 to 0.13±0.01 (P<0.005) respectively. Cyclohex-pretreated PTX PTH-infused rats failed to respond to both 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3, and CP/CIN, which rose after PTH, remained 0.32±0.05 and 0.29±0.03 respectively. In vitro, both 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 inhibited the PTH-induced activation of adenylate cyclase in the renal isolated membrane fractions. Pretreatment with cyclohex abolished this effect of vitamin D metabolites. These results show that cyclohex blocks the antiphosphaturic effects of both 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 but does not alter the response to PTH. These findings are consistent with the possibility that the acute renal action of vitamin D depends on de novo synthesis of protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bordier Ph, Hioco D, Rouguier M (1969) Effects of intravenous vitamin D on bone and phosphate metabolism in osteomalacia. Calc Tiss Res 4:78–83
Bronner F (1982) Vitamin D and membrane structure and function. Introduction. Fed Proc 41:60
Bronner F, Lipton J, Pansu D, Buckley M, Singh R, Miller A III (1982) Molecular and transport effects 1,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D3 in rat duodenum. Fed Proc 41:61–65
Calabresi P, Parks RE Jr (1975) Alkylating agents antimetabolites, hormones and other antiproliferative agents. In: Goodman LS, Gilman AG (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 5th edition. MacMillan Inc. New York, p 1287
Caskey CT (1973) Inhibitors of protein synthesis. In: Hochster RM, Krates M, Quartel JH (eds) Metabolic inhibitors, vol 4. Academic Press Inc., New York, pp 162–163
Chase LR, Aurbach GD (1968) Anatomically separate site for parathyroid hormone and vasopressin. Science 159:545–546
Edelman IS (1975) Mechanism of action of steroid hormones. J Steroid Biochem 6:147–159
Farese RV, Bidot-Lopez P, Sabir A, Smith JS, Schinbeckler B, Larson R (1980) Parathyroid hormone acutely increases polyphosphoinositides of the rabbit kidney cortex by a cycloheximidesensitive process. J Clin Invest 65:1523–1526
Gilman AG (1970) A protein binding assay for adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA 67:305–313
Lowry OH, Roseborough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Popovtzer MM, Robinette JB, DeLuca HF, Holick MF (1974) The acute effect of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol on renal handling of phosphorus. Evidence for a parathyroid hormone-dependent mechanism. J Clin Invest 53:913–921
Popovtzer MM, Robinette JB (1975) Effect of 25(OH)vitamin D3 on urinary excretion of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Am J Physiol 229:907–910
Popovtzer MM, Blum MS, Flis RS (1977) Evidence for the interference of 25(OH)vitamin D3 with phosphaturic action of calcitonin. Am J Physiol 232:E515-E521
Popovtzer MM, Mehandru S, Saghafi D, Blum MS (1978) Interactions between PTH, vitamin D metabolites and other factors in tubular reabsorption of phosphate. Adv Expt Med Biol 103:11–19
Popovtzer MM, Wald H (1981) Evidence for interference of 25(OH)vitamin D3 with phosphaturic action of glucagon. Am J Physiol 240:F269-F275
Puschett JB, Kuhrman MS (1978) Renal tubular effects of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3: interactions with vasopressin and parathyroid hormone. J Lab Clin Med 92:895–903
Puschett JB, Szramowski J (1978) Importance of 25-hydroxylation to the renal tubular actions of vitamin of metabolites. Adv Exp Biol Med 103:105–109
Singh RP, Bronner F (1980) Vitamin D acts posttranscriptionally—in vitro studies with the vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein of rat duodenum. In: Siegel FL, Carafoli E, Kreutsinger RH, MacLennan DH, Wasserman RH (eds) Calcium-binding proteins: structure and function. North-Holland, New York, pp 379–383
Tsai HC, Midgett RJ, Norman AW (1973) Studies on claciferol metabolism. VII. The effects of actinomycin D and cycloheximide on the metabolism, tissue and subcellular localization and action of vitamin D3. Arch Bioch Biophys 157:339–347
Wald H, Popovtzer MM (1980) Antagonistic effects of 25(OH)vitamin D3 and peptide hormones on the activation of adenylate cyclase/cyclic AMP system in renal tissue in vitro. Adv Exp Med Biol 128:625–633
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
An abstract of this work appeared in Clinical Research, 28 (2) A 387, 1980.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brezis, M., Wald, H., Shilo, R. et al. Blockade of the renal tubular effects of vitamin D by cycloheximide in the rat. Pflugers Arch. 398, 247–252 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657160
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657160