Abstract
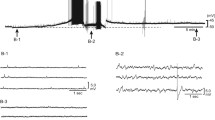
Intracellular recordings were obtained from sympathetic preganglionic neurones (SPN) of the third thoracic segment in cats. Based on differences in their active and passive electrophysiological properties, three different types of SPNs were discerned:
-
1)
Type A neurones had a high resting membrane potential (RMP) (−60 to −86 mV) and a low input resistance (RN) 12–23 MΩ). Action potentials of these neurones had a pronounced IS-SD inflexion and a prominent shoulder in their falling phase. Spikes were rarely generated from the on-going synaptic activity.
-
2)
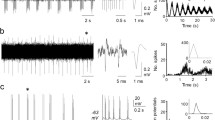
Type B neurones had a lower RMP (−48 to −65 mV) and a higher RN (21–37 MΩ). Their action potentials were characterized by an after-depolarization; they showed a slight IS-SD inflexion and a less pronounced shoulder in their falling phase. The after-depolarization was abolished by membrane hyperpolarization in a time dependent way. A hyperpolarization of at least 50 ms duration was required for its abolition. The after-depolarization was also abolished during repetitive discharges. In most of these neurones spikes were generated at irregular intervals and low rates (0.06–4.6 spikes/s) from the synaptic activity.
-
3)
Type C neurones were similar to type B neurones, but their action potentials did not show the after-depolarization. Additionally, spikes were generated at fairly regular intervals and rather high rates (0.8–6.5 spikes/s).
The rate of spike repolarization of all neurones was markedly increased by hyperpolarization and decreased by membrane depolarization. Current-voltage curves of some type B and C neurones showed a marked rectification upon membrane hyperpolarization. In all type B and C neurones the presence of the A-current is indicated by the voltage trajectory at the end of hyperpolarizing current pulses. Current-frequency curves of type B and C neurones revealed discharge rates of SPNs as high as 100 spikes/s.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams PR, Brown DA, Constanti A (1982a) M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 330:537–572
Adams PR, Constanti A, Brown DA, Clark RB (1982b) Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature 296:746–749
Backman SB, Henry JL (1984) Physiological properties of sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the thoracic intermediolateral nucleus of the cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 62:1183–1193
Baldissera F (1976) Relationships between the spike components and the delayed depolarization in cat spinal neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 259:325–338
Belluzzi O, Sacchi O, Wanke E (1985a) A fast transient outward current in the rat sympathetic neurone studied under voltageclamp conditions. J Physiol (Lond) 358:91–108
Belluzzi O, Sacchi O, Wanke E (1985b) Identification of delayed potassium and calcium currents in the rat sympathetic neurone under voltage clamp. J Physiol (Lond) 358:109–129
Brock LG, Coombs JS, Eccles JC (1953) Intracellular recording from antidromically activated motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 122:429–461
Calvin WH, Schwindt PC (1972) Steps in production of motoneuron spikes during rhythmic firing. J Neurophysiol 35:297–310
Connors BW, Gutnick MJ, Prince DA (1982) Electrophysiological properties of neocortical neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol 48:1302–1320
Coote JH, Westbury DR (1979) Intracellular recordings from sympathetic pregnaglionic neurones. Neurosci Lett 15:171–175
Dembowsky K, Czachurski J, Seller H (1983) An intracellular study of properties of sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the cat. Neurosci Lett (Suppl) 14:S87
Dembowsky K, Czachurski J, Seller H (1984) An intracellular study of sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the cat: properties, synaptic input and morphology. XIXth Int Congress of Neurovegetative Research, Berlin, March 19–24
Dembowsky K, Czachurski J, Seller H (1985a) An intracellular study of the synaptic input to sympathetic preganglionic neurones of the third thoracic segment of the cat. J Auton Nerv Syst 13:201–244
Dembowsky K, Czachurski J, Seller H (1985b) Morphology of sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the thoracic spinal cord of the cat: an intracellular horseradish peroxidase study. J Comp Neurol 238:453–465
Dunlap K, Fischbach GD (1981) Neurotransmitters decrease the calcium conductance activated by depolarization of embryonic chick sensory neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 317:519–535
Fernandez de Molina A, Kuno M, Perl ER (1965) Antidromically evoked responses from sympathetic preganglionic neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 180:321–335
Galvan M, Adams PR (1982) Control of calcium current in rat sympathetic neurons by norepinephrine. Brain Res 244:135–144
Galvan M, Sedlmeir C (1984) Outward currents in voltage-clamped rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 356:115–133
Granit R, Kernell D, Smith RS (1963) Delayed depolarization and the repetitive response to intracellular stimulation of mammalian motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 168:890–910
Harada Y, Takahashi T (1983) The calcium component of the action potential in spinal motoneurones of the rat. J Physiol (Lond) 335:89–100
Heyer EJ, MacDonald RL (1982) Calcium-and sodium-dependent action potentials of mouse spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. J Neurophysiol 47:641–655
Hirst GDS, Holman ME, Spence I (1974) Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol (Lond) 236:303–326
Horn JP, McAfee DA (1980) Alpha-adrenergic inhibition of calcium-dependent potentials in rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 301:191–204
Jänig W, Szulczyk P (1980) Functional properties of lumbar preganglionic neurones. Brain Res 186:115–131
Jahnsen H, Llinás R (1984) Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones: an in vitro study. J Physiol (Lond) 349:205–226
Llinás R, Yarom Y (1981a) Electrophysiology of mammalian inferior olivary neurones in vitro. Different types of voltagedependent ionic conductances. J Physiol (Lond) 315:549–567
Llinás R, Yarom Y (1981b) Properties and distribution of ionic conductances generating electroresponsiveness of mammalian inferior olivary neurones in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 315:569–584
MacDermott AB, Weight FF (1982) Action potential repolarization may involve a transient, Ca2+-sensitive outward current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature 300:185–188
Mannard A, Polosa C (1973) Analysis of background firing of single sympathetic preganglionic neurons of cat cervical nerve. J Neurophysiol 36:398–408
McAfee DA, Yarowsky PJ (1979) Calcium-dependent potentials in the mammalian sympathetic neurone. J Physiol (Lond) 290:507–523
McLachlan EM, Hirst GDS (1980) Some properties of preganglionic neurons in upper thoracic spinal cord of the cat. J Neurophysiol 43:1251–1265
Murase K, Randić M (1983) Electrophysiological properties of rat spinal dorsal horn neurones in vitro: calcium-dependent action potentials. J Physiol (Lond) 334:141–153
Nelson PG, Burke RE (1967) Delayed depolarization in cat spinal motoneurons. Exp Neurol 17:16–26
Nishi S, North RA (1973) Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol (Lond) 231:471–491
North RA (1973) The calcium-dependent slow, after-hyperpolarization in myenteric plexus neurones with tetrodotoxin-resistant action potentials. Br J Pharmacol 49:709–711
Oldfield BJ, McLachlan EM (1981) An analysis of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons projecting from the upper thoracic spinal roots of the cat. J Comp Neurol 196:329–345
Polosa C (1968) Spontaneous activity of sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 46:887–896
Polosa C, Schondorf R, Laskey W (1982) Stabilization of the discharge rate of sympathetic preganglionic neurons. J Auton Nerv Syst 5:45–54
Puil E, Werman R (1981) Internal cesium ions block various K conductances in spinal motoneurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 59:1280–1284
Schwindt PC, Calvin WH (1972) Membrane-potential trajectories between spikes underlying motoneuron firing rates. J Neurophysiol 35:311–325
Seller H (1973) The discharge pattern of single units in thoracic and lumbar white rami in relation to cardiovascular events. Pflügers Arch 343:317–330
Wong RKS, Prince DA (1981) Afterpotential generation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol 45:86–97
Yoshimura M, Nishi S (1982) Intracellular recordings from lateral horn cells of the spinal cord in vitro. J Auton. Nerv Syst 6:5–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dembowsky, K., Czachurski, J. & Seller, H. Three types of sympathetic preganglionic neurones with different electrophysiological properties are identified by intracellular recordings in the cat. Pflugers Arch. 406, 112–120 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586671
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586671