Summary
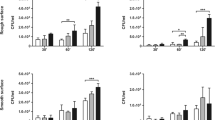
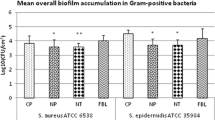
In orthopedic surgery one of the most significant complications is the infection of implants by microorganisms. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether an adhesion of microbes to femoral ballheads consisting of aluminium oxide, zirconium oxide and CoCrMo-alloy is possible, especially to the smoothly polished surface, and whether this implant component might play a role in respect of the mode of infection. The femoral ballheads were contaminated with strains of Staphylococcus aureus and exopolysaccharide producing Staphylococcus epidermidis and incubated in two fractions for 36 and 72 hours. The present experiment documents that the strains of microorganisms tested adhere well to all ballheads used. However, the surfaces of the zirconium oxide ballheads manifest the most pronounced bacterial lawn with the strains investigated.In comparison to aluminium oxide ballheads which also show several layers of colonisation over large areas, these are overgrown with plate-like microbial lawns. Due to the surface tension and surface energy the microbial adhesion is found on metal (CoCrMo-alloy) ballheads initially in small rounded areas with tendency to confluence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lidwell OM, Lowbury EJL, Whyte W, Blowers R, Stanley SJ, Lowe D (1983) Airborn contamination of wounds in joint replacement operations: the relationship to sepsis rates. J Hosp. Infect. 4:111–131.
Maderazo EG, Judson S, Pasternak H (1988) Late infections of total joint prostheses: a review. and recommendations for prevention. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 229:131–142
Burton DS, Schurman DJ (1975) Hematogenous infection in bilateral total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg, 57 A:1004–1005
Gristina AG, Hobgood CD, Webb LX, Myrvik QN (1987) Adhesive colonization of biomaterials and antibiotic resistance, Biomaterials, 8, 423–426.
Gristina AG (1987) Biomaterial — centered infection: microbial adhesion versus tissue integration, Science 237(4822):1588–95
Oga M, Sugioka Y, Hobgood CD, Gristina AG, Myrvik QN (1988) Surgical biomaterials and differential colonization by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biomaterials, 9, 287–289
Merritt K, Chang CC (1991) Factors influencing bacterial adherence to biomaterials. J Biomater APPI. 5(3):185–203
van Dijk J, Herkstroter K, Busscher H, Weerkamp A, Jansen H, Arends J (1987) Surface free energy and bacterial adhesion. An in vivo study in beagle dogs. J.Clin.Periodontol. 14(5): 300–4
Leckband DE, Israelachvili JN, Schmitt FJ, Knoll W (1992) Long range attraction and molecular rearrangements in receptor ligand interactions. Science 255(5050):1419–21
An YH, Friedman J (1998) Concise Review of Mechanisms of Bacterial Adhesion to Biomaterial Surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res (Appl Biomater) 43:338–348
Barth E, Myrvik QM, Wagner W, Gristina AG (1989) In vitro and in vivo comparative colonization of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis on orthopaedic implant materials. Biomaterials 10:325–28
Voytek A, Gristina AG, Barth E, Myrvik QN, Switalski L, Hook M (1988) Staphylococcal adhesion to collagen in intraarticular sepsis. Biomaterials, 9:107–110
Delmi M, Vaudaux P, Lwe DP, Vasey H (1994) Role of Fibronectin in Staphylococcal Adhesion to Metallic Surfaces Used As Models of Orthopaedic Devices. J Orthop Res 12:432–438
Arens S, Schlegel U, Printzen G, Ziegler WJ, Perren SM, Hansis M (1996) Influence of materials for fixation implants on local infection. J Bone Joint Surg.[Br] 78-B:647–51
Gabriel BL, Gold J, Gristina AG, Kasemo B, Lausmaa J, Harrer C, Myrvic QM (1994) Sitespecific adhesion of Staphylococcus epidermidis (RP12) in Ti-AI-V metal systems. Biomaterials 15(8):628–34
Baier RE, Meyer AE, Natiella JR, Natiella RR, Carter JM (1984) Surface properties determine Bioadhesive autcomes: methods and results.J Biomed MaterRes.18(4):327–55
Gristina AG, Costerton JW (1985) Bacterial adherence to biomaterials and tissue. The significance of its role in clinical sepsis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 67 (2):246–73
Huber J, Walter A, Plitz W, Refior HJ (1996) Der Einfluß der Oberflächenenergie auf das Abriebverhalten von Materialpaarungen für das künstliche Hüftgelenk. Biomed. Technik 41: 32–34
Willmann G, Früh HJ, Pfaff HG (1996) Wear characteristics of sliding pairs of zirconia (Y- TZP) for hip endoprosthesis. Biomaterials 17: 2157–2162
Brown AR, Taylor GJ, Gregg PJ (1996) Air contamination during skin preparation and draping in joint replacement surgery. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 78(1): 92–4
Steckelberg JM, Osmon DR (1989) Prosthetic joint infections In: Infections Associated with Indwelling Medical Devices, A.L. Bisno and F.A. Waldvogel (eds.),American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp.259–290
Foster MR, Heppenstall RB, Friedenberg ZB, Hozack WJ (1990) A prospective assessment of nutritional status and complications in patients with fractures of the hip. J Orthop Trauma 4: 49–57
Horowitz SM, Lane JM, Otis JC, Healey JH (1991) Prosthetic arthroplasty of the knee after resection of a sarcoma in the proximal end of the tibia. A report of sixteen cases. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] Vol. 73: 286–293
Jensen JE, Jensen TG, Smith KT, Johnston DA, SJ Dudrick (1982) Nutrition in orthopaedics. J Bone Joint Surg. [Am] Vol. 64: 1263–1272
Murray RP, Bourne MH, Fitzgerald RH Jr (1991) Metachronous infections in patients who have had more than ohne total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. [Am] Vol. 73A: 1469–1473
Poss R, Thornhill TS, Ewald FC, Thomas WH, Batte NJ, Sledge CB (1984) Factors influencing the incidence and outcome of infection following total joint arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. 182 117–126
Lintner F, Huber M, Attems J, Böhm G (1995) Gefäßveränderungen: mögliche Konsequenzen für die Endoprothetik≫, In: 15 Jahre Zweymüller-Hüftendoprothese, III. Wiener Symposium.Verlag Hans Huber, ISBN 3-456-82597-8, PP.113–125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huber, M., Lintner, F. Bacterial adhesion to femoral ballhead surfaces of artificial hipjoints in vitro. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 9, 245–250 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00573332
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00573332