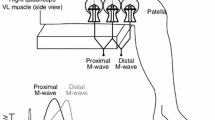
Summary
Within a set of repeated measurements, 12 male subjects performed the following types of muscle contraction: (1) running at constant velocity (12 km· h−1); (2) one-leg hopping at the frequency preferred; (3) both-legs hopping at the frequency preferred; (4) drop jumps from a height of 0.40 m. The surface electromyographs (EMG) from the left and right legs were recorded, together with the averaged signals from vertical ground reaction forces and angular displacement of the ankle joint. Reliability coefficients for the day to day and the week to week comparison were calculated. In addition, on any one test day the positions of the electrodes were systematically changed. The analysis of various EMG parameters (integrated-EMG) revealed high coefficients for both comparisons as well as for the total set of measurements. Qualitative comparisons of the EMG showed a high reproducibility of the shape of the patterns. If the relative position of the electrodes with respect to the belly of the muscle is changed, the amplitudes of the EMG recordings are markedly reduced. It is concluded that surface EMG is a reliable method for studies of the neuromuscular system. On the basis of the data presented, it is suggested that the term “reliability” should be replaced by the term “reproducibility” in order to cover both the aspect of the relative stability plus the aspects of linear changes and the scattering of the data in repeated measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosco C (1982) Stretch-shortening cycle in skeletal muscle function. Studies in sport, physical eduction and health, no. 15. University of Jyväskylä, Jyväskylä
De Vries HA (1986) Efficiency of electrical activity as a physiological measure of the functional state of muscle tissue. Am J Phys Med 47:10–22
Gollhofer A (1987) Komponenten der Schnellkraftleistung im Dehnungs-Verkiirzungs-Zyklus. SET, Erlensee
Gollhofer A, Schmidtbleicher D (1987) Muscle activation patterns of human leg extensors and force-time-characteristics in jumping exercises under increased stretching loads. In: De Groot G, Hollander AP, Huijing PA, Van Ingen Schenau GJ (eds) International series on biomechanics, Biomechanics XI-A. Free University Press, Amsterdam, pp 143–148
Horstmann GA, Gollhofer A, Dietz V (1988) Reproducibility and adaptation of the EMG responses of the lower leg following perturbations of the upright stance. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 70:447–452
Komi PV (1973) Relationship between muscle tension, EMG and velocity of contraction and concentric and eccentric work. In: Desmedt JE (ed) New development in electromyography and clinical neurophysiology, vol. 1. Karger, Basle, pp 596–606
Komi PV (1984) Physiological and biomechanical correlates of muscle function: effects of muscle structure and stretch-shortening cycle on force and speed. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 12:81–121
Komi PV, Buskirk ER (1970) Reproducibility of electromyographic measurements with inserted wire electrodes and surface electrodes. Electromyogr 10:357–367
Komi PV, Viitasalo JT (1977) Changes in motor unit activity and metabolism in human skeletal muscle during and after repeated eccentric and concentric contractions. Acta Physiol Scand 100:246–254
Schmidtbleicher D, Gollhofer A, Frick U (1987) Effects of stretchshortening type training of the performance capability and innervation characteristics of leg extensor muscles. In: De Groot G, Hollander AP, Huijing PA, Van Ingen Schenau GJ (eds) International series on biomechanics, biomechanics XI-A. Free University Press, Amsterdam, pp 185–189
Trousil T (1980) Messung der Sprungkraft. Leistungssport 10:150–153
Viitasalo JT, Komi PV (1975) Signal characteristics of EMG with special reference to reproducibility of measurement. Acta Physiol Scand 93:313–318
Viitasalo JT, Komi PV (1980) EMG, reflex and reaction time components, muscle structure, and fatigue during intermittent isometric contractions in man. Int J Sports Med 1:185–190
Viitasalo JT, Saukonen S, Komi PV (1980) Reproducibility of measurements of selected neuromuscular performance variables in man. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 20:487–501
Vredenbregt J, Rau G (1973) Surface electromyography in relation to force, muscle length and endurance. In: Desmedt JE (ed) New development in electromyography and clinical neurophysiology, vol. 1. Karger, Basle, pp 607–622
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design. McGraw-Hill, Tokyo, pp 206 and 291
Zipp P (1978) Effect of electrode parameters on the bandwidth of the surface EMG power density spectrum. Med Biol Eng Comput 16:537–541
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gollhoferl, A., Horstmann, G.A., Schmidtbleicher, D. et al. Reproducibility of electromyographic patterns in stretch-shortening type contractions. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 60, 7–14 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572179
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572179