Abstract
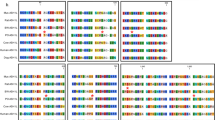
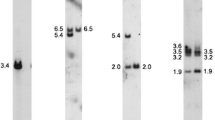
The murine polycystic kidney disease gene,pcy, is an autosomal recessive trait located on chromosome 9. To determine the genetic locus ofpcy, 222 intraspecific backcross mice were obtained by mating C57BL/6FG-pcy andMus molossinus. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of 70 of the 222 backcross progeny showed thatpcy, dilute coat color (d), and cholecystokinin (Cck) were located in the orderd—pcy—Cck from the centromere. Simple sequence repeat length polymorphism analysis of DNA of all 222 backcross mice was carried out using four markers which were located near the central regions ofd andCck. One and eight recombinations were detected betweenD9Mit24 andpcy and betweenD9Mit16 andpcy, respectively. However, no recombinant was observed amongpcy, D9Mit14, andD9Mit148. These findings strongly suggest thatD9Mit14 andD9Mit148 are located near thepcy gene and are good markers for chromosomal walking to this gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atala, A., Freemen, M. R., Mandell, J., and Beier, D. R. (1993). Juvenile cystic kidneys (jck): A new mouse mutation which causes polycystic kidneys.Kidney Int. 431081.
Copeland, N. G., Hutchison, K. W., and Jenkins, N. A. (1983). Excision of the DBA ecotropic provirus in dilute coat-color revertants of mice occurs by homologous recombination involving the viral LTRs.Cell 33379.
Dietrich, W. F., Miller, J. C., Steen, R. G., Merchant, M., Damron, D., Nahf, R., Gross, A., Joyce, D. C., Wessel, M., Dredge, R. D., Marquis, A., Stein, L. D., Goodman, N., Page, D. C., and Lander, E. S. (1994). A genetic map of the mouse with 4,006 simple sequence length polymorphisms.Nature Genet. 7220.
European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium (1994). The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14 kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16.Cell 77881.
Friedman, J. M., Schneider, B. S., Barton, D. E., and Francke, U. (1989). Level of expression and chromosome mapping of the mouse cholecystokinin gene: Implications for murine models of genetic obesity.Genomics 5463.
Gabow, P. A., Johnson, A. M., Kaehny, W. D., Kimberling, W. J., Lezotte, D. C., Duley, I. T., and Jones, R. H. (1992). Factors affecting the progression of renal disease in autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease.Kidney Int. 411311.
Gattone, V. H., II, Calvet, J. P., Cowley, B. D., Jr., Evan, A. P., Shaver, T. S., Helmstadter, K., and Grantham, J. J. (1988). Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease in a murine model: A gross and microscopic description.Lab. Invest. 59231.
Grantham, J. J. (1991). Polycystic kidney disease: Neoplasia in disguise.Am. J. Kidney Dis. 15110.
Grantham, J. J. (1992). Polycystic kidney disease. I. Etiology and pathogenesis.Hosp. Pract. 2751.
Grünfeld, J. P., Chauveau, D., and Knebelmann, B. (1992). Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: From molecular genetics to the patients.Clin. Invest. 70791.
Himmelbauer, H., Pohlschmidt, M., Snarey, A., Germino, G. G., Weinstat-Saslow, D., Somlo, S., Reeders, S. T., and Friscauf, A.-M. (1992). Human-mouse homologies in the region of the polycystic kidney disease gene (PKD1).Genomics 1335.
Imai, K., Nass, S. J., Olowson, M., and Balling, R. (1993). The genetic map around the tail kinks (tk) locus on mouse chromosome 9.Mammal. Genome 4560.
Kaspareit-Rittinghausen, J., Rapp, K., Deerberg, F., Wcislo, A., and Messow, C. (1989). Hereditary polycystic kidney disease associated with osteorenal syndrome in rats.Vet. Pathol. 26195.
Kimberling, W. J., Kumar, S., Gabow, P. A., Kenyon, J. B., Connolly, C. J., and Somlo, S. (1993). Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Localization of the second gene to chromosome 4q13-q23.Genomics 18467.
Kingsley, D. M. (1993). Mouse chromosome 9.Mammal. Genome 4:S136.
Nagao, S., Hibino, T., Koyama, Y., Marunouchi, T., Konishi, H., and Takahashi, H. (1991). Strain difference in expression of the adult-type polycystic kidney disease gene,pcy, in the mouse.Exp. Anim. 4045.
Nauta, J., Ozawa, Y., Sweeney, W. E., Jr., Rutledge, J. C., and Avner, E. D. (1993). Renal and biliary abnormalities in a new murine model of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease.Pediatr. Nephrol. 7163.
O'Brien, S. J., Womack, J. E., Lyons, L. A., Moore, K. J., Jenkins, N. A., and Copeland, N. G. (1993). Anchored reference loci for comparative genome mapping in mammals.Nature Genet. 3103.
Ohno, K., and Kondo, K. (1989). A mutant rat with congenital skeletal abnormalities and polycystic kidney.Exp. Anim. 38139.
Parfrey, P. S., Bear, J. C., Morgan, J., Carmer, B. C., McManamon, P. J., Gault, M. H., Churchill, D. N., Singh, M., Hewitt, R., Somlo, S., and Reeders, S. T. (1990). The diagnosis and prognosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.N. Engl. J. Med. 3231085.
Peters, D. J. M., Spruit, L., Saris, J. J., Ravine, D., Sandkuijl, L. A., Fossdal, R., Boersma, J., van Eijk, R., Nørby, S., Constantinou-Deltas, C. D., Pierides, A., Brissenden, J. E., Frants, R. R., van Ommen, G.-J. B., and Breuning, M. H. (1993). Chromosome 4 localization of a second gene for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Nature Genet. 5359.
Preminger, G. M., Koch, W. E., Fried, F. A., McFarland, E., and Mandell, J. (1982). Murine congenital polycystic kidney disease: A model for studying development of cystic disease.J. Urol. 127556.
Rahilly, M. A., Samuel, K., Ansell, J. D., Micklem, H. S., and Fleming, S. (1992). Polycystic kidney disease in the CBA/N immunodeficient mouse.J. Pathol. 168335.
Ravine, D., Walker, R. G., Gibson, R. N., Forrest, S. M., Richards, R. I., Friend, K., Sheffield, L. J., Kincaid-Smith, P., and Danks, D. M. (1992). Phenotype and genotype heterogeneity in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Lancet 3401330.
Reeders, S. T., Breuning, M. H., Corney, G., Jeremiah, S. J., Meera, Khan, P., Davies, K. E., Hopkinson, D. A., Pearson, P. L., and Weatherall, D. J. (1986). Two genetic markers closely linked to adult polycystic kidney disease on chromosome 16.Br. Med. J. 292851.
Takahashi, H., Calvet, J. P., Dittemore-Hoover, D., Yoshida, K., Grantham, J. J., and Gattone, V. H., II (1991). A hereditary model of slowly progressive polycystic kidney disease in the mouse.J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1980.
Wahl, G. M., Stern, M., and Stark, G. R. (1979) Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 763683.
Watanabe, T., Miyashita, N., Nishimura, M., Saitou, N., Hayashi, Y., and Moriwaki, K. (1989). Evolutionary relationships between laboratory mice and subspecies ofMus musculus based on the restriction fragment length variants of the chymotrypsin gene at thePrt-2 locus.Biochem. Genet. 27119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagao, S., Watanabe, T., Ogiso, N. et al. Genetic mapping of the polycystic kidney gene,pcy, on mouse chromosome 9. Biochem Genet 33, 401–412 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00554598
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00554598