Summary
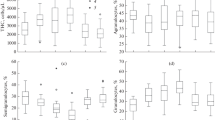
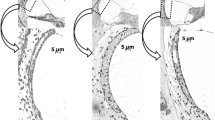
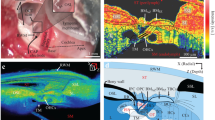
Using the microprobe for energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis, the elemental compositions of both the individual cells of the stria vascularis and of the endolymph were followed simultaneously under normal conditions and after the administration of 120 mg/kg ethacrynic acid (EA). Marginal cells and intermediate cells showed reversible increases in potassium and decreases in sodium concentrations. Shifts in the ionic composition of endolymph occurred later than after elemental changes in the strial cells. The present results indicate that the marginal and the intermediate cells are the primary target for EA-induced ototoxicity. However, generalized toxic effects of EA are also indicated, with a general leakage of different elements occurring during the 30–60 min period after EA administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anniko M (1978) Reversible and irreversible changes of the stria vascularis. An evaluation of the effects of ethacrynic acid separately and in combination with atoxyl. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 85:349–359
Anniko M, Wroblewski R (1981) Elemental composition of the developing inner ear. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 90:25–32
Anniko M, Thornell L-E, Wroblewski R (1987) Recent advances in inner ear cytochemistry. Microanalytical and immunohistochemical investigations. Prog Neurobiol (in press)
Anniko N, Thornell L-E, Virtanen I (1987) Cytoskeletal organization of the human inner ear. II. Characterization of intermediate filaments in the cochlea. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) [Suppl] 437:29–54
Arnold W, Nadol JB, Weidauer H (1981) Temporal bone histopathology in human ototoxicity due to loop diuretics. Scand Audiol [Suppl] 14:201–213
Bosher SK (1980) The nature of the ototoxic actions of ethacrynic acid upon the mammalian endolymph system. I. Functional aspects. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 89:407–418
Bosher SK, Smith C, Warren RL (1973) The effects of ethacrynic acid upon the cochlear endolymph and stria vascularis. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 75:184–191
Cohn ES, Gordes EH, Brusilow SW (1971) Ethacrynic acid effect on the compositon of cochlear fluids. Science 171:910
Fox KE, Brummett RE (1979) The relationship between the cytotoxicity of kanamycin and ethacrynic acid for mammalian cells in vitro and their ototoxicity in vivo. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 87:72–78
Jahnke K (1980) The blood-perilymph barrier. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 228:29–34
Lim DJ, Freilich IW (1981) Ultrastructure of the stria vascularis, vestibular dark cells and endolymphatic sac following acute diuretic ototoxicity. Scand Audiol [Suppl] 14: 139–155
Marks SC, Schacht J (1981) Effect of ototoxic diuretics on cochlear Na+/K+-ATPase and adenylate cyclase. Scand Audiol [Suppl] 14:131–138
Matz GJ (1976) The ototoxic effects of ethacrynic acid in man and animals. Laryngoscope 86:1065–1086
Matz GJ, Beal DD, Krames L (1969) Ototoxicity of ethacrynic acid. Demonstrated in a human temporal bone. Arch Otolaryngol 90:152–155
Quick CA, Duvall AJ (1970) Early changes in the cochlear duct from ethacrynic acid: an electron microscopic evaluation. Laryngoscope 80:954–965
Sterkers O, Saumon G, Tran Ba Huy P, Ferrary E, Amiel C (1984) Electrochemical heterogeneity of the cochlear endolymph. Am J Physiol 246:47–53
Thalmann R (1981) Effects of loop diuretic mercurials, and other diuretic substances upon the physiological chemistry of the cochlea. Scand Audiol [Suppl] 14:119–129
Trump BF, Ginn FL (1969) The pathogenesis of subcelluiar reaction to lethal injury. Methods Achiev Exp Pathol 4:1–29
West BA, Brummett RE, Hirnes DL (1973) Interaction of kanamycin and ethacrynic acid. Arch Otolaryngol 98:32–37
Wroblewski R, Anniko M (1986) X-ray microanalytical studies of time dependent changes in individual cells of stria vascularis and endolymph following ethacrynic acid exposure. Proceedings of the XI International Congresson Electron Mircroscopy, Kyoto, Japan, pp 3251–3252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Swedish Medical Research Council (12X-7305 and 12X-720), the Ragnar and Torsten Söderberg Foundation, the Foundation Tysta Skolan, the University of Umeå and Karolinska Institute
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anniko, M., Wróblewski, R. Simultaneous investigations of elemental changes in individual cells of the stria vascularis and in endolymph. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 244, 346–349 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00497462
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00497462