Abstract
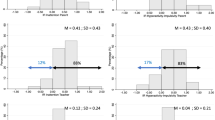
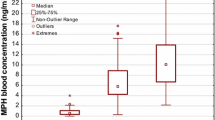
The relationship between methylphenidate (MP) oral dose and plasma concentration to social and cognitive behaviors was studied in 25 boys diagnosed as having “attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity”. Children were administered successive 1-week treatment conditions under the following schedule of fixed oral doses given twice daily: placebo; 0.25 mg/kg; 0.50 mg/kg; 1.0 mg/kg; placebo. Teacher and parent ratings showed increased improvement in social behavior as a function of MP dose. No drug effects were obtained on cognitive performance. MP plasma concentrations were significantly associated with oral dose and with measures of social behavior. No relationship was found with cognitive behavior. Side effects at the largest dose were severe enough to require discontinuation of treatment for five children, but were relatively mild for the remaining children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown RT, Sleator EK (1979) Methylphenidate in hyperactive children: Differences in dose effects on impulsive behavior. Pediatrics 64:408–411
Cantwell DP, Carlson GA (1978) Stimulants. In: Werry JS (ed) Pediatric psychopharmacology: The use of behavior modifying drugs in children. Bruner Mazel, New York, pp 171–207
Conners CK (1969) A teacher rating scale for use in drug studies with children. Am J Psychiatry 126:884–888
Halliday R, Gnauck K, Rosenthal JR, McKibben JL, Callaway E (1980) The effects of methylphenidate dosage on school and home behavior of the hyperactive child. In: Knights RM, Bakker DJ (eds) Treatment of hyperactive and learning disordered children: Current research. University Park, Baltimore, pp 237–247
Hungund BL, Hanna M, Winsberg BG (1978) A sensitive gas chromatographic method for the determination of methylphenidate (Ritalin) and its major metabolite alpha-phenyl-2-piperidine acetic acid (ritalinic acid) in human plasma using nitrogen-phosphorous detector. Commun Psychopharmacol 2:203–208
Hungund BL, Perel JM, Hurwic MC, Sverd J, Winsberg BG (1979) Pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate in hyperactive children. Br J Pharmacol 8:571–576
McNutt BA, Ballard JE, Boileau R, Sprague RL, von Neumann A (1976) The effects of long-term stimulant medication on growth and body composition of hyperactive children. Psychopharmacol Bull 12:13–15
Safer D, Allen R (1975) Side effects from long-term use of stimulants in children. Int J Ment Health 4:105–118
Schowalter JE (1979) Paying attention to attention deficit disorder. Pediatrics 64:546–547
Sprague RL, Berger BD (1980) Drug effects on learning performance: Relevance of animal research to pediatric psychopharmacology. In: Knights RM, Bakker DJ (eds) Treatment of hyperactive and learning disordered children: Current research. University Park, Baltimore, pp 167–183
Sprague RL, Sleator EK (1977) Methylphenidate in hyperkinetic children: Differences in dose effects on learning and social behavior. Science 198:1274–1276
Werry JS, Aman MG (1975) Methylphenidate and haloperidol in children: Effects on attention, memory, and activity. Arch Gen Psychiatry 32:790–795
Werry JS, Aman MG, Diamond E (1979) Imipramine and methylphenidate in hyperactive children. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 21:27–35
Werry JS, Sprague RL (1974) Methylphenidate in children: Effect of dosage. Aust NZ J Psychiatry 8:9–19
Werry JS, Sprague RL (1970) Hyperactivity. In: Costello CG (ed) Symptoms of psychopathology: A handbook. Wiley, New York, pp 397–417
Winsberg BG, Yepes LE, Bialer I (1976) Pharmacologic management of children with hyperactive/aggressive/inattentive behavior disorders. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 15:471–477
Yepes LE, Balka EB, Winsberg BG, Bialer I (1977) Amitriptyline and methylphenidate treatment of behaviorally disordered children. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 18:39–52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winsberg, B.G., Kupietz, S.S., Sverd, J. et al. Methylphenidate oral dose plasma concentrations and behavioral response in children. Psychopharmacology 76, 329–332 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00449120
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00449120