Summary
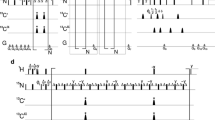
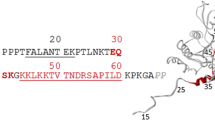
We present the complete 15N and 1H NMR assignment and the secondary structure of an immunoglobulin-like domain from the giant muscle protein titin. The assignment was obtained using homonuclear and 15N heteronuclear 2D and 3D experiments. The complementarity of 3D TOCSY-NOESY and 3D 15N NOESY-HSQC experiments, using WATERGATE for water suppression, allowed an efficient assignment of otherwise ambiguous cross peaks and was helpful in overcoming poor TOCSY transfer for some amino acids. The secondary structure is derived from specific NOEs between backbone α- and amide protons, secondary chemical shifts of α-protons and chemical exchange for the backbone amide protons. It consists of eight β-strands, forming two β-sheets with four strands each, similar to the classical β-sandwich of the immunoglobulin superfamily, as previously predicted by sequence analysis. Two of the β-strands are connected by type II β-turns; the first β-strand forms a β-bulge. The whole topology is very similar to the only intracellular immunoglobulin-like domain for which a structure has been determined so far, i.e., telokin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BaxA. and DavisD.G. (1985) J. Magn. Reson., 65, 533–535.
BorkP., HolmL. and SanderC. (1994) J. Mol. Biol., 242, 309–320.
ErnstR.R., BodenhausenG. and WokaunA. (1987) Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions, International Series of Monographs on Chemistry, Vol. 14, Oxford Science Publications, Oxford.
FürstD.O., OsbornM. and WeberK. (1988). J. Cell Biol., 106, 1563–1572.
FürstD.O., VinkemeierU. and WeberK. (1992) J. Cell Sci., 102, 769–778.
GautelM., LeonhardK. and LabeitS. (1993) EMBO J., 10, 3827–3834.
GriesingerC., OttingG., WüthrichK. and ErnstR.R. (1988) J. Am. Chem. Soc., 110, 7870–7872.
GrzesiekS. and BaxA. (1993) J. Biomol. NMR, 3, 627–638.
HarpazY. and ChothiaC. (1994) J. Mol. Biol., 238, 528–539.
HoldenH.M., ItoM., HartshorneD.J. and RaymentI. (1992) J. Mol. Biol., 227, 840–851.
KadkhodaeiM., HwangT.-L., TangJ. and ShakaA.J. (1993) J. Magn. Reson. Ser. A., 105, 104–107.
LabeitS., GautelM., LakeyA. and TrinickJ. (1992) EMBO J., 11, 1711–1716.
LämmliU.K. (1970) Nature, 227, 680–685.
LeGriceS.F.J. and Grüninger-LeitchF. (1990) Eur. J. Biochem., 87, 307–314.
LiY.-C. and MontelioneG.T. (1994) J. Magn. Reson., 105, 45–51.
MaruyamaK., MatsubaraS., NatoriR., NonomuraY., KimuraS., OhashiK., MurakamiF., HandaS. and EguchiG. (1977) J. Biochem., 82, 317–337.
MaruyamaK. (1994) Biophys. Chem., 50, 73–85.
MitschangL., CieslarC., HolakT.A. and OschkinatH. (1991) J. Magn. Reson., 92, 208–217.
NaveR., FürstD.O. and WeberK. (1989) J. Cell Biol., 109, 2177–2187.
PastoreA. and SaudekV. (1990) J. Magn. Reson., 90, 165–176.
PiottoM., SaudekV. and SklenářV. (1992) J. Biomol. NMR, 2, 661–665.
PolitouA.S., GautelM., JosephC. and PastoreA. (1994a) FEBS Lett., 352, 27–31.
PolitouA.S., GautelM., PfuhlM., LabeitS. and PastoreA. (1994b) Biochemistry, 33, 4730–4737.
RichardsonJ.S., GetzoffE.D. and RichardsonD.C. (1978) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 75, 2574–2578.
SaikiR.K., ScharfS.J., FaloonaF., MullisG.T. and EhrlichH.A. (1985) Science, 230, 1350–1354.
SklenářV., PiottoM., LeppikR. and SaudekV. (1993) J. Magn. Reson., 102, 241–245.
StonehouseJ., ShawG.L., KeelerJ. and LaueE.D. (1994) J. Magn. Reson., 107, 178–184.
StudierF.W., RosenbergA.H. and DubendorfJ.W. (1990) Methods Enzymol., 185, 62–89.
StudierF.W. and MoffatB.A. (1991) J. Mol. Biol., 189, 113–130.
VinkemeierU., ObermannW., WeberK. and FürstD.O. (1993) J. Cell Sci., 106, 319–330.
Wang, K. and Ramirez-Mitchell, R. (1979) J. Cell Biol., 83, 389a.
WishartD.S., SykesB.D. and RichardsF.M. (1991) J. Mol. Biol., 222, 311–333.
WüthrichK. (1976) NMR of Amino Acids and Nucleotides, North Holland, Amsterdam.
WüthrichK., BilleterM. and BraunW. (1984) J. Mol. Biol., 180, 715–740.
WüthrichK. (1986) NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids, Wiley, New York, NY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfuhl, M., Gautel, M., Politou, A.S. et al. Secondary structure determination by NMR spectroscopy of an immunoglobulin-like domain from the giant muscle protein titin. J Biomol NMR 6, 48–58 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417491
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417491