Abstract
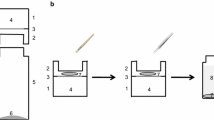
Using the system vapor/membrane/liquid, permeability coefficients of cuticular transpiration (P ct) were determined as functions of water activity in the vapor (a wv). Enzymatically isolated cuticular membranes (CM) of Citrus aurantium L. and nonisolated CM of onion bulb scales and eggplant fruits were investigated. P ct of Citrus and eggplant CM decreased with decreasing a wv, while permeability coefficients of CM of onion were independent of a wv. Extraction of soluble cuticular lipids (SCL) from the CM of Citrus increased permeability coefficients by a factor of approximately 500. This extraction had no effect on the dependence of P ct on a wv.
Treating cuticular membranes as a resistance network consisting of SCL and the polymer matrix, it is shown that the permeability of onion CM is determined by the resistance of the SCL arranged in series with the polymer matrix. In this type of CM liquid and vapor are separated by a continuous, nonporous layer of SCL, and the driving force of transpiration is the gradient of partial pressure of water vapor across the SCL layer. In the CM of Citrus and eggplant, the SCL layer is traversed by polar pores that swell or shrink depending on a wv. However, liquid continuity is maintained across these membranes down to a wv=0.22, the lowest value used. In this type of membrane the driving force of transpiration is the water potential gradient across the membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CM:
-
cuticular membrane
- MX:
-
polymer matrix
- SCL:
-
soluble cuticular lipids
- HEPES:
-
N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethane sulfonic acid
- MES:
-
(N-morpholino)ethane sulfonic acid
- SADH:
-
succinic acid 2,2-dimethyl hydrazide
References
Baker, E.A., Procopiou, J.: The cuticles of Citrus species II. Composition of intracuticular lipids of leaves and fruits. J. Sci. Food Chem. 26, 1347–1352 (1975)
Baker, E.A., Procopiou, J., Hunt, G.M.: The cuticles of Citrus species. Composition of leaf and fruit waxes. J. Sci. Food Chem. 26, 1093–1101 (1975)
Barnes, G.T., LaMer, V.K.: The evaporation resistance of monolayers of long-chain acids and alcohols and their mixtures. In: Retardation of evaporation by monolayers: Transport processes. pp. 9–33. LaMer, V.K., ed. New York, London: Academic Press 1962
Cowan, I.R., Milthrope, F.L.: Plant factors influencing the water status of plant tissues. In: Water deficits and plant growth. Kozlowski, T.T., ed. New York, San Francisco, London: Academic Press 1968
Ginzburg, B.Z., Katchalsky, A.: The frictional coefficients of the flows of non-electrolytes through artificial membranes. J. Gen. Physiol 47, 403–418 (1963)
Martin, J.T., Juniper, B.E.: The cuticle of plants. London: Edward Arnolds 1970
Orgell, W.H.: The isolation of plant cuticle with pectic enzymes. Plant Physiol. 30, 78–80 (1955)
Schönherr, J.: Water permeability of isolated cuticular membranes: The effect of pH and cations on diffusion, hydrodynamic permeability and size of polar pores in the cutin matrix. Planta 128, 113–126 (1976a)
Schönherr, J.: Water permeability of isolated cuticular membranes: The effect of cuticular waxes on diffusion of water. Planta 131, 159–164 (1976b)
Schönherr, J., Bukovac, M.J.: Ion exchange properties of isolated tomato fruit cuticular membrane: Exchange capacity, nature of fixed charges and cation selectivity. Planta 109, 73–93 (1973)
Schönherr, J., Huber, R.: Plant cuticles are polyelectrolytes with isoelectric points around three. Plant Physiol. 59, 145–150 (1977)
Sitte, P., Rennier, R.: Untersuchungen an cuticularen Zellwandschichten. Planta 60, 19–40 (1963)
Slatyer, R.O.: Plant-water relationships. London, New York: Academic Press 1937
Solomon, A.K.: Characterization of biological membranes by equivalent pores. J. Gen. Physiol. 51, 335s-246s (1968)
Taylor, R.L., Herrmann, D.B., Kemp, A.R.: Diffusion of water through insulating materials. Industr. Engin. Chem. 28, 1255–1263 (1936)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schönherr, J., Schmidt, H.W. Water permeability of plant cuticles. Planta 144, 391–400 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391583
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391583