Abstract
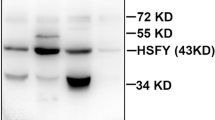
Mouse spermatogenic cells are known to express HSP70-2, a member of the HSP70 family of heatshock proteins. The purpose of the present study was to characterize further the expression and localization of HSP70-2 in meiotic cells of mice and hamsters. After separating mouse spermatogenic cells into cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, proteins were separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and detected with HSP-specific antibodies. Of several HSP70 proteins identified in the cytoplasm, only HSC70 and HSP70-2 were also detected in the nucleus. Immunocytological analyses of spermatocyte prophase cells revealed that HSP70-2 was associated with the synaptonemal complex. Surfacespread synaptonemal complexes at pachytene and diplotene stages labeled distinctly with the antiserum to HSP70-2. Synaptonemal complexes from fetal mouse oocytes failed to show any evidence of HSP70-2. Reverse-transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analyses of gene expression confirmed this sex specificity; Hsp70-2 mRNA was detected in mouse testes, but not ovaries. These findings are suggestive of a previously unsuspected sexual dimorphism in structure and/or function of the synaptonemal complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RL, O'Brien DA, Jones CC, Rockette DL, Eddy EM (1988) The expression of heat shock proteins by isolated mouse spermatogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol 8: 3260–3266
Bonnycastle LLC, Yu C-E, Hunt CR, Trask BJ, Clancy KP, Weber JL, Patterson D, Schellenberg GD (1994) Cloning, sequencing, and mapping of the human chromosome 14 heat shock protein gene (HSPA2). Genomics 23: 85–93
Counce SJ, Meyer GF (1973) Differentiation of the synaptonemal complex and the kinetochore in Locusta spermatocytes studied with whole-mount electron microscopy. Chromosoma 44: 234–253
Dix DJ, Allen JW, Collins BW, Mori C, Nakamura N, Poorman-Allen P, Goulding EH, Eddy EM (1996) Targeted gene disruption of Hsp 70-2 results in failed meiosis, germ cell apoptosis, and male infertility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (in press)
Dobson MJ, Pearlman RE, Karaiskakis A, Spyropoulos B, Moens PB (1994) Synaptonemal complex proteins: occurrence, epitope mapping and chromosome disjunction. J Cell Sci 107: 2749–2760
Dresser M (1987) The synaptonemal complex and meiosis: an immunocytochemical approach. In: Moens PB (ed) Meiosis. Academic Press, New York, pp 245–274
Dresser M, Pisetsky D, Warren R, McCarty G, Moses M (1987) A new method for the cytological analysis of autoantibody specificities using whole-mount, surface-spread meiotic nuclei. J Immunol Methods 104: 111–121
Georgopoulos C, Welch WJ (1993) Role of the major heat shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Cell Biol 9: 601–634
Gething M-J, Sambrook J (1992) Protein folding in the cell. Nature 355: 33–45
Haaf T, Machens A, Schmid M (1989) Immunocytogenetics II. Human autoantibodies to synaptonemal complexes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 50: 6–13
Hawley RS, Arbel T (1993) Yeast genetics and the fall of the classical view of meiosis. Cell 72: 301–303
Hendrey J, Kola I (1991) Thermolability of mouse oocytes is due to the lack of expression and/or inducibility of Hsp 70. Mol Reprod Dev 28: 1–8
Heyting C, Dettmers RJ, Dietrich AJJ, Redeker EJW, Vink ACG (1988) Two major components of synaptonemal complexes are specific for meiotic prophase nuclei. Chromosoma 96: 325–332
Johnson GD, Nogueira Araujo GM de C (1981) A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods 43: 349–350
Laszlo A, Li GC (1985) Heat-resistant variants of Chinese hamster fibroblasts altered in expression of heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 8029–8033
Maekawa M, O'Brien DA, Allen RL, Eddy EM (1989) Heat-shock cognate protein (hsc71) and related proteins in mouse spermatogenic cells. Biol Reprod 40: 843–852
Merrick BA, He C, Craig WA, Clark GC, Corsini E, Rosenthal GJ, Mansfield BK, Selkirk JK (1992) Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of cellular and secreted proteins from rat alveolar macrophages after lipopolysaccharide treatment. Appl Theor Electrophor 2: 177–187
Meuwissen RLJ, Offenberg HH, Dietrich AJJ, Riesewijk A, Iersel M van, Heyting C (1992) A coiled-coil related protein specific for synapsed regions of meiotic prophase chromosomes. EMBO J 11: 5091–5100
Moens PB (1994) Molecular prespectives of chromosome pairing at meiosis. Bioessays 16: 101–106
Moens PB, Earnshaw WC (1989) Anti-topoisomerase II recognizes meiotic chromosome cores. Chromosoma 98: 317–322
Moens PB, Heyting C, Dietrich AJJ, Raamsdonk W van, Chen Q (1987) Synaptonemal complex antigen location and conservation. J Cell Biol 105: 93–103
Moens PB, Spyropoulos B, Dobson M, Karaiskakis A, Pearlman RE (1992) Searching for synaptonemal complex proteins and their genes. Dev Genet 13: 435–439
Moses MJ (1968) Synaptonemal complex. Annu Rev Genet 2: 363–412
Moses MJ, Poorman PA (1984) Synapsis, synaptic adjustment and DNA synthesis in mouse oocytes. In: Bennett MD Gropp A, Wolf U (eds) Chromosomes Today, vol. 8. G. Allen and Unwin, London, pp 90–103
O'Brien DA (1987) Stage-specific protein synthesis by isolated spermatogenic cells throughout meiosis and early spermiogenesis in the mouse. Biol Reprod 37: 147–157
O'Brien DA (1993) Isolation, separation, and short-term culture of spermatogenic cells. Methods Toxicol 3A: 246–264
Parsell DA, Lindquist S (1993) The function of heat-shock protteins in stress tolerance: Degradation and reactivation of damaged proteins. Annu Rev Genet 27: 437–496
Raab LS, Polakoski KL, Hancock LW, Hamilton DW (1995) Characterization of the heat shock protein P70 in rat spermatogenic cells. Mol Reprod Dev 40: 186–195
Rosario MO, Perkins SL, O'Brien DA, Allen RL, Eddy EM (1992) Identification of the gene for the developmentally expressed 70 kDa heat-shock protein (P70) of mouse spermatogenic cells. Dev Biol 150: 1–11
Selkirk JK, Merrick BA, Stackhouse BL, He C (1994) Multiple p53 protein isoforms and formation of oligomeric complexes with heat shock proteins Hsp 70 and Hsp90 in the human mammary tumor. T47D, cell line. Appl Theor Electrophor 4: 11–18
Smith A, Benavente R (1992) Identification of a structural protein component of rat synaptonemal complexes. Exp Cell Res 198: 291–297
Zakeri ZF, Wolgemuth DJ, Hunt CR (1988) Identification and sequence analysis of a new member of the mouse HSP70 gene family and characterization of its unique cellular and developmental pattern of expression in the male germ line. Mol Cell Biol 8: 2925–2932
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Although the research in this article has been supported by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, it has not been subjected to Agency review and therefore does not necessarily reflect the views of the Agency and no official endorsement should be inferred. Mention of trade names or commercial products does not constitute endorsement or recommendation for use
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, J.W., Dix, D.J., Collins, B.W. et al. HSP70-2 is part of the synaptonemal complex in mouse and hamster spermatocytes. Chromosoma 104, 414–421 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352265
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352265