Abstract
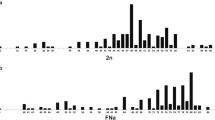
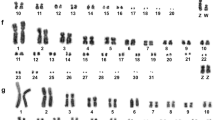
Karyotypes were compared in 48 species, including 6 subspecies, of birds from 12 orders: Casuariiformes, Rheiformes, Sphenisciformes, Pelecaniformes, Ciconiiformes, Anseriformes, Phoenicopteriformes, Gruiformes, Galliformes, Columbiformes, Falconiformes and Strigiformes. — With the exception of the family Accipitridae, all the species studied are characterized by typical bird karyotypes with several pairs of macrochromosomes and a number of microchromosomes, though the boundary between the two is not necessarily sharp. The comparative study of complements revealed that a karyotype with 3 morphologically distinct pairs of chromosomes is frequently encountered in all orders except the Strigiformes. Those 3 pairs, submetacentric nos. 1 and 2, and a subtelocentric or telocentric no. 3, are not only morphologically alike but also have conspicuous homology revealed by the G-banding patterns. Furthermore, G-banding analysis provided evidence for the derivation of the owl karyotype from a typical bird karyotype.—The above cytogenetic features led to the assumption that the 3 pairs of marker chromosomes had been incorporated into an ancestral bird karyotype. It seems probable that those chromosomes have been transmitted without much structural changes from a common ancestor of birds and turtles, since the presence of the same marker chromosomes in the fresh water turtle Geoclemys reevesii is ascertained by G-banding patterns. — A profile of a primitive bird karyotype emerged through the present findings. Hence, it has become possible to elucidate mechanisms involved in certain structural changes of macrochromosomes observed in birds. It was concluded that a major role had been played by centric fission as well as fusion, translocation, and pericentric inversion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkin, N. B., Mattinson, G., Beçak, W., Ohno, S.: The comparative DNA content of 19 species of placental mammals, reptiles, and birds. Chromosoma (Berl.) 17, 1–10 (1965)
Bachmann, K., Harrington, B. A., Craig, J. P.: Genome size in birds. Chromosoma (Berl.) 37, 405–416 (1972)
Baker, R. J., Bull, J. J., Mengden, G. A.: Chromosomes of Elaphe subocularis (Reptilia: Serpentes), with the description of an in vivo technique for preparation of snake chromosomes. Experientia (Basel) 27, 1228–1229 (1971)
Beçak, M. L., Beçak, W., Roberts, F. L., Shoffner, R. N., Volpe, E. P.: Chromosome atlas: Fish, amphibian, reptiles and birds, vol. 1. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1971
Bianchi, N. O., Beçak, W., de Bianchi, M. S. A., Beçak, M. L., Rabello, M. N.: Chromosome replication in four species of snakes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 26, 188–200 (1969)
Bloom, S. E.: A current list of chromosome numbers and variations for species of the avian subclass Carinatae. J. Hered. 60, 217–220 (1969)
Comings, D. E., Mattoccia, E.: Studies of microchromosomes and a G-C rich DNA satellite in the quail. Chromosoma (Berl.) 30, 202–214 (1970)
Egozcue, J.: A possible case of centric fission in a primate. Experientia (Basel) 27, 969–970 (1971)
Evans, H. J., Buckland, R. A., Sumner, A. T.: Chromosome homology and heterochromatin in goat, sheep and ox studied by banding techniques. Chromosoma (Berl.) 42, 383–402 (1973)
Fredga, K., Bergström, U.: Chromosome polymorphism in the root vole (Microtus oeconomus). Hereditas (Lund) 66, 145–152 (1970)
Galton, M., Bredbury, P. R.: DNA replication patterns of the sex chromosomes of the pigeon (Columba livia domestica). Cytogenetics 5, 295–306 (1966)
Grouchy, J. de, Turleau, C., Roubin, M., Klein, M.: Evolutions caryotypiques de l'homme et du chimpanze. Etude comparative des topographies de bandes apres denaturation menagee. Ann. Génét. 15, 79–84 (1972)
Hammer, B.: The karyotypes of nine birds. Hereditas (Lund) 55, 367–385 (1966)
Hammer, B.: The karyotypes of thirty-one birds. Hereditas (Lund) 65, 29–58 (1970)
Hsu, T. C., Mead, R. A.: Mechanisms of chromosomal changes in mammalian speciation. In: Comparative mammalian cytogenetics (K. Benirschke ed.). Berlin-Heidelberg-New York:Springer 1969
Itoh, M., Ikeuchi, T., Shimba, H., Mori, M., Sasaki, M., Makino, S.: A comparative karyotype study in fourteen species of birds. Japan. J. Genet. 44, 163–170 (1969)
John, B., Hewitt, G. M.: Patterns and pathways of chromosome evolution within the Orthoptera. Chromosoma (Berl.) 25, 40–74 (1968)
Kato, H., Sagai, T., Yosida, T. H.: Stable telocentric chromosomes produced by centric fission in Chinese hamster cells in vitro. Chromosoma (Berl.) 40, 183–192 (1973)
Krishan, A., Haiden, G. J., Shoffner, R. N.: Mitotic chromosomes and the W-sex chromosome of the great horned owl (Bubo v. virginianus). Chromosoma (Berl.) 17, 258–263 (1966)
Ligon, J. D.: Relationships of the cathartid vultures. Occas. Pap., Univ. Mich. Mus. Zool. 651, 1–26 (1967)
Mayr, E., Amadon, D.: A classification of recent birds. Amer. Mus. Nov. no. 1496, 1–42 (1951)
Ohno, S.: Sex chromosomes and sex-linked genes. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1967
Ohno, S., Stenius, C., Christian, L. C., Beçak, W., Beçak, M. L.: Chromosomal uniformity in the avian subclass Carinatae. Chromosoma (Berl.) 15, 280–288 (1964)
Owen, J. J. T.: Karyotype studies on Gallus domesticus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 16, 601–608 (1965)
Pathak, S., Hsu, T. C., Shirley, L., Helm, III, J. D.: Chromosome homology in the climbing rats, genus Tylomys (Rodentia: Cricetidae). Chromosoma (Berl.) 42, 215–228 (1973)
Ray-Chaudhuri, R., Sharma, T., Ray-Chaudhuri, S. P.: A comparative study of the chromosomes of birds. Chromosoma (Berl.) 26, 148–168 (1969)
Renzoni, A., Vegni-Talluri, M.: The karyograms of some Falconiformes and Strigiformes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 20, 133–150 (1966)
Sasaki, M., Itoh, M.: Preliminary notes on the karyotype of two species of turtles, Clemmys japonica and Geoclemys reevesii. Chromosome Inform. Service (Tokyo) 8, 21–22 (1967)
Seabright, M.: A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet 1971 II, 971–972
Singh, L.: Evolution of karyotypes in snakes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 38, 185–236 (1972)
Sinha, A. K., Pathak, S., Nora, J. J.: A human family suggesting evidence for centric fission and stability of a telocentric chromosome. Human Hered. 22, 423–429 (1972)
Southern, D. I.: Stable telocentric chromosomes produced following centric mis-division in Myrmeleotettix maculatus (Thunb.). Chromosoma (Berl.) 26, 140–147 (1969)
Stenius, C., Christian, L. C., Ohno, S.: Comparative cytological study of Phasianus colchicus, Meleagris gallopavo and Gallus domesticus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 13, 515–520 (1963)
Stock, A. D., Hsu, T. C.: Evolutionary conservation in arrangement of genetic material. A comparative analysis of chromosome banding between the Rhesus macaque (2n=42, 84 arms) and the african green monkey (2n=60, 120 arms). Chromosoma (Berl.) 43, 211–224 (1973)
Takagi, N.: A comparative study of the chromosome replication in 6 species of birds. Jap. J. Genet. 47, 115–123 (1972)
Takagi, N., Itoh, M., Sasaki, M.: Chromosome studies in four species of Ratitae (Aves). Chromosoma (Berl.) 36, 281–291 (1972)
Takagi, N., Makino, S.: A revised study on the chromosomes of three species of birds. Caryologia (Firenze) 19, 443–455 (1966)
Todd, N. B.: Karyotypic fissioning and canid phylogeny. J. theor. Biol. 26, 445–480 (1970)
Yosida, T. H., Sagai, T.: Similarity of Giemsa banding patterns of chromosomes in several species of the genus Rattus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 41, 93–101 (1973)
Wahrman, J., Goiten, R., Nevo, E.: Mole rat Spalax: Evolutionary significance of chromosome variation. Science 164, 82–84 (1969)
Webster, T. P., Hall, W. P., Williams, E. E.: Fission in the evolution of a lizard karyotype. Science 177, 611–613 (1972).
Wetmore, A.: A classification for the birds of the world. Smiths. Misc. Coll. 139, 1–37 (1960)
White, M. J. D.: Animal cytology and evolution, 3rd. ed. London: Cambridge University Press 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takagi, N., Sasaki, M. A phylogenetic study of bird karyotypes. Chromosoma 46, 91–120 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00332341
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00332341