Summary
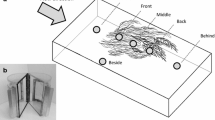
Woody debris is a major structural component of south-eastern Australian lowland streams, and the decayed wood substrates provide a structurally complex habitat for macroinvertebrate colonization. I tested for the presence of a species richness-habitat complexity relationship for macroinvertebrate species inhabiting the surfaces of decayed submerged logs (snags) in a lowland stream in northern Victoria. The species-habitat complexity relationship is defined as the increase in species richness due to increased structural complexity of a habitat when area is held constant. The response of macroinvertebrates to seven treatments of artificial and natural substrates of differing levels and types of structural complexity were examined using cluster analyses and MANOVAs. These analyses revealed a significant species-habitat complexity relationship. In addition, a comparison of species evenness between simple and complex habitats supported the hypothesis that more complex habitats contained more species because they possessed more resources. Analysis of species richness, though informative, masked the complexity of species responses revealed by multivariate analyses of species abundances. These analyses showed that different species groups selected different microhabitats on snags, particularly in response to the level of sediment deposition, which was greater on more structurally complex snags. In comparison with the benthos, snags were significantly richer in species abundances, possibly related to low levels of dissolved oxygen in benthic habitats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin MP, Belbin L (1982) A new approach to the species classification problem in floristic analysis. Aust J Ecol 7:75–89
Belbin L (1988) PATN Reference Manual. CSIRO Division of Wildlife and Ecology, Canberra A.C.T. Australia
Benke AC, Van Arsdall TC, Gillespie DM, Parrish FK (1984) Invertebrate productivity in a subtropical blackwater river: the importance of habitat and life history. Ecol Monogr 54:25–63
Boulton AJ (1985) A sampling device that quantitatively collects benthos in flowing or standing waters. Hydrobiologia 127:31–39
Cadwallader PL, Eden AK, Hook RA (1980) Role of streamside vegetation as a food source for Galaxias olidus Gunther (Pisces: Galaxiidae). Aust J Mar Freshwat Res 31:257–262
Connor EF, McCoy ED (1979) The statistics of the species-area relationship. Am Nat 113:791–833
Dean RL, Connell JH (1987a) Marine invertebrates in algal succession. II. Tests of hypotheses to explain changes in diversity with succession. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 109:217–247
Dean RL, Connell JH (1987b) Marine invertebrates in algal succession. III. Mechanisms linking habitat complexity with diversity. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 109:249–273
Doeg TJ, Lake PS (1981) A technique for assessing the composition and density of the macroinvertebrate fauna of large stones in streams. Hydrobiologia 80:3–6
Frontier S (1987) Applications of fractal theory to ecology. In: Legendre P and Legendre L (eds) Developments in Numerical Ecology, NATO ASI Series, vol G14. Springer, Berlin, pp 335–378
Gibbons MJ (1988) The impact of sediment accumulations, relative habitat complexity and elevation on rocky shore meiofauna. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 122:225–241
Hart DD (1978) Diversity in stream insects: regulation by rock size and microspatial complexity. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 20:1376–1381
Heck KL, Wetstone GS (1977) Habitat complexity and invertebrate species richness and abundance in tropical seagrass meadows. J Biogeog 4:135–142
Hurlbert SH (1981) A gentle depilation of the niche: Dicean resource sets in resource hyperspace. Evolutionary Theory 5:177–184
Kohn AJ, Leviten PJ (1976) Effect of habitat complexity on population density and species richness in tropical intertidal predatory gastropod assemblages. Oecologia 25:199–210
Lance GN, Williams WT (1967) A general theory of classificatory sorting strategies. I. Hierarchical systems. Comput J 9:373–380
Land Conservation Council Report (1983) Report on the Murray Valley area. Victorian Land Conservation Council, Melbourne
Ludwig JA, Reynolds JF (1988) Statistical Ecology: A primer on methods and computing. John Wiley & Sons, New York, Brisbane
MacArthur RH, MacArthur JW (1961) On bird species diversity. Ecology 42:594–598
McGuinness KA (1984) Equations and explanations in the study of species-area curves. Biol Rev 59:423–440
McGuinness KA, Underwood AJ (1986) Habitat structure and the nature of communities on intertidal boulders. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 104:97–123
Minshall GW (1984) Aquatic insect-substratum relationships. In: Resh VH, Rosenberg DM (eds) The ecology of aquatic insects. Praeger Publishers New York, pp 358–400
Nilsson SG, Bengtsson J, As S (1988) Habitat diversity or area per se? Species richness of woody plants, carabid beetles and land snails on islands. J Anim Ecol 57:685–704
Rosenzweig ML, Winakur J (1969) Population ecology of desert rodent communities: habitats and environmental complexity. Ecology 50:558–572
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1981) Biometry 2nd ed. Freeman, San Francisco, CA U.S.A.
Tonn WM, Magnuson JJ (1982) Patterns in the species composition and richness of fish assemblages in northern Wisconsin lakes. Ecology 63:1149–1166
Wilcox RR (1987) Pairwise comparisons of J independent regression lines over a finite interval, simultaneous pairwise comparisons of their parameters, and the Johnson-Neyman procedure. Brit J Math Stat Psych 40:80–93
Wilkinson L (1975) Response variable hypotheses in the multivariate analysis of variance. Psych Bull 82:408–412
Wilkinson L (1989) SYSTAT: The system for statistics. SYSTAT Inc. Evanston IL USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Connor, N.A. The effects of habitat complexity on the macroinvertebrates colonising wood substrates in a lowland stream. Oecologia 85, 504–512 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323762
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323762