Summary
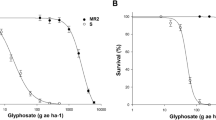
The acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) gene from the Arabidopsis thaliana mutant line GH90 carrying the imidazolinone resistance allele imr1 was cloned. Expression of the AHAS gene under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter in transgenic tobacco resulted in selective imidazolinone resistance, confirming that the single base-pair change found near the 3′ end of the coding region of this gene is responsible for imidazolinone resistance. A chimeric AHAS gene containing both the imr1 mutation and the csr1 mutation, responsible for selective resistance to sulfonylurea herbicides, was constructed. It conferred on transgenic tobacco plants resistance to both sulfonylurea and imidazolinone herbicides. The data illustrate that a multiple-resistance phenotype can be achieved in an AHAS gene through combinations of separate mutations, each of which individually confers resistance to only one class of herbicides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaleff RS, Mauvais CJ (1984) Acetolactate synthase is the site of action of two sulfonylurea herbicides in higher plants. Science 224:1443–1444
Chaleff RS, Ray TB (1984) Herbicide — resistant mutants from tobacco cell cultures. Science 223:1148–1151
Charest PJ, Hattori J, DeMoor J, Iyer VN, Miki BL (1990) In vitro study of transgenic tobacco expressing Arabidopsis wildtype and mutant acetohydroxyacid synthase genes. Plant Cell Rep 8:643–646
Creason GL, Chaleff RS (1988) A second mutation exhances resistance of a tobacco mutant to sulfonylurea herbicides. Theor Appl Genet 76:177–182
Dale RMK, McClure BA, Houchins JP (1985) A rapid singlestranded cloning stategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing. Application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18S rDNA. Plasmid 13:31–40
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragment to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Gabard JM, Charest PJ, Iyer VN, Miki BL (1989) Cross-resistance to short residual sulfonylurea herbicides in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 91:574–580
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Haughn GW, Smith J, Mazur B, Somerville C (1988) Transformation with a mutant Arabidopsis acetolactate synthase gene renders tobacco resistant to sulfonylurea herbicides. Mol Gen Genet 211:266–271
Haughn GW, Somerville C (1986) Sulfonylurea — resistant mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 204:430–434
Haughn GW, Somerville C (1990) A mutation causing imidazolinone resistance maps to the csrl locus of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 92:1081–1085
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffman NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231
La Rossa RA, Schloss JV (1984) The sulfonylurea herbicide sulfometuron methyl is an extremely potent and selective inhibitor of acetolactate synthase in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem 259:8753–8757
Lee KY, Lund P, Lowe K, Dunsmuir P (1990) Homologous recombination in plant cells after Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Plant Cell 2:415–425
Lee KY, Townsend J, Tepperman J, Black M, Chui C-F, Mazur B, Dunsmuir P, Bedbrook J (1988) The molecular basis of sulfonylurea herbicide resistance in tobacco. EMBO J 7:1241–1248
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbour, New York
Mazur BJ, Chui C-F, Smith JK (1987) Isolation and characterization of plant genes coding for acetolactate synthase, the target enzyme for two classes of herbicides.Plant Physiol 85:1110–1117
Mazur BJ, Falco SC (1989) The development of herbicide-resistant crops. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 40:441–470
Miflin BJ (1971) Cooperative feedback control of barley acetohydroxyacid synthetase by leucine, isoleucine and valine. Arch Biochem Biophys 146:512–550
Miki BL, Labbé H, Hattori J, Ouellet T, Gabard J, Sunohara G, Charest PJ, Iyer VN (1990) Transformation of Brassica napus canola cultivars with Arabidopsis thaliana acetohydroxyacid synthase genes and analysis of herbicide resistance. Theor Appl Genet 80:449–458
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Ray TB (1984) Site of action of chlorsulfuron. Inhibition of valine and isoleucine biosynthesis in plants. Plant Physiol 75:827–831
Relton JM, Wallsgrove RM, Bourgin J-P, Bright SWJ (1986) Altered feedback sensitivity of acetohydroxyacid synthase from valine-resistant mutants of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Planta 169:46–50
Rutledge RG, Ouellet T, Hattori J, Miki BL (1991) Molecular characterization and genetic origin of the Brassica napus acetohydroxyacid synthase multigene family. Mol Gen Genet 229:31–40
Sathasivan K, Haughn GW, Murai N (1990) Nucleotide sequence of a mutant acetolactate synthase gene from an imidazolinoneresistant Arabidopsis thaliana var. Columbia. Nucleic Acids Res 18:2188
Saxena PK, King J (1988) Herbicide resistance in Datura innoxia. Cross-resistance of sulfonylurea-resistant cell lines to imidazolines. Plant Physiol 86:863–867
Saxena PK, King J (1990) Lack of cross-resistance of imidazolinone-resistant cell lines of Datura innoxia P. Mill. to chlorsulfuron. Evidence for separable sites of action on the target enzyme. Plant Physiol 94:1111–1115
Schloss JV, Ciskanik LM, VanDyk DE (1988) Origin of the herbicide-binding site of acetolactate synthase. Nature 331:360–362
Shaner DL, Anderson PC, Stidham MA (1984) Imidazolinones. Potent inhibitors of acetohydroxyacid synthase. Plant Physiol 76:545–546
Subramanian MV, Gerwick BC (1989) Inhibition of acetolactate synthase by triazolopyrimidines. A review of recent developments — In: Whitaker JR, Sonnet PE (eds) Biocatalysis in agricultural biotechnology. Am Chem Soc Symp Ser, vol 389, pp 227–288
Swanson EB, Herrgesell MJ, Arnoldo M, Sippell DW, Wong RSC (1989) Microspore mutagenesis and selection: Canola plants with field tolerance to the imidazolinones. Theor Appl Genet 78:525–530
Wiersma PA, Schmiemann MG, Condie JA, Crosby WL, Moloney MM (1989) Isolation, expression and phylogenetic inheritance of an acetolactate synthase gene from Brassica napus. Mol Gen Genet 219:413–420
Winder T, Spalding MH (1988) Imazaquin and chlorsulfuron resistance and cross resistance in mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Gen Genet 213:394–399
Zambryski P, Joos H, Genetello C, Leemans J, VanMontagu M, Schell J (1983) Ti-plasmid vector for the introduction of DNA into plant cells without alteration of their normal regeneration capacity. EMBO J 2:2143–2150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Schell
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hattori, J., Rutledge, R., Labbé, H. et al. Multiple resistance to sulfonylureas and imidazolinones conferred by an acetohydroxyacid synthase gene with separate mutations for selective resistance. Molec. Gen. Genet. 232, 167–173 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279993
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279993