Summary
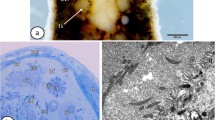
Thin sections of normal testes from the cyprinodont Aphanius dispar were studied by electron microscopy after intravascular injection of live specimens with horseradish peroxidase. The intercellular space in the spermatogenic cysts is marked differently by the tracer according to the degree of differentiation of the germ cells. Spermatogonia and gonocytes undergoing meiosis are surrounded by a dark band of the marker. This band gradually disappears during spermiogenesis. In cysts containing ripe spermatozoa, the marker penetrates a short distance between the bases of adjoining Sertoli cells bordering the cysts, but is arrested by tight junctional complexes near the lumina of the cysts. The tight junctions between the Sertoli cells provide a permeability barrier between the vascular spaces of the stroma and the lumina of ripe cysts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BM :
-
basement membrane
- BTB :
-
blood-testis barrier
- HRP :
-
horseradish peroxidase
References
Abraham M, Rahamim E, Tibika H (1979) The blood-testis barrier in Teleostei, Abstracts, 10th Conference, European Society for Comp Endocrinol, Sorrento
Billard R, Jalabert B, Breton B (1972) Les cellules de Sertoli des poissons téléostéens. Ann Biol Anim Bioch Biophys 12 (1):19–32
Bouffard G (1906) Injection des couleurs de benzidine aux animaux normaux. Ann Inst Pasteur 20:539–546
Brökelmann J (1963) Fine structure of germ cells and Sertoli cells during the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 58:820–850
Burgos MH, Vitale-Calpe R, Aoki A (1970) Fine structures of the testis and its functional significance. In: Johnson AD, Gomes WR, Vandemark NL (eds) The Testis. Academic Press, New York London, Vol 1, pp 551–649
Chakraborty J, Nelson L, Ihunjhunwala J, Young M, Kropp K (1976) Basal lamina of human seminiferous tubule — its role in material transport. I. In presence of tunica vaginal hydrocoel. Cell Tissue Res 174:261–271
Dym M (1973) The fine structure of the monkey (Macaca) Sertoli cell and its role in maintaining the blood-testis barrier. Anat Rec 175:639–656
Dym M, Fawcett DW (1970) The blood-testis barrier in the rat and the physiological compartmentalization of the seminiferous epithelium. Biol Reprod 3:308–326
Dym M, Cavicchia J (1977) Further observations on the blood-testis barrier in monkeys. Biol Reprod 17:390–403
Fawcett DW, Leak LV, Heidger PM Jr (1970) Electron microscopic observations on the structural components of the blood-testis barrier. J Reprod Fertil Suppl 10:105–122
Flickinger CJ (1967) The postnatal development of the Sertoli cells of the mouse. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 78:92–113
Gravis CJ, Chen I-Li, Yates RD (1977) Ultrastructure and cytochemistry of the epinephrine induced testicular degeneration. In: Yates RD, Gordon M (eds) Male Reproductive System: Fine Structure Analysis by Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy. Masson Publishing USA Incorporated, New York
Karnovsky MJ (1967) The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol 35 (1):213–236
Kormano M (1967) Dye permeability and alkaline phosphatase activity of testicular capillaries in the post-natal rat. Histochemie 9:327–338
Kormano M (1968) Penetration of intravenous trypan blue into the rat testis and epididymis. Acta Histochem 30:133–136
Kretser DM de, Kerr JB, Paulsen CA (1975) The peritubular tissue in the normal and pathological human testis. An ultrastructural study. Biol Reprod 12:317–324
Lacroix M, Smith FE, Fritz IB (1977) Secretion of plasminogen activator by Sertoli cells enriched cultures. Mol Cell Endocrinol 9:227–236
Marcaillou C, Szöllösi A (1980) The “blood-testis” barrier in a nematode and a fish: a generalizable concept. J Ultrastruct Res 70:128–136
Ribbert H (1904) Die Abscheidung intravenös injizierten gelösten Karmins in den Geweben. Z Allgem Physiol 4:201–214
Ross M, Grant L (1968) On the structural integrity of basement membrane. Exp Cell Res 50:277–285
Setchell BP, Waites GMH (1975) The blood-testis barrier. In: Hamilton DW, Greep RO (eds) Handbook of Physiology. Section 7: Endocrinology, Vol V. Male Reproductive System. American Physiol Society, Washington, pp 143–172
Szöllösi A, Marcaillou C (1977) Electron microscope study of the blood-testis barrier in an insect: Locusta migratoria. J Ultrastruct Res 59:158–172
Vilar O (1973) Spermatogenesis. In: Hafez ESE, Evans TN (eds) Human Reproduction. Harper and Row Publishers, New York, pp 12–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by a grant from the National Council for Research and Development, Israel, and the GKSS Geesthacht-Tesperhude, Federal Republic of Germany
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abraham, M., Rahamim, E., Tibika, H. et al. The blood-testis barrier in Aphanius dispar (Teleostei). Cell Tissue Res. 211, 207–214 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236443
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236443