Abstract
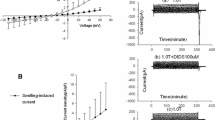
Cell swelling has been shown to increase the permeability of the plasma membrane to ions such as K+, Na+, Ca2+ or Cl− in many types of cells. In cardiac cells, swelling has been reported to increase Cl− conductance, but whether cation-selective currents are activated by swelling is not known. Low Cl− or Cl−-free solutions were used to study the presence of such currents. Lowering the osmolarity of the extracellular medium from 299 to 219 mOsm resulted in cell swelling and concurrent activation of a cation-selective whole-cell current. When cell-attached patches were formed on swollen cells, opening of bursting single channel currents were observed in 18% of the patches studied. Ion substitution experiments indicated that the channel discriminated poorly among monovalent cations, and was impermeable to Cl−. The channel was permeable to Ca2+. In symmetrical 140 mM K+, the current-voltage relation was linear with a single channel conductance of 36 ± 3 pS. Depolarization increased channel open probability. Interestingly, depending on the membrane patch studied, application of negative pressure to the pipette caused either an increase or a decrease in the open probability of the channel already activated by swelling. Thus, the sensitivity to tension of the swelling-activated channel was different from those of previously reported stretch-activated channels. These findings suggest that nonselective cation channels exist in rat atrial cells and may be involved in swelling-induced changes in cell function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, J., Lassalles, J.-P. 1991. Hydrostatic and osmotic pressure activated channel in plant vacuole. Biophys. J. 60:1326–1336
Banderali, U., Roy, G. 1992. Activation of K+ and Cl− channels in MDCK cells during volume regulation in hypotonie media. J. Membrane Biol. 126:219–234
Bear, C.E. 1990. A nonselective cation channel in rat liver cells is activated by membrane stretch. Am. J. Physiol. 258:C421-C428
Busch, A.E., Varnum, M., Adelman, J.P., North, R.A. 1992. Hypotonic solution increases the slowly activating potassium current I SK expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 184:804–810
Bustamante, J.O., Ruknudin, A., Sachs, F. 1991. Stretch-activated channels in heart cells: Relevance to cardiac hypertrophy. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 17(Suppl.):S110-S113
Chan, H.C., Nelson, D.J. 1992. Chloride-dependent cation conductance activated during cellular shrinkage. Science 257:669–671
Christensen, O. 1987. Mediation of cell volume regulation by Ca2+ influx through stretch-activated channels. Nature 330:66–68
Christensen, O., Hoffmann, E.K. 1992. Cell swelling activates K+ and Cl− channels as well as nonselective, stretch-activated cation channels in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J. Membrane Biol. 129:13–36
Clemo, H.F., Feher, J.J., Baumgarten, C.M. 1992. Modulation of rabbit ventricular cell volume and Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransport by cGMP and atrial natriuretic factor. J. Gen. Physiol. 100:89–113
Colquhoun, D., Sakmann, B. 1985. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J. Physiol. 369:501–557
Coulombe, A., Duclohier, H., Coraboeuf, E., Touzet, N. 1987. Single chloride-permeable channels of large conductance in cultured cardiac cells of new-born rats. Eur. Biophys. J. 14:155–162
Craelius, W., Chen, V., El-Sherif, N. 1988. Stretch activated ion channels in ventricular myocytes. Biosci. Rep. 8:407–414
Drewnowska, K., Baumgarten, C.M. 1991. Regulation of cellular volume in rabbit ventricular myocytes: bumetanide, chlorothiazide, and ouabain. Am. J. Physiol. 260:C122-C131
Falke, L.C., Misler, S. 1989. Activity of ion channels during volume regulation by clonal N1E115 neuroblastoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:3919–3923
Fatt, P., Ginsborg, B.L. 1958. The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in crustacean muscle fibers. J. Physiol. 142:516–543
Franco, A., Jr., Eansman, J.B. 1990. Calcium entry through stretch-inactivated ion channels in mdx myotubes. Nature 344:670–673
French, A.S. 1992. Mechanotransduction. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 54:135–152
Hagiwara, N., Masuda, H., Shoda, M., Irisawa, H. 1992. Stretch-activated anion currents of rabbit cardiac myocytes. J. Physiol. 456:285–302
Harmill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Hamill, O.P., McBride, D.W., Jr. 1992. Rapid adaptation of single mechanosensitive channels in Xenopus oocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89:7462–7466
Kim, D. 1991. Modulation of acetylcholine-activated K+ channel function in rat atrial cells by phosphorylation. J. Physiol. 437:133–155
Kim, D. 1992. A mechanosensitive K+ channel in heart cells: activation by arachidonic acid. J. Gen. Physiol. 100:1–20
Kim, D. 1993. Novel cation-selective mechanosensitive ion channel in the atrial cell membrane. Circ. Res. 72:225–231
Lewis, S.A., Donaldson, P. 1990. Ion channels and cell volume regulation: chaos in an organized system. News in Physiol. Sci. 5:112–119
Macknight, A.D.C., Leaf, A. 1977. Regulation of cellular volume. Physiol. Rev. 57:510–573
Marban, E., Koretsune, Y. 1990. Cell calcium, oncogenes, and hypertrophy. Hypertension 15:652–658
Moody, W.J., Bosma, M.M. 1989. A nonselective cation channel activated by membrane deformation in oocytes of the Ascidian Boltenia villosa. J. Membrane Biol. 107:179–188
Morris, C.E. 1990. Mechanosensitive ion channels. J. Membrane Biol. 113:93–107
Morris, C.E., Sigurdson, W.J. 1989. Stretch-inactivated ion channels coexist with stretch-activated ion channels. Science 243:807–809
Roos, K.P. 1986. Length, width, and volume changes in osmotically stressed myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 251:H1373-H1378
Rothstein, A., Mack, E. 1992. Volume-activated calcium uptake: its role in cell volume regulation of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Am. J. Physiol. 262:C339-C347
Sachs, F. 1986. Biophysics of mechanoreception. Memb. Biochem. 6:173–195
Sackin, H. 1989. A stretch-activated K+ channel sensitive to cell volume. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:1731–1735
Sato, N., Wang, X., Greer, M.A., Greer, S.E., McAdams, S., Oshima, T. 1990. Medium hyposmolarity stimulates prolactin secretion in GH4C1 cells by inducing an increase in cytosolic free calcium. Endocrinology 127:957–964
Sigurdson, W.J., Morris, C.E., Brezden, B.L., Gardner, D.L. 1987. Stretch activation of a K+ channel in molluscan heart cells. J. Exp. Biol. 127:191–209
Sigurdson, W., Ruknudin, A., Sachs, F. 1992. Calcium imaging of mechanically induced fluxes in tissue-cultured chick heart: role of stretch-activated ion channels. Am. J. Physiol. 262:H1110-H1115
Sigworth, F.J., Sine, S.M. 1987. Data transformations for improved display and fitting of single-channel dwell time histograms. Biophys. J. 52:1047–1054
Sorota, S. 1992. Swelling-induced chloride-sensitive current in canine atrial cells revealed by whole cell patch-clamp method. Circ. Res. 70:679–687
Sparks, H.V., Jr., Wrangler, R.D., Dewitt, D.F. 1984. Control of the coronary circulation. In: Physiology and Pathophysiology of the Heart. N. Sperelakis, editor; pp. 797–817. Martinus Nijhoff Publishing, Boston
Tokola, H., Uusimaa, P.A., Taskinen, T., Hassinen, I.E., Ruskoaho, H. 1991. Effect of hypoosmolality on atrial natriuretic peptide gene expression in neonatal cultured cardiomyocytes. Acta Physiol. Scand. 143:223–224
Tseng, G. 1992. Cell swelling increases membrane conductance of canine cardiac cells: evidence for a volume-sensitive Cl− channel. Am. J. Physiol. 262:C1056-C1068
Ubl, J., Murer, H., Kolb, H.-A. 1988. Ion channels activated by osmotic and mechanical stress in membranes of oppossum kidney cells. J. Membrane Biol. 104:223–232
Vislie, T. 1980. Cell volume regulation in isolated, perfused heart ventricle of the flounder (Platichthys flesus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 65A:19–27
Wong, S.M.E., Chase, H.S., Jr. 1986. Role of intracellular calcium in cellular volume regulation. Am. J. Physiol. 250:C841-C852
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dr. Kim is an Established Investigator of the American Heart Association.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D., Fu, C. Activation of a nonselective cation channel by swelling in atrial cells. J. Membarin Biol. 135, 27–37 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234649
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234649