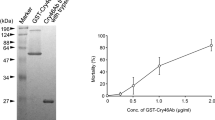
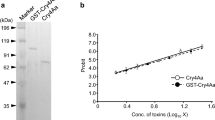
Summary
Previous studies in our laboratory have shown that CryIC, a lepidopteran-specific toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis, triggers calcium and chloride channel activity in SF-9 cells (Spodoptera frugiperda, fall armyworm). Chloride currents were also observed in SF-9 membrane patches upon addition of CryIC toxin to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. In the present study the ability of activated CryIC toxin to form channels was investigated in a receptor-free, artificial phospholipid membrane system. We demonstrate that this toxin can partition in planar lipid bilayers and form ion-selective channels with a large range of conductances. These channels display complex activity patterns, often possess subconducting states and are selective to either anions or cations. These properties appeared to be pH dependent. At pH 9.5, cation-selective channels of 100 to 200 pS were most frequently observed. Among the channels recorded at pH 6.0, a 25–35 pS anion-selective channel was often seen at pH 6.0, with permeation and kinetic properties similar to those of the channels previously observed in cultured lepidopteran cells under comparable pH environment and for the same CryIC toxin doses. We conclude that insertion of CryIC toxin in SF-9 cell native membranes and in artificial planar phospholipid bilayers may result from an identical lipid-protein interaction mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronson, A.I., Beckman, W., Dunn, P. 1986. Bacillus thuringiensis and related insect pathogens. Microbiol. Rev. 50:1–24
Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254
Bretag, A.H. 1987. Muscle chloride channels. Physiol. Rev. 67:618–724
Brousseau, R., Masson, L. 1988. Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal toxins: gene structure and mode of action. Biotechnol. Adv. 6:697–724
Bullock, J.O. 1992. Ion selectivity of colicin E1: Modulation by pH and membrane composition. J. Membrane Biol. 125:255–271
Crawford, D.N., Harvey, W.R. 1988. Barium and calcium block Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies kurstaki δ-endotoxin inhibition of potassium current across isolated midgut of larval Manduca sexta. J. Exp. Biol. 137:277–286
Davidson, E.W. 1989. Insect cell cultures as tools in the study of bacterial protein toxins. In: Advances in Cell Culture. K. Maramorosh, editor. Vol. 7, pp. 125–146. Academic, New York
Devereux, J., Haeberli, P., Smithies, O. 1984. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 12:387–395
Ellar, D.J., Thomas, W.E., Knowles, B.H., Ward, S., Todd, J., Drobniewski, F., Lewis, J., Sawyer, T., Last, D., Nichols, C. 1985. Biochemistry, genetics, and mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxins. In: Molecular Biology of Microbial Differentiation. J.A. Hoch and P. Setlow, editors. pp. 230–239. ASM Public, Washington
English, L.H., Cantley, L.C. 1985. Delta endotoxin inhibits Rb+ uptake, lowers cytoplasmic pH and inhibits a K+-ATPase in Manduca sexta CHE cells. J. Membrane Biol. 85:199–204
Fox, J.A. 1987. Ion channel subconductance states. J. Membrane Biol. 97:1–8
Gringorten, J.L., Witt, D.P., Milne, R.E., Fast, P.G., Sohi, S.S., van Frankenhuyzen, K. 1990. An in vitro system for testing Bacillus thuringiensis toxins: the lawn assay. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 56:237–242
Himeno, M. 1987. Mechanism of action of delta-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Toxicol.-Toxin Rev. 6:45–71
Hoch, D.H., Finkelstein, A. 1985. Gating of large toxin channels by pH. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 456:33–35
Hodgman, T.C., Ellar, D.J. 1990. Models for the structure and function of the Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxins determined by compilational analysis. DNA Sequence—J. DNA Sequencing and Mapping. 1:97–106
Höfte, H., Whiteley, H.R. 1989. Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol. Rev. 53:242–255
Knowles, B.H., Blatt, M.R., Tester, M., Horsnell, J.M., Carroll, J., Menestrina, G., Ellar, D.J. 1989. A cytolytic δ-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis forms cation-selective channels in planar lipid bilayers. FEBS Lett. 244:259–262
Knowles, B.H., White, P.J., Nicholls, C.N., Ellar, D.J. 1992. A broad-spectrum cytolytic toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis var. kyushuensis. Proc. R. Soc. London B 248:1–7
Knowles, B.H., Ellar, D.J. 1987. Colloid-osmotic lysis is a general feature of the mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensiss δ-endotoxins with different insect specificity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 924:509–518
Laemmli, U.K., Favre, M. 1973. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J. Mol. Biol. 80:575–599
Li, J., Carroll, J., Ellar, D.J. 1991. Crystal structure of insecticidal δ-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature 353:815–821
Masson, L., Préfontaine, G., Péloquin, L., Lau, P.C.K., Brousseau, R. 1989. Comparative analysis of the individual protoxin components in P1 crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki isolates NRD-12 and HD-1. Biochem. J. 269:507–512
Miller, C., Racker, E. 1976. Calcium-induced fusion of fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum with artificial planar bilayers. J. Membrane Biol. 30:271–282
Müller, P., Rudin, D.O., Tein, H.T., Wescott, W.C. 1963. Methods for formation of single bimolecular lipid membranes in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. 67:534–535
Pattus, F., Massotte, D., Wilmsen, H.U., Lakey, J., Tsernoglou, D., Tucker, A., Parker, M.W. 1990. Colicins: prokaryotic killer-pores. Experientia 46:180–192
Pfannenstiel, M.A., Couche, G.A., Ross, E.J., Nickerson, K.W. 1986. Immunological relationships among proteins making up the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis crystalline toxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 52:644–649
Raymond, L., Slatin, S.L., Finkelstein, A. 1985. Channels formed by Colicin E1 in planar lipid bilayers are large and exhibit pH-dependent ion selectivity. J. Membrane Biol. 84:173–181
Ropele, M., Menestrina, G. 1990. Aspects of the molecular architecture of the channel formed by E. coli hemolysin in planar lipid membranes. In: Bacterial Protein Toxins. Rappuoli et al., editors. Zbl. Bakt. Suppl. 19, pp. 73–74. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart
Sacchi, V.F., Parenti, P., Hanozet, G.M., Giordana, B., Lüthy, P., Wolfersberger, M.G. 1986. Bacillus thuringiensis toxin inhibits K+-gradient-dependent amino acid transport across the brush border membrane of Pieris brassicae midgut cells. FEBS Lett. 204:213–218
Schwartz, J.L., Garneau, L., Masson, L., Brousseau, R. 1991. Early response of cultured lepidopteran cells to exposure to δ-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis: involvement of calcium and anionic channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1065:250–260
Slatin, S.L., Abrams, C.K., English, L. 1990. Delta-endotoxins form cation-selective channels in planar lipid bilayers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 169:765–772
Tocanne, J.F., Teissié, J. 1990. Ionization of phospholipids and phospholipid-supported interfacial lateral diffusion of protons in membrane model systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1031:111–142
Van der Goot, F.G., Gonźalez-Mañas, J.M., Lakey, J.H., Pattus, F. 1991. A “molten-globule” membrane-insertion intermediate of the pore-forming domain of colicin A. Nature 354:408–410
Wolfersberger, M.G. 1989. Neither barium nor calcium prevents the inhibition by Bacillus thuringiensis gd-endotoxin of sodiumor potassium gradient-dependent amino acid accumulation by tobacco hornworm midgut brush border membrane vesicles. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 12:267–277
Wolfersberger, M.G., Hofmann, C., Lüthy, P. 1986. Interaction of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin with membrane vesicles isolated from lepidopteran larval midgut. In: Bacterial Protein Toxins. Falmagne et al., editors. Zbl. Bakt. Suppl. 15, pp. 237–238. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The assistance of A. Mazza and G.A.R. Mealing is gratefully acknowledged. The trypsin-activated, HPLC-purified CryIC toxin isolated from B. thuringiensis var. entomocidus crystal was a kind gift from M. Pusztai, Institute for Biological Sciences, NRC, Ottawa.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwartz, JL., Garneau, L., Savaria, D. et al. Lepidopteran-specific crystal toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis form cation- and anion-selective channels in planar lipid bilayers. J. Membarin Biol. 132, 53–62 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233051
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233051