Summary
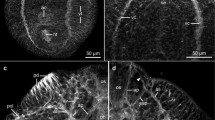
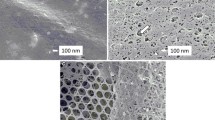
The peripheral nervous system of the polyclad flatworm Notoplana acticola is described from electron microscopic observations. There are two components, a subepithelial system and a submuscular plexus. The subepithelial system lies among muscle cells beneath the basement membrane of the epithelium. Axons and processes containing clear or dense-cored vesicles were found. The subepithelial system is in the form of a feltwork of fibers rather than a nerve-net. The submuscular plexus has both specialized and primitive aspects to its organization. In the former category are sheathed axons and complex synaptic configurations while the latter can be seen in the numerous naked axons, somata lying deep in the nerve tissue and islands of neuropil scattered along the nerve tracts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ax, P.: Verwandtschaftsbeziehungen und Phylogenie der Turbellarien. Ergebn. Biol. 24, 1–68 (1961)
Ax, P.: Relationships and phylogeny of the Turbellaria. In: The Lower Metazoa, ed. E. C. Dougherty, Z. N. Brown, E. D. Hanson and W. D. Hartman, p. 191–224. Berkeley: University of California Press 1963
Beklemishev, V. N.: On the relationship of the Turbellaria to other groups of the animal kingdom. In: The Lower Metazoa, ed. E. C. Dougherty, A. N. Brown, E. D. Hanson and W. D. Hartman, p. 234–244. Berkely: University of California Press 1963
Beklemishev, V. N.: Principles of comparative anatomy of invertebrates. Chicago: University of Chicago Press 1969
Best, J. B.: The neuroanatomy of the planarian brain and some functional implications. In: Chemistry of learning: Invertebrate research, ed. W. C. Corning and S. C. Ratner, p. 144–163. New York: Plenum Press 1967
Bullock, T. H., Horridge, G. A.: Structure and function in the nervous systems of invertebrates. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman and Co. 1965
Chien, P., Koopowitz, H.: The ultrastructure of neuromuscular systems in Notoplana acticola, a free-living polyclad flatworm. Z. Zellforsch. 133, 277–288 (1972)
Corning, W. C., Kelly, S.: Platyhelminth.es: The Turbellarians. In: Invertebrate learning, ed. W. C. Corning, J. A. Dyal and A.O.D. Willows, p. 171–224. New York: Plenum Press 1973
Gruber, S. A., Ewer, D. W.: Observations on the myo-neural physiology of the polyclad, Planocera gilchristi. J. exp. Biol. 39, 459–477 (1962)
Hadenfeldt, D.: Das Nervensystem von Stylochoplana maculata und Notoplana atomata. Z.wiss. Zool. 133, 586–638 (1929)
Hadzi, J.: The evolution of the metazoa. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1963
Hanson, E. D.: On the origin of the Eumetazoa. Syst. Zool. 7, 16–47 (1958)
Hanson, E. D.: Homologies and the ciliate origin of the Eumetazoa. In: The Lower Metazoa, ed. E. C. Dougherty, Z. N. Brown, E. D. Hanson and W. D. Hartman, p. 7–22. Berkeley:University of California Press 1963
Hyman, L.: The invertebrates: Platyhelminthes and Rhyncocoela. New York: McGraw-Hill 1951
Josephson, R. K.: Cnidarian neurobiology. In: Coelenterate biology, ed. L. Muscantine and H. M. Lenhoff. New York: Academic Press 1974 (in press)
Karnovsky, M. J.: Simple methods of “staining with lead” at high pH in electron microscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 11, 729–732 (1961)
Kato, K.: On the development of some Japanese polyclads. Jap. J. Zool. 8, 537–574 (1940)
Kato, K.: Platyhelminthes. In: Invertebrate embryology, ed. M. Kumé and K. Dan (translated by K. C. Dan). Belgrade: NOLIT, Publishing House 1968
Koopowitz, H.: Feeding behavior and the role of the brain in the polyclad flatworm Planocera gilchristi. Anim. Behav. 18, 31–35 (1970)
Koopowitz, H.: Organization of primitive nervous systems. Neuromuscular physiology of Gyrocotyle urna, a parasitic flatworm. Biol. Bull. 144, 489–502 (1973)
Koopowitz, H.: Some aspects of the physiology and organization of the nerve plexus in polyclad flatworms. In: Biology of the Turbellaria, ed. N. W. Riser and M. R. Morse. New York: McGraw-Hill 1974
Lang, A.: Die Polycladen des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeresabschnitte. Fauna u. Flora Neapel 11, 1–688 (1884)
Lentz, T. L.: Primitive nervous systems. New Haven: Yale University Press (1968)
Morita, M.: Electron microscopic studies on planaria. I. Fine structure of muscle fibers in the head of the planarian Dugesia darotochephala. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 13, 383–295 (1965)
Morita, M., Best, J. B.: Electron microscopic studies of planaria. III. Some observations on the fine structure of planarian nervous tissue. J. exp. Zool. 161, 391–412 (1966)
Oosaki, T., Ishii, S.: Observations on the ultrastructure of nerve cells in the brain of the planarian Dugesia gonocephala. Z. Zellforsch. 66, 782–793 (1965)
Reisinger, E.: Untersuchungen am Nervensystem der Bothrioplana semperi Braun. Z. Morph.Ökol. Tiere 5, 119–149 (1925)
Reisinger, E.: Was ist Xenoturbella ? Z. wiss. Zool. 164, 188–198 (1960)
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–213 (1963)
Turner, R. S.: Observations on the central nervous system of Leptoplana acticola. J. comp. Neurol. 85, 53–65 (1946)
Westfall, J. A.: Ultrastructural evidence for neuromuscular systems in coelenterates. Amer. Zool. 13, 237–246 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koopowitz, H., Chien, P. Ultrastructure of the nerve plexus in flatworms. Cell Tissue Res. 155, 337–351 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222810
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222810