Summary
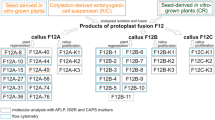
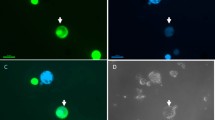
Somatic hybrid cell lines were constructed by the fusion of protoplasts isolated from cell suspensions of Zea mays L. (maize, 2n = 20) and Triticum sect, trititrigia MacKey (trititrigia, 2n = 35), a perennial hybrid of T. durum Desf. and Elytrigia intermedium (Host) Nevski. Iodoacetamide-inactivated protoplasts of maize were fused with trititrigia protoplasts, which were sensitive to the PEG/DMSO fusion treatment at high pH and high calcium. Based on physiological complementation, approximately 0.002% of the total protoplasts cultured following fusion treatment developed into cell colonies, and 79 lines of them, almost a half, were singled out and subcultured. Among the subcultured lines three were, in comparison with the parents, identified as somatic hybrids by their coupled XbaI restriction patterns of total DNAs probed with the ribosomal DNA of rice. Southern analysis of the digested total DNAs with a mitochondrial gene, atpA., from pea, or a chloroplast gene, trnK, from rice, revealed that all the hybrids carried only the organellar DNAs of trititrigia, which excluded the possibilities of a chimeric callus or any DNA contamination. Cytogenetically, one hybrid was mixoploid with a 2n of 46–67 in which chromosomal endoreduplication, characterized by the appearance of diplochromosomes, was occasionally observed. Its hybridity was reconfirmed by the fact that it bore the satellite chromosomes of both maize and trititrigia, which were distinguishable from each other by size. In contrast, the other two hybrids were aneuploids. The potential of gene transfer between Zea and Triticum species was thus conclusively established.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brettell RIS, Banks PM, Cauderon Y, Chen X, Cheng ZM, Larkin PJ, Waterhouse PM (1988) A single wheatgrass chromosome reduces the concentration of barley yellow dwarf virus in wheat. Ann Appl Biol 113:599–603
Cai QG, Kuo CS, Qian YQ, Jiang RX, Zhou YL (1987) Plant regeneration from protoplasts of corn (Zea mays L.). Acta Bot Sin 29:453–458
Chien YC, Kao KN, Wetter LR (1982) Chromosomal and isozyme studies of Nicotiana tabacum-Glycine max hybrid cell lines. Theor Appl Genet 62:301–304
Chu CC, Wang CC, Sun CS, Hsu C, Yin KC, Chu CY (1975) Establishment of an efficient medium for anther culture of rice through comparative experiments on the nitrogen sources. Sci Sin 18:659–668
Coe E, Hoisington D, Chao S (1990) Gene list and working maps. Maize Genet Coop Newslett 64:134–163
Evans DA, Wetter LR, Gamborg OL (1980) Somatic hybrid plants of Nicotiana glauca and Nicotiana tabacum obtained by protoplast fusion. Physiol Plant 48:225–230
Fedak G (1985) Alien species as sources of physiological traits for wheat improvement. Euphytica 34:673–680
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Gleba YY, Sytnik EM (1984) Protoplast fusion. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Goodman RM, Hauptli H, Crossway A, Knauf VC (1987) Gene transfer in crop improvement. Science 236:48–54
Handley LW, Nickels RL, Cameron MW, Moore PP, Sink KC (1986) Somatic hybrid plants between Lycopersicon esculentum and Solanum lycopersicoides. Theor Appl Genet 71:691–697
Hayashi Y, Kyozuka J, Shimamoto K (1988) Hybrids of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and wild Oryza species obtained by cell fusion. Mol Gen Genet 214:6–10
Hutchinson J (1959) The families of flowering plants. Vol. 2, Monocotyledons. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Kao KN (1977) Chromosomal behaviour in somatic hybrids of soybean-Nicotiana glauca. Mol Gen Genet 150:225–230
Kao KN, Michayluk MR (1974) A method for high frequency intergeneric fusion of plant protoplasts. Planta 115:355–367
Kao KN, Constabel F, Michayluk MR, Gamborg OL (1974) Plant protoplast fusion and growth of intergeneric hybrid cells. Planta 120:215–227
Kostenyuk I, Lubaretz O, Borisyuk N, Voronin V, Stockigt, Gleba YY (1991) Isolation and characterization of intergeneric somatic hybrids in the Apocynaceae family. Theor Appl Genet 82:713–716
Laurie DA, Bennett MD (1986) Wheat x maize hybridization. Can J Genet Cytol 28:313–316
Laurie DA, O'Donoughue LS, Bennett MD (1990) Wheat x maize and other wide sexual hybrids: their potential for genetic manipulation and crop improvement. In: Gustafson JP (ed) Gene manipulation in plant improvement, vol 2. Plenum Press, New York, pp 95–126
Maliga P, Menczel L (1986) Chloroplast transfer and recombination through protoplast fusion. In: Vasil IK (ed) Cell culture and somatic cell genetics, vol III. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 601–612
Mathre DE, Johnston RH (1990) A crown barrier related to Cephalosporium stripe resistance in wheat relatives. Can J Bot 68:1511–1514
Medgyesy P, Menczel L, Maliga P (1980) The use of cytoplasmic streptomycin resistance-chloroplast transfer from Nicotiana tabacum into Nicotiana sylvestris and isolation of their somatic hybrids. Mol Gen Genet 179:693–698
Menczel L, Nagy F, Kiss Z, Maliga P (1981) Streptomycin-resistant and sensitive somatic hybrids of N. tabacum x N. knightiana: correlation and resistance to N. tabacum plastids. Theor Appl Genet 59:191–198
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of highmolecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
O'Connell MA, Hanson MR (1985) Somatic hybridization between Lycopersicon esculentum and Lycopersicon pennelli. Theor Appl Genet 70:1–12
Sakamoto K, Taguchi T (1991) Regeneration of intergeneric somatic hybrids between Lycopersicon esculentum and Solanum muricatum. Theor Appl Genet 81:509–513
Sidorov VA, Menczel L, Nagy F, Maliga P (1981) Chloroplast transfer in Nicotiana based on metabolic complementation between irradiated and iodoacetate-treated protoplasts. Planta 152:341–345
Sproule A, Donaldson P, Dijak M, Bevis E, Pandeya R, Keller WA, Gleddie S (1991) Fertile somatic hybrids between transgenic Nicotiana tabacum and transgenic N. debneyi selected by dual-antibiotic resistance. Theor Appl Genet 82:450–456
Tabaeizadeh Z, Ferl RJ, Vasil IK (1986) Somatic hybridization in the Gramineae: Saccharum officinarum L. (sugarcane) and Pennisetum americanum (L.) K. Schum. (pearl millet). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:5616–5619
Terada R, Kyozuka J, Nishibayashi S, Shimamoto K (1987) Plantlet regeneration from somatic hybrids o rice (Oryza sativa L.) and barnyard grass (Echinochloa oryzicola Vasing). Mol Gen Genet 210:39–43
Thomas MR, Johnson LB, White FF (1990) Selection of interspecific somatic hybrids of Medicago by using Agrobacterium-transformed tissues. Plant Sci 69:189–198
Tremblay C, Cloutier C, Comeau A (1989) Resistance to the bird cherr-oat aphid, Rhopalosiphum padi L. (Homopterce: Aphididae), in perennial Gramineae and wheat x perennial Gramineae hybrids. Envir Ent 18:921–932
Wang TB, Qian YQ, Li JL, Qu GP, Cai QG (1990) Plant regeneration from protoplasts of trititrigia (Triticum sect, trititrigia MacKey). Acta Bot Sin 32:329–336
Wetter LR (1977) Isozymes patterns in soybean-Nicotiana somatic hybrid cell lines. Mol Gen Genet 150:231–235
Zhang SB, Guo ZS, Qian YQ, Qu GP, Cai QG, Zhou YL (1990) Factors influencing isolation, division and plant regeneration in maize (Zea mays L.) protoplast culture. Chinese J Bot 2:18–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by Y. Gleba
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T.B., Niizeki, M., Harada, T. et al. Establishment of somatic hybrid cell lines between Zea mays L. (maize) and Triticum sect, trititrigia MacKey (trititrigia). Theoret. Appl. Genetics 86, 371–376 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222104
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222104