Conclusion
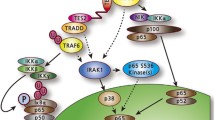
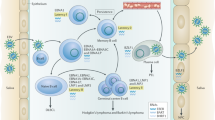
In summary, information obtained from single gene transfer into EBV-negative cell lines is consistent with molecular genetic analysis of in vitro transformation by the whole virus in emphasizing the role for EBNA2 and LMP-1 in cell growth transformation. In addition, the functions of the latent infection proteins in tissue culture cells is consistent with the pathology of the EBV-associated lesions. The repertoire of viral proteins displayed in vivo varies with the different tissues infected and the differentiation state of infected cells, and is likely to reflect, in part, the activity of the latent infection promoters in these cells. Recent methods for obtaining specific virus mutants will enable more complete characterization of the EBV latent infection proteins and their roles in EBV-induced immortalization and pathogenesis [79].
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfieri C, Birkenbach M, Kieff E (1991) Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B-lymphocytes. Virology 181: 595.
Allday MJ, Crawford DH, Griffin BE (1989) Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B cell immortalization. J Gen Virol 70: 1755.
Ambinder RF, Mullen M, Chang Y-N, Hayward GS, Hayward SD (1991) Functional domains of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA-1. J Virol 65: 1466.
Clarke PA, Sharp NA, Clemens MJ (1990) EBER-1 can prevent ds RNA-activated inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro. Eur J Biochem 193: 635.
Clarke PA, Schwemmle M, Schickinger J, Hilse K, Clemens MJ, (1991) Binding of Epstein-Barr virus small nuclear RNA EBER-1 to the double stranded RNA-activated protein kinase DA1. Nucleic Acids Res 19: 243.
Cohen JI (1991) Epstein-Barr virus lymphoproliferative disease associated with acquired immunodeficiency. Medicine 70: 137.
Cohen JI, Wang F, Mannick J, Kieff E (1989) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 is a key determinant of lymphocyte transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 86: 9558.
Cohen JI, Wang F, Kieff E (1991) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 mutations define essential domains for transformation and transactivation. J Virol 65: 2545.
Cooper NR, Moore MD, Nemerow GR (1988) Immunobiology of CR2, the B lymphocyte receptor for Epstein-Barr virus and the C3d complement receptor. Annu Rev Immunol 6: 85.
Dambaugh T, Wang F, Hennessy K, Woodland E, Rickinson A, Kieff E (1986) Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 in rodent cells. J Virol 59: 453.
Dawson CW, Rickinson AB, Young LS (1990) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein inhibits human epithelial cell differentiation. Nature 344: 777.
DeCaprio JA, Ludlow JW, Figge J, Shew J-Y, Huang C-M, Lee W-H, Marsilio E, Paucha E, Livingston DM (1988) SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell 54: 275.
De Souza YG, Greenspan D, Felton JR, Hartzog GA, Hammer M, Greenspan JS (1989) Localization of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in the epithelial cells of oral hairy leukoplakia by in situ hybridization on tissue sections. N Engl J Med 320: 1559.
Dyson N, Howley PM, Munger K, Harlow E (1989) The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science 243: 934.
Fahraeus R, Fu H-L, Ernberg I, Finke J, Rowe M, Klein G, Falk K, Wilson E, Yadav M, Busson P, Tursz T, Kallin B (1988) Expression of Epstein-Barr virus encoded proteins in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Int J Cancer 42: 329.
Falk K, Ernberg I, Sakthivel R, Davis J, Christensson B, Luka J, Okano M, Grierson HL, Klein G, Purtillo DT (1990) Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded proteins and B cell markers in fatal infectious mononucleosis. Int J Cancer 46: 976.
Friedman-Kien AE (1986) Viral origin of hairy leukoplakia. Lancet II: 694.
Furukawa Y, DeCaprio JA, Freedman A, Kanakura Y, Nakamura M, Ernst TJ, Livingston DM, Griffin JD (1990) Expression and state of phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product in cycling and noncycling human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 87: 2770.
Gilligan K, Sato H, Rajadurai P, Busson P, Young L, Rickinson A, Tursz T, Raab-Traub N (1990) Novel transcription from the Epstein-Barr virus terminal Eco RI fragment, DIJhet, in a nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Virol 64: 4948.
Gilligan K, Rajaduri P, Resnick L, Raab-Traub N (1990) Epstein-Barr virus small nuclear RNAs are not expressed in permissively infected cells in AIDS-associated leukoplakia. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 87: 8790.
Gordon J, Walker L, Guy G, Rowe M, Rickinson A (1986) Control of human B-lymphocyte replication: transforming Epstein-Barr virus exploits three distinct viral signals to undermine three separate control points in B-cell growth. Immunology 58: 591.
Gratama JW, Zotter MM, Minarovits J, Oosterveer MAP, Thomas ED, Klein G, and Ernberg I (1991) Expression of EBV-encoded rowth-transformation associated proteins in lymphoproliferations of bone-marrow transplant recipients. Int J Cancer 47: 188.
Greenspan JS, Greenspan D, Lennette ET (1985) Replication of Epstein-Barr virus within the epithelial cells of oral hairy leukoplakia, an AIDS-associated lesion. N Engl J Med 985: 1564.
Gregory CD, Tursz T, Edwards CE, Tetaud C, Talbot M, Caillou B, Rickinson A, Lipinski M (1987) Identification of a subset of normal B cells with a Burkitt's lymphoma (BL)-like phenotype. J Immunol 139: 313.
Gregory CD, Dive C, Henderson S, Smith CA, Williams GT, Gordon J, Rickinson AB (1991) Activation of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes protects human B cells from death by apoptosis. Nature 349: 612.
Hammerschmidt W, Sugden B (1989) Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature 340: 393.
Henderson S, Rowe M, Gregory C, Croom-Carter D, Wang F, Longnecker R, Kieff E, Rickinson A (1991) Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell 65: 1107.
Henle W, Henle G, Andersson J, Ernberg I, Klein G, Horwitz CA, Marklund G, Rymo L, Wellinder C, Strauss SE (1987) Antibody responses to Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA)-1 and EBNA-2 in acute and chronic Epstein-Barr virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 570.
Hitt MM, Allday MJ, Hara T, Jones MD, Busson P, Tursz T, Ernberg I, Griffin BE (1989) EBV gene expression in an NPC-related tumour. EMBO J 8: 2639.
Howe JG, Steitz JA (1986) Localization of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 9006.
Joab I, Rowe D, Bodescot M, Nicolas J, Farrell P, Perricaudet M (1987) Mapping of the gene coding for Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen EBNA3 and its transient overexpression in a human cell line by using an adenovirus expression vector. J Virol 61: 3340.
Kallin B, Dillner J, Ernberg I, Ehlin-Henriksson B, Rosen A, Henle W, Henle G, Klein G (1986) Four virally determined nuclear antigens are expressed in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 83: 1499.
Kelly K, Cochran BH, Stiles CD, Leder P (1983) Cell-specific regulation of the cmyc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell 35: 603.
Klein G (1979) The relationship of the virus to nasopharyngeal carcinoma. In: Epstein MA, Achong BC (eds) The Epstein-Barr virus. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 340–350.
Knutson J (1990) The level of c-fgr RNA is increased by EBNA-2, an Epstein-Barr virus gene required for B cell immortalization. J Virol 64: 2530.
Lacy J, Summers WP, Watson M, Glazer PM, Summers WC (1987) Amplification and deregulation of myc following Epstein-Barr virus infection of a human B-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 5838.
Lerner MR, Andrews NC, Miller G, Steitz JA (1981) Two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus and complexed with protein are precipitated by antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78: 805.
Lerner MR, Andrews NC, Miller G, Steitz JA (1981) Two novel classes of small ribonucleoproteins detected by antibodies associated with lupus erythematosus. Science 211: 400.
Liebowitz D, Wang D, Kieff E (1986) Orientation and patching of the latent infection membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 58: 233.
Liebowitz D, Kopan R, Fuchs E, Sample J, Kieff E (1987) An Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein associates with vimentin in lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol 7: 2299.
Longnecker R, Kieff E (1990) A second Epstein-Barr virus membrane protein (LMP2) is expressed in latent infection and colocalizes with LMP1. J Virol 64: 2319.
Longnecker R, Druker B, Roberts TM, Kieff E (1991) An Epstein-Barr virus protein associated with cell growth transformation interacts with a tyrosine kinase. J Virol 65: 3681.
Martin J, Sugden B (1991) Transformation by the oncogenic latent membrane protein correlates with its rapid turnover, membrane localization, and cytoskeletal association. J Virol 65: 3246.
Moss DJ, Sculley TB, Pope JM (1986) Induction of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens. J Virol 58: 988.
Munger K, Werness BA, Dyson N, Phelps WC, Harlow E, Howley PM (1989) Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J 8: 4099.
Murray R, Kurilla M, Griffin H, Brooks J, Mackett M, Arrand J, Rowe M, Burrows S, Moss D, Kieff E, Rickinson A (1990) Human cytotoxic T cell responses against Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens demonstrated using recombinant vaccinia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 2906.
Palleson G, Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Rowe M, Young LS (1991) Expression of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene products in tumour cells of Hodgkin's disease. Lancet 337: 320.
Petti L, Sample C, Kieff E (1990) Subnuclear localization and phosphorylation of Epstein-Barr virus latent infection nuclear proteins. Virology 176: 563.
Rabbitts TH (1985) The c-myc proto-oncogene: involvement in chromosomal abnormalities. Trends Genet 1: 327.
Rabson ML, Gradiville L, Heston L, Miller G (1982) Nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus: a deletion mutant of its transforming parent, Jijoye. J Virol 44: 834.
Rawlins DR, Milman G, Hayward SD, Hayward GS (1985) Sequence-specific binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell 42: 659.
Reisman D, Sugden B (1986) Trans activation of the Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen 1. Mol Cell Biol 6: 3838.
Reisman D, Yates J, Sugden B (1985) A putative origin of replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus is composed of two cis-acting components. Mol Cell Biol 5: 1822.
Rickinson A, Young L, Rowe M (1987) Influence of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA2 on the growth phenotype of virus transformed B cells. J Virol 61: 1310.
Rooney C, Howe JG, Speck SH, Miller G (1989) Influences of Burkitt's lymphoma and primary B cells on latent gene expression by the nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 63: 1531.
Rosa MD, Gottlieb E, Lerner MR, Steitz JA (1981) Striking similarities are exhibited by two small Epstein-Barr virus encoded ribonucleic acids and the adenovirus associated ribonucleic acids VA1 and VA2. Mol Cell Biol 1: 785.
Rowe M, Rowe DT, Gregory CD, Young LS, Farrell PJ, Rupani H, Rickinson AB (1987) Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt lymphoma cells. EMBO J 6: 2743.
Rowe M, Finke J, Szigeti R, Klein G (1988) Characterization of the serological response in man to the latent membrane protein and the six nuclear antigens encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Gen Virol 69: 1217.
Sample J, Kieff E (1990) Transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus genome during latency in growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol 64: 1667.
Sample J, Hummel M, Braun D, Birkenbach M, Kieff E (1986) Nucleotide sequences of messenger RNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins reveals a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 5096.
Sample J, Liebowitz D, Kieff E (1989) Two related Epstein-Barr virus membrane proteins are encoded by separate genes. J Virol 63: 933.
Sample J, Brooks L, Sample C, Young L, Rowe M, Gregory C, Rickinson A, Kieff E (1991) Restricted Epstein-Barr virus protein expression in Burkitt lymphoma is due to a different Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 6343.
Sixbey JW, Nedrud JG, Raab-Traub N, Hanes RA, Pagano JS (1984) Epstein-Barr virus replication in oropharyngeal epithelial cells. N Engl J Med 310: 1225.
Sixbey JW, Davis DS, Young LS, Hutt-Fletcher L, Tedder TF, Rickinson AB (1987) Human epithelial cell expression of an Epstein-Barr virus receptor. J Gen Virol 68: 805.
Sixbey JW, Shirley P, Israele V (1986) Detection of a transformation-incompetent Epstein-Barr virus genotype in a seronegative host. In: Ablashi DV, Faggioni A, Krueger GRF, Pagano JS, Pearson GR (eds) Epstein-Barr virus and human disease. Humana Press, New Jersey, pp 131–134.
Sixbey JW, Shirley P, Sloas M, Raab-Traub N, Israele V (1991) A transformation-incompetent, nuclear antigen 2-deleted Epstein-Barr virus associated with replicative infection. J Infect Dis 163: 1008.
Sung NS, Kenney S, Gutsch D, Pagano JS (1991) EBNA-2 transactivates a lymphoid specific enhancer in the BamHI C promoter of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 65: 2164.
Swaminathan S, Thompkinson B, Kieff E (1991) Recombinant Epstein-Barr virus with small RNA (EBER) genes deleted transforms lymphocytes and replicates in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 88: 1546.
Thomas JA, Crawford DH (1989) Epstein-Barr virus associated B cell lymphomas in AIDS and after organ transplantation. Lancet I: 1075.
Thorley-Lawson DA, Mann KP (1985) Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection provide a model for B cell activation. J Exp Med 162: 45.
Toczyski DPW, Steitz JA (1991) EAP, a highly conserved cellular protein associated with Epstein-Barr virus small RNAs (EBERs). EMBO J 10: 459.
Walker L, Guy G, Brown G, Rowe M, Milner AE, Gordon J (1986) Control of human Blymphocyte replication: characterization of novel activation states that precede the entry of G. B cells into cycle. Immunology 58: 583.
Wang D, Liebowitz D, Kieff E (1985) An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell 43: 831.
Wang D, Liebowitz D, Kieff E (1988) The truncated form of the Epstein-Barr virus latent-infection membrane protein expressed in virus replication does not transform rodent fibroblasts. J Virol 62: 2337.
Wang D, Liebowitz D, Wang F, Gregory C, Rickinson A, Larson R, Springer T, Kieff E (1988) Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol 62: 4173.
Wang F, Petti L, Braun D, Sung S, Kieff E (1989) A bicistronic Epstein-Barr virus mRNA encodes two nuclear proteins in latently infected, growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol 61: 945.
Wang F, Gregory C, Sample C, Rowe M, Liebowitz D, Murray R, Rickinson A, Kieff E (1990) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol 64: 2309.
Wang F, Tsang S-F, Kurilla M, Cohen JI, Kieff E (1990) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates latent membrane protein LMP1. J Virol 64: 3407.
Wang F, Marchini A, Kieff E (1991) Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) recombinants: use of a positive selection markers to rescue mutants in EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. J Virol 65: 1701.
Wang F, Kikutani H, Tsang S-F, Kishimoto T, Kieff E (1991) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates a cis-acting CD23 DNA element. J Virol 65: 4101.
Wennborg A, Aman P, Saranath D, Pear W, Sumegi J, Klein G (1987) Conversion of lymphoma line (BJAB) by Epstein-Barr virus into phenotypically altered sublines is accompanied by increased cmyc mRNA levels. Int J Cancer 40: 202.
Whyte P, Williamson NM, Harlow E (1989) Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell 56: 67.
Wilson JB, Weinberg W, Johnson R, Yupsa S, Levine AJ (1990) Expression of the BNLF-1 oncogene of Epstein-Barr virus in the skin of transgenic mice induces hyperplasia and aberrant expression of Keratin 6. Cell 61: 1315.
Yates J, Warren N, Reisman D, Sugden B (1984) A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr virus genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 3806.
Yokata A, Kikutani H, Tanaka T, Sato R, Barsumian EL, Suemura M, Kishimoto T (1988) Two species of human FcE receptor II (FcERII/CD23): tissue specific and IL4 specific regulation of gene expression. Cell 55: 611.
Young LS, Dawson CW, Clark D, Rupani H, Busson P, Tursz T, Johnson A, Rickinson AB (1988) Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Gen Virol 69: 1051.
Young LS, Finerty S, Brooks L, Scullion F, Rickinson AB, Morgan AJ (1989) Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in malignant lymphomas induced by experimental virus infection of cottontop tamarins. J Virol 63: 1967.
Young LS, Alfieri C, Hennessy K, Evans H, O'Hara C, Anderson KC, Ritz J, Shapiro RS, Rickinson A, Kieff E, Cohen JI (1989) Expression of Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N Engl J Med 321: 1080.
Young LS, Lau R, Rowe M, Niedobitek G, Packham G, Shanahan F, Rowe DT, Greenspan D, Greenspan JS, Rickinson AB, Farrell PJ (1991) Differentiation-associated expression of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 transactivator protein in oral hairy leukoplakia. J Virol 65: 2868.
ZimberStrobl U, Suentzenich K-O, Laux G, Eick D, Cordier M, Calender A, Billaud M, Lenoir GM, Bornkamm GW (1991) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 activates transcription of the terminal protein gene. J Virol 65: 415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sample, C., Kieff, E. Molecular basis for Epstein-Barr virus induced pathogenesis and disease. Springer Semin Immunopathol 13, 133–146 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201464
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201464