Summary
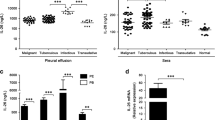
The ability of Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton (N-CWS) to augment macrophage cytotoxicity function was examined using human pleural macrophages prepared from 32 malignant pleural effusions and 53 pleural washings. The cytostatic activity of pleural macrophages for human lung cancer cells (PC-9) was augmented following incubation of pleural mononuclear cells with 10 μg/ml N-CWS for 24 h. Macrophage activity was increased by direct interaction of macrophages with N-CWS or by incubation of macrophages with supernatant culture fluids from pleural lymphocytes with N-CWS. The cytotoxic potential of the pleural macrophages obtained from patients treated with 500 μg of N-CWS intrapleurally was also increased. The heat and acid stability studies revealed that the culture fluids from pleural lymphocytes treated with N-CWS contained macrophage activation factor in addition to interferon-γ. These results suggest that direct and indirect macrophage activation is part of the mechanism in which N-CWS has a clinical effect on malignant pleural effusions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander P, Evans R (1971) Endotoxin and double-stran-RNA render macrophage cytotoxic. Nature 232:76
Cameron DJ, Churchill WH (1980) Cytotoxicity of human macrophages for tumor cells: Enhancement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol 127:708
Evans R, Alexander P (1970) Cooperation of immune lymphoid cells with macrophages in tumor immunity. Nature 228:620
Fidler IJ (1985) Macrophages and metastasis — a biological approach to cancer therapy: Presidential address. Cancer Res 45:4714
Fidler IJ, Jessup JM, Fogler WE, Staerkel R, Mazumder A (1986) Activation of tumoricidal properties in peripheral blood monocytes of patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res 46:994
Kagawa K, Yamashita T, Tsubura E, Yamamura Y (1984) Inhibition of pulmonary metastasis by Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton, with special reference to macrophage activation. Cancer Res 44:665
Kleinerman ES, Randy Z, Sarin PS, Gallo RC, Fidler IJ (1984) Constitutive production and release of a lymphokine with macrophage-activating factor activity distinct from γ-interferon by a human T-cell leukemia virus-positive cell line. Cancer Res 44:4470
Kleinerman ES, Wiltrout RH, Zicht R, Fidler IJ (1985) Human lymphokine preparations which generate tumoricidal properties of human monocytes in vitro may be distinct from gamma interferon. Cancer Immunol Immunother 20:151
Kleinerman ES, Ceccorulli LM, Zwelling LA, Twilley T, Herberman JJ, Gelmann EP (1985) Activation of monocytemediated activity in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Oncol 3:1005
Klostergaad J, Turpin J, Berestein GL (1986) Effector mechanisms of human monocyte-mediated tumor cytotoxicity in vitro: Parameters of induction of cytotoxins from peripheral blood monocytes isolated by counterflow elutriation. Cancer Res 46:662
Le J, Prensky W, Yip YK, Chang Z, Hoffman T, Stevenson HC, Blazs I, Sadlik JR, Vilćek J (1983) Activation of human monocyte cytotoxicity by natural and recombinant immune interferon. J Immunol 131:2821
Lopez-Berestein G, Metha K, Metha R, Juliano R, Hersh EM (1983) The activation of human monocytes by liposome-encapsulated muramyl dipeptide analogues. J Immunol 130:1500
Mantovani A, Dean JH, Jerrels TR, Herbermann RB (1980) Augmentation of tumoricidal activity of human monocytes and macrophages by lymphokines. Int J Cancer 25:691
Masuno T, Hayashi S, Ito M, Ikeda T, Ogura T, Kishimoto S, Yamamura Y (1896) Mechanisms of in vitro macrophage activation with Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton (N-CWS). Cancer Immunol Immunother 22:132
Meltzer MS, Benjamin WR, Farrar JJ (1982) Macrophage activation for tumoricidal activity by lamphokines from EL-4, a continuous T-cell line. J Immunol 129:2802
Ogura T, Namba M, Hirao F, Yamamura Y, Azuma I (1979) Association of macrophage activation with antitumor effect on rat syngeneic fibrosarcoma by Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton. Cancer Res 39:4706
Ogura T, Shindo H, Shinzato O, Namba M, Masuno T, Inoue T, Kishimoto S, Yamamura Y (1982) In vitro tumor cell killing by peritoneal macrophages from mitomycin-C-treated rats. Cancer Immunol Immunother 13:112
Ogura T, Shinzato O, Sakatani M, Shindo H, Namba M, Kishimoto S, Yamamura Y (1982) Analysis of therapeutic effect in experimental chemoimmunotherapy for rat ascitic tumor. Cancer Immunol Immunother 14:67
Olivotto M, Bomford R (1974) In vitro inhibition of tumor cell growth and DNA synthesis by peritoneal and lung macrophages from mice injected with Corynebacterium parvum. Int J Cancer 13:478
Pollack S, Micall A, Kinne DW, Gellen N, Oettigen HF, Hoffman MK (1983) Endotoxin-induced in vitro release of interleukin-1 by cancer patients' monocytes. Int J Cancer 32:733
Siddigi M, Iype PT (1975) Studies on the uptake of 2-deoxy-D-glucose in normal and malignant rat epithelial liver cells in culture. Int J Cancer 15:773
Sone S, Pollack VA, Fidler IJ (1980) Direct activation of tumoricidal properties in rat alveolar macrophages by Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton. Cancer Immunol Immonother 9:227
Sone S, Poste G, Fidler IJ (1980) Rat alveolar macrophages are suceptible to activation by free and liposome-encapsulated lymphokines. J Immunol 124:2197
Sone S, Moriguchi S, Shimizu E, Ogushi F, Tsubura E (1982) In vitro generation of tumoricidal properties in human alveolar macrophages following interaction with endotoxin. Cancer Res 42:2227
Stoychov JN, Schultz RM, Chirigos MA, Pavlidis NA, Goldin A (1979) Effect of adriamycin and cyclophosphamide treatment on induction of macrophage cytotoxicity function in mice. Cancer Res 39:3014
Wang BS, Lumanglas AL, Ruszala-Mallon VM, Durr FE (1984) Activation of tumor-cytostatic macrophages with the antitumor agent 9, 10-anthracene di-carboxaldehyde bis [(4,5-dihydro-1-H-imidazole-2-yl)hydrazone] dihydrochloride (bisantrene). Cancer Res 44:2363
Weiberg JB, Chapman HA, Hibbs JB Jr (1978) Characterization of the effects of endotoxin on macrophage tumor cell killing. J Immunol 121:72
Yamamura Y, Ogura T, Sakatani M, Hirao F, Kishimoto S, Fukuoka M, Takada M, Kawahara M, Furuse K, Kuwahara O, Ikegami H, Ogawa N (1983) Randomized controlled study of adjuvant immunotherapy with Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for inoperable lung cancer. Cancer Res 43:5575
Zwilling BS, Campolito LB (1977) Destruction of tumor cells by BCG-activated alveolar macrophages. J Immunol 119:838
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakatani, M., Ogura, T., Masuno, T. et al. Effect of Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton on augmentation of cytotoxicity function in human pleural macrophages. Cancer Immunol Immunother 25, 119–125 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199951
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199951