Summary
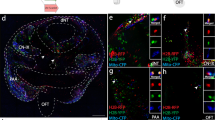
The rhombencephalic neural crest, crucial to the patterning and development of many craniofacial structures, migrates laterally from the dorsal hindbrain, but not as a continuous sheet. We have used a vital dye to demonstrate a discontinuous pattern of cell death in the dorsal midline of the avian rhombencephalon associated with the migration of the neural crest. Whilst cell death commences in the dorsal midline of the presumptive mesencephalon at stage 8, two distinct domains of cell death are apparent in the rhombencephalon by stage 11. The rostral domain lies over primary rhombomere RhA1 and rhombomere rh3, while the caudal domain occurs on the neural midline between the otic vesicles, in the region of rh5. Using a marker for the neural crest, we show that the rostral and caudal domains of cell death correlate with the absence of neural crest migration from rh3 and rh5. Thus segment-specific cell death in the dorsal region of particular rhombomeres may account for their subsequent failure to contribute to the cranial neural crest.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson CB, Meier S (1981) The influence of the metameric pattern in the mesoderm on migration of cranial neural crest cells in the chick embryo. Dev Biol 85:385–402
Baroffio A, Dupin E, Le Douarin N (1991) Common precursors for neural and mesectodermal derivatives in the cephalic neural crest. Development 112:301–305
Bowen ID (1981) Techniques for demonstrating cell death. In: Bowen ID, Lockshin RA (eds) Cell death in biology and pathology. Chapman & Hall, London New York, pp 379–444
Bronner-Fraser ME (1986) Analysis of the early stages of the trunk neural crest migration in avian embryos using monoclonal antibody HNK-1. Dev Biol 115:44–55
Fraser S, Keynes R, Lumsden A (1990) Segmentation in the chick embryo hindbrain is defined by cell lineage restrictions. Nature 334:431–435
Hall BK (1987) Tissue interactions in head development and evolution. In: Maderson PA (ed) Developmental and evolutionary aspects of the neural crest. Wiley, New York, pp 215–259
Hamburger V, Hamilton HL (1951) A series of normal stages in the development of the chick embryo. J Morphol 88:49–82
Hill RE, Jones PF, Rees AR, Sime CM, Justice MJ, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Graham E, Davidson DR (1989) A new family of mouse homeo-box containing genes: molecular structure, chromosomal location and developmental expression of Hox-7.1. Genes Dev 3:26–37
Hinchliffe JR (1981) Cell death in Embryogenesis. In: Bowen ID, Lockshin RA (eds) Cell death in biology and pathology. Chapman & Hall, London New York, pp 35–78
Holland PWH, Hogan BLM (1988) Expression of Homeo box genes during mouse development: a review. Genes Dev 2:773–782
Hunt P, Whiting J, Muchamore I, Marshall H, Krumlauf R (1991) Homeobox genes and models for patterning the hindbrain and branchial arches. Development [Suppl] 1:187–196
Jeffs PS, Osmond MK (1992) A segmented pattern of cell death during development of the chick embryo. Anat Embryol 185:589–598
Kuratani SC (1991) Alternate expression of the HNK-1 epitope in rhombomeres of the chick embryo. Dev Biol 144:215–219
Lim TM, Lunn ER, Keynes RJ, Stern CD (1987) The differing effects of occipital and trunk somites on neural development in the chick embryo. Development 100:525–533
Loring JF, Erickson CA (1987) Neural crest migratory pathways in the trunk of the chick embryo. Dev Biol 121:220–236
Lumsden A (1990) The development and significance of hindbrain segmentation. Sem Dev Biol 1:117–125
Lumsden A, Keynes R (1989) Segmental patterns of neuronal development in the chick hindbrain. Nature 337:424–428
Martin-Partido G, Alvarez IS, Rodríguez-Gallardo L, Navasscués J (1986) Differential staining of dead and dying embryonic cells with a simple new technique. J Microsc 142:101–106
Meier S, Packard DS (1984) Morphogenesis of the cranial segments and distribution of neural crest in the embryos of the snapping turtle, Chelydra serpentina. Dev Biol 102:309–323
Newgreen DF, Powell ME, Moser B (1990) Spatiotemporal changes in HNK-1/L2 glycoconjugates on avian embryo somite and neural crest cells. Dev Biol 139:100–120
Noden A (1984) Craniofacial development: new views on old problems. Anat Rec 208:1–13
Noden A (1988) Interactions and fates of avian craniofacial mesenchyme. Development [Suppl] 107:121–140
Pannett CA, Compton A (1924) The cultivation of tissues in saline embryonic juice. Lancet 1:381–384
Rickmann M, Fawcett JW, Keynes RJ (1985) The migration of neural crest cells and the growth of motor axons through the rostral half of the chick somite. J Embryol Exp Morphol 90:437–455
Saunders JW, Gasseling MT, Saunders LC (1962) Cellular death in morphogenesis of the avian wing. Dev Biol 5:147–178
Tabin CJ (1991) Retinoids, homeoboxes and growth factors: toward molecular models for limb development. Cell 66:199–217
Tucker GC, Aoyama H, Lipinski M, Turz T, Thiery JP (1984) Identical reactivity of monoclonal antibody HNK-1 and NC-1: conservation in vertebrates on cells derived from neural primordium and on some leucocytes. Cell Differ 14:223–230
Vaaga S (1969) The segmentation of the primitive neural tube in chick embryos (Gallus domesticus). In: Brodal A, Hild W, Ortmann R, Schiebler TH, Töndury G, Wolff E (eds) Advances in anatomy, embryology and cell biology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 8–57
Waters BH (1891) Primitive segmentation of the vertebrate brain. Q J Microsc Sci 33:457–476
Wilkinson DG (1990) Segmental gene expression in the developing mouse hindbrain. Sem Dev Biol 1:127–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeffs, P., Jaques, K. & Osmond, M. Cell death in cranial neural crest development. Anat Embryol 185, 583–588 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185617
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185617