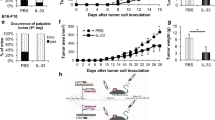
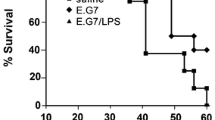
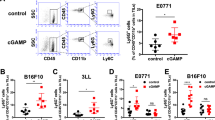
Recombinant human interferon alpha A/D (αA/D) restored or augmented host defense systems against tumors in immunosuppressed mice. In normal C57BL/6 mice, inoculation of B16 melanoma F1 cells caused few pulmonary metastasis, whereas in mice pretreated with cyclophosphamide (CY) it caused a high incidence of pulmonary metastasis, leading to earlier death than in the normal mice inoculated with the same dose of the tumor. αA/D given after the CY treatment counteracted the deleterious effects of the CY treatment. Since such restorative activity was seen even against the subline of B16 F1 which had been made resistant to its direct antiproliferative effect, αA/D seems to exert its effect indirectly through host defense systems. However, this activity of αA/D in the mice pretreated with CY was abrogated by inoculation of anti-asialo GM1 serum but not by i-carrageenan. The CY treatment reduced NK activity, while α A/D given after the CY treatment restored or augmented the NK cell activity in lung cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, but not in spleen cells. These findings suggest that the restoration or augmentation of NK activity in the lung and/or peripheral blood might be the major factor leading to the antimetastatic activity of αA/D in the mice treated with CY.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brouty-Boys, D., 1980, Inhibitory effects of interferons on cell multiplication. Lymphokine reports 1, edited by E. Pick (New York: Academic Press), pp. 99–112.
Brunda, M. J., and Rosenbaum, D., 1984, Modulation of murine natural killer cell activity in vitro and in vivo by recombinant human interferons. Cancer Research, 44, 597–601.
Brunda, M. J., Rosenbaum, D., and Stern, L., 1984, Inhibition of experimentally-induced murine metastases by recombinant alpha interferon: Correlation between the modulatory effect of interferon treatment on natural killer cell activity and inhibition of metastases. International Journal of Cancer, 34, 421–426.
Hanna, N., 1980, Expression of metastatic potential of tumor cells in young nude mice is correlated with low levels of natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. International Journal of Cancer, 26, 675–680.
Hanna, N., 1982, Role of natural killer cells in control of cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Review, 1, 45–64.
Hanna, N., and Fidler, I. J., 1980, Role of natural killer cells in destruction of circulating tumor emboli. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 65, 801–809.
Hanna, N., and Fidler, I. J., 1981, Relationship between metastatic potential and resistance to natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity in three murine tumor systems. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 66, 1183–1190.
Herberman, R. B., Ortaldo, J. R., Mantovani, A., Hobbs, D. S., Kung, H., and Pestka, S., 1982, Effect of human recombinant interferon on cytotoxic activity of natural killer (NK) cells and monocytes. Cellular Immunology, 67, 160–167.
Ishizaka, S., Otani, S., and Morisawa, S., 1977, Effects of carrageenan on immune responses. I. Studies on the macrophage dependency of various antigens after treatment with carrageenan. Journal of Immunology, 118, 1213–1218.
Kasai, M., Iwamori, M., Nagai, Y., Okumura, K., and Tada, T., 1980, A glycolipid on the surface of mouse natural killer cells. European Journal of Immunology, 10, 175–180.
Kramer, M. J., Dennin, R., Kramer, C., Jones, G., Connell, E., Rolon, N., Gruarin, A., Kale, R., and Trown, P. W., 1983, Cell and virus sensitivity studies with recombinant human alpha interferon. Journal of Interferon Research, 3, 425–435.
Milas, L., and Peters, L. J., 1984, Conditioning of tissues for metastasis formation by radiation and cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Invasion and Metastasis, edited by G. L. Nicolson and L. Milas (New York: Raven Press), pp. 321–336.
Nishimura, J., Mitsui, K., Ishikawa, T., Tanaka, Y., Yamamoto, R., Suhara, Y., and Ishitsuka, H., 1986, Antitumor and antimetastatic activities of human recombinant interferon alpha A/D in mice through augmentation of the host defense system. Clinical and Experimental Metastasis, 3, 295–304.
Rehberg, E., Kelder, B., Hoal, E. G., and Pestka, S., 1982, Specific molecular activities of recombinant and hybrid leukocyte intefereons. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 257, 11497–11502.
Rosenberg, S. A., Mulé, J. J., Spiess, P. J., Reichert, C. M., and Schwarz, S. L., 1985, Regression of established pulmonary metastases and subcutaneous tumor mediated by the systemic administration of high-dose recombinant interleukin 2. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 161, 1169–1188.
Rubinstein, S., Familletti, P. C., and Pestka, S., 1981, Convenient assay for interferons. Journal of Virology, 37, 755–758.
Shalaby, M. R., and Weck, P. K., 1983, Bacteria-derived human leukocyte interferons alter in vitro humoral and cellular immune responses. Cellular Immunology, 82, 269–281.
Sonnenfeld, G., 1980, Modulation of immunity by interferon. Lymphokine Reports 1, edited by E. Pick, (New York: Academic Press), pp. 113–131.
Stutman, O., Paige, C. J., and Figarella, E. F., 1978, Natural cytotoxic cells against solid tumors in mice. I. Strain and age distribution and target cell susceptibility. Journal of Immunology, 121, 1819–1826.
Talmadge, J. E., Meyers, K. M., Prleur, D. J., and Starkey, J. R., 1980, Role of natural killer cells in tumor growth and metastasis: C57BL/6 normal and beige mice. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 65, 929–935.
Targan, S., and Stebbing, N., 1982, In vitro interactions of purified cloned human interferons on NK cells: enhanced activation. Journal of Immunology, 129, 934–935.
Weck, P. K., Rinderknecht, E., Estell, D. A., and Stebbing, N., 1982, Antiviral activity of bacteria derived human alpha interferons against encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mice. Infection and Immunity, 35, 660–665.
Wiltrout, R. H., Herberman, R. B., Zhang, S.-R., Chirigos, M. A., Ortaldo, J. R., Green, K. M. Jr, and Talmadge, J. E., 1985, Role of organ-associated NK cells in decreased formation of experimental metastases in lung and liver. Journal of Immunology, 134, 4267–4275.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishimura, J., Mitsui, K., Tanaka, Y. et al. Restoration by recombinant interferon alpha A/D of host defense systems against tumor in immunosuppressed mice. Clin Exp Metast 4, 35–44 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00053471
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00053471