Abstract
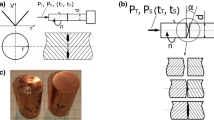
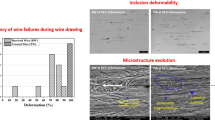
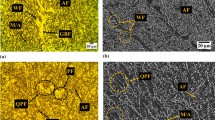
In this study, cracks or scabs formed during hot rolling of Bi-S–based free-machining steel wire rods were analyzed, and their formation mechanisms were clarified in relation with microstructure. Detailed microstructural analyses of large-diameter rods showed that the rod having low carbon content was cracked, whereas the rod having higher carbon content was not, because oxides formed during hot rolling were penetrated into the relatively soft surface, thereby leading to the surface cracking. While the crack-free, large-diameter rod containing high carbon content was subsequently rolled to make a small-diameter rod, a few scabs of 1 to 2 mm in size were formed on the surface as some protrusions were folded during hot rolling. Thus, in order to prevent the cracking or scab formation in wire rods, (1) the increase in hot-rolling temperature for homogeneous rolling of rods, (2) the minimization of temperature drop of rolled rods upon descaling treatment, and (3) the increase of rolling passes and the decrease of reduction ratio of each pass were suggested. Using these methods, crack- or scab-free wire rods could be successfully fabricated.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
References
K. Kishi and H. Eda: Wear, 1976, vol. 38, pp. 29–42.
S.K. Cho: J. Kor. Inst. Met. Mater., 1996, vol. 34, pp. 822–29.
H. Yaguchi: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1989, vol. 5, pp. 255–67.
S. Dinda and W.R. Warke: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1976, vol. A24, pp. 199–208.
W. Roberts, B. Lehtinen, and K.E. Easterling: Acta Metall., 1976, vol. 24, pp. 745–58.
T.J. Baker, F.P.L. Kavishe, and J. Wilson: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1986, vol. 2, pp. 576–82.
M. Toshiyuki, T. Kunikazu, and S. Tetsuo: JFE Techn. Rep., 2010, vol. 15, pp. 10–16.
S. Yamamoto, S. Takamori, Y. Osawa, and A. Sato: Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi, 2001, vol. 65, pp. 614–20.
T. Fukui: Honda Environmental Annual Report, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Sept. 2007.
G. Sridhar, S.K. Das, and N.K. Mukhopadhyay: Eng. Fail. Anal., 1999, vol. 6, pp. 155–72.
H. Yaguchi: J. Appl. Metalworking, 1986, vol. 4, pp. 214–25.
T. Akasawa, H. Sakurai, M. Nakamura, T. Tanaka, and K. Takano: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, vols. 143–144, pp. 66–71.
J.L. Nazabal, J.J. Urcola, and M. Fuentes: Metallography, 1984, vol. 17, pp. 439–54.
J.C. Lynn, W.R. Warke, and P. Gordon: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1975, vol. A18, pp. 51–62.
E. Ervasti and U. Stahlberg: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1999, vol. 94, pp. 141–50.
E. Ervasti and U. Stahlberg: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, vol. 101, pp. 312–21.
D.C.J. Farrugia: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, vol. 177, pp. 486–92.
A. Foster, J. Lin, D. Farrugia, and T. Dean: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, vol. 177, pp. 497–500.
M. Manjohme, T. Ono, K. Yoshimura, and H. Mikami: Nippon Steel Technical Report, 2007, vol. 96, pp. 12–20.
P.E.J. Rivera-Diaz-Del-Castillo, S. Zwaag, and J. Sietsma: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 425–33.
B. Hwang, H. Lee, Y. Kim, and S. Lee: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. A402, pp. 177–87.
D.B. Park, J.W. Lee, Y.S. Lee, K.T. Park, and W.J. Nam: Met. Mater. Int., 2009, vol. 15, pp. 197–202.
J.I. Hwang, T.G. Jhee, Y.K. Kim, and T.Y. Hwang: Met. Mater. Int., 2010, vol. 16, pp. 693–99.
B.W. Choi, D.H. Seo, and J. Jang: Met. Mater. Int., 2009, vol. 15, pp. 373–78.
J.W. Park, H.C. Lee, and S. Lee: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 399–409.
M.F. Frolish, M. Krzyzanowski, W.M. Rainforth, and J.H. Beynon: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, vol. 177, pp. 36–40.
T. Inoue, F. Yin, Y. Kimura, and K. Nagai: J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 2005, vol. 69, pp. 943–52.
H.H. Bok, M.G. Lee, H.D. Kim, and M.B. Moon: Met. Mater. Int., 2010, vol. 16, pp. 185–95.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by POSCO under Contract No. 20108008. The authors thank Dr. Yu Hwan Lee, Technical Research Laboratories, POSCO, for his help with experimental analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 24, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y., Kim, H., Shin, S.Y. et al. Cracking Phenomenon Occurring in Bi-S–Based Free-Machining Steel Wire Rods During Hot Rolling. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 3095–3105 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0736-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0736-6