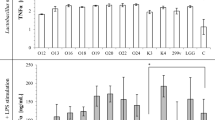
Abstract
Lactoferrin is an iron-binding glycoprotein that exhibits a range of health benefits including immune regulation and disease prevention derived from its structural properties. The present study employed immune cell models and a colon epithelial cell model to investigate the protective effects of bovine lactoferrin (BLf) on both immune cells and colon epithelium cells. BLf caused significant reduction of faecal genotoxin-induced DNA damage in HT29 cells, and down-regulation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage cell stress and endotoxic response, in an infection status.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelmelk BJ, An YQ, Geerts M, Thijs BG, de Boer HA, MacLaren DM, de Graaff J, Nuijens JH (1994) Lactoferrin is a lipid A-binding protein. Infect Immun 62:2628–2632
Glei M, Klenow S, Sauer J, Wegewitz U, Richter K, Pool-Zobel BL (2006) Hemoglobin and hemin induce DNA damage in human colon tumor cells HT29 clone 19A and in primary human colonocytes. Mutat Res 594:162–171
Iigo M, Alexander DB, Long N, Xu J, Fukamachi K, Futakuchi M, Takase M, Tsuda H (2009) Anticarcinogenesis pathways activated by bovine lactoferrin in the murine small intestine. Biochimie 91:86–101
Klinder A, Forster A, Caderni G, Femia AP, Pool-Zobel BL (2004) Fecal water genotoxicity is predictive of tumor-preventive activities by inulin-like oligofructoses, probiotics (Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium lactis), and their synbiotic combination. Nutr Cancer 49:144–155
Lonnerdal B (2009) Nutritional roles of lactoferrin. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 12:293–297
Park EK, Jung HS, Yang HI, Yoo MC, Kim C, Kim KS (2007) Optimized THP-1 differentiation is required for the detection of responses to weak stimuli. Inflamm Res 56:45–50
Sekine K, Ushida Y, Kuhara T et al (1997) Inhibition of initiation and early stage development of aberrant crypt foci and enhanced natural killer activity in male rats administered bovine lactoferrin concomitantly with azoxymethane. Cancer Lett 121:211–216
Tsuda H, Sekine K, Takasuka N, Toriyama-Baba H, Iigo M (2000) Prevention of colon carcinogenesis and carcinoma metastasis by orally administered bovine lactoferrin in animals. Biofactors 12:83–88
Tsuda H, Sekine K, Fujita K, Ligo M (2002) Cancer prevention by bovine lactoferrin and underlying mechanisms—a review of experimental and clinical studies. Biochem Cell Biol 80:131–136
Venturi M, Hambly RJ, Glinghammar B, Rafter JJ, Rowland IR (1997) Genotoxic activity in human faecal water and the role of bile acids: a study using the alkaline comet assay. Carcinogenesis 18:2353–2359
Zhang GH, Mann DM, Tsai CM (1999) Neutralization of endotoxin in vitro and in vivo by a human lactoferrin-derived peptide. Infect Immun 67:1353–1358
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by a Technology in Industry Fellowship to H.T., awarded by the New Zealand Foundation for Research, Science and Technology, and by Drapac Ltd. The experimental work was carried out by H.T. under the supervision of her PhD supervisors, I.S.M, L.R.F and Q.S. All authors contributed to the manuscript. There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, H., Maddox, I.S., Ferguson, L.R. et al. Evaluation of the cytoprotective effects of bovine lactoferrin against intestinal toxins using cellular model systems. Biometals 23, 589–592 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9301-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9301-9