Abstract
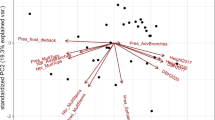
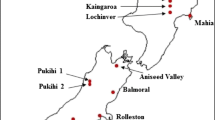
A common-garden study of Populus trichocarpa Torr. & Gray was established in spring 1986 with 128 clones collected from sites along two mesic (Hoh and Nisqually) and two xeric (Dungeness and Yakima) river valleys in Washington. Two replicate plantations, one in Puyallup and the other in Wenatchee, Wash., were established with this material. Over 2 years data were taken on stem growth, leaf/crown characters, spring/autumn phenology, and the incidence of Melampsora occidentalis leaf rust. Combining clones from all four sources, correlation/regression analyses were used to examine clonal stability of traits between test sites and trait relationships with stem growth; broad-sense heritabilities (H 2) and genetic correlations revealed the genetic strength of these traits. At Puyallup, many leaf/crown traits predicted stem growth moderately to very well (r 2>0.50), e.g., total leaf area (TLA) to diameter gave an r 2 of 0.91 and current-terminal leaf size, of 0.79. Some regressions were quadratic, suggesting a threshold level in a trait (e.g., leaf size) beyond which stem growth levels off. Upper-crown TLA was more closely related to height than TLA of the lower sylleptics, but the reverse was true for diameter. A decline in r 2 values from upper to lower crown positions was sharper for correlations of TLAs with height than with diameter. Thus, leaf area allocation seems to differentially affect stem growth. When autumn leaf fall (LF) and rust incidence (R) were regressed with growth, r 2 values ranged from 0.58 to 0.71, but those of spring flush (SF) were only 0.10 to 0.12. Early LF and high R, both negatively affecting growth, had a strong geographic component as it occurred mainly on lower-elevation Yakima clones. At Wenatchee, field conditions were harsher and microsites more variable, so trait/growth relationships were weaker. Genetic correlations with growth revealed similar trends as phenotypic analyses. Unlike leaf/crown traits, clonal scores of LF, SF, and R were fairly stable across the two test sites (r 2: 0.58–0.80). These traits also showed strong genetic control (H 2: 0.96–0.98). The trait/growth relationships as well as trait stability within clones have implications for selecting clonal stock in poplar culture and conservation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 February 1998 / Accepted: 7 May 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunlap, J., Stettler, R. Genetic variation and productivity of Populus trichocarpa and its hybrids. X. Trait correlations in young black cottonwood from four river valleys in Washington. Trees 13, 28–39 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009735
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009735