Abstract.
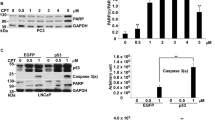
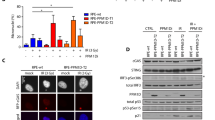
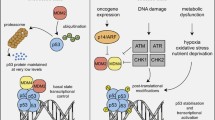
Activation of the p53 tumour suppressor protein by distinct forms of stress leads to inhibition of cellular proliferation by inducing cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor roscovitine has been shown to induce nuclear accumulation of wild-type p53 in human untransformed and tumour-derived cells. We analyzed the response of different human tumour cell lines to roscovitine treatment with respect to their p53 status. Striking induction of wild-type p53 protein and dramatic enhancement of p53-dependent transcription, coinciding with p21WAF1 induction, was observed in wild-type, but not mutant, p53-bearing tumour cells after treatment with roscovitine. The transcriptional activity of p53 was substantially higher in roscovitine-treated cells than in cells irradiated with ultraviolet C or ionizing radiation, even though all these agents induced a similar amount of p53 accumulation. These results highlight the therapeutic potential of roscovitine as an anticancer drug, especially in tumours retaining a functional wild-type p53 pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 15 May 2001; accepted 13 June 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotala, V., Uldrijan, S., Horky, M. et al. Potent induction of wild-type p53-dependent transcription in tumour cells by a synthetic inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58, 1333–1339 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000944
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000944