Abstract.
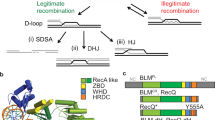
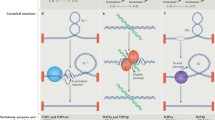
Maintenance of genomic stability relies on the efficient and accurate execution of DNA repair pathways, and is essential for cell viability and the prevention of cancer. Mutation of genes encoding RecQ helicases or topoisomerases gives rise to genomic instability through excessive recombination. Here, we review the recent biochemical and genetic evidence to indicate that these two classes of protein act in concert in a conserved pathway to maintain genomic stability by preventing inappropriate recombination.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 17 November 2000; received after revision 8 January 2001; accepted 18 January 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Hickson, I. RecQ helicases and topoisomerases: components of a conserved complex for the regulation of genetic recombination. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58, 894–901 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000909
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000909