Abstract
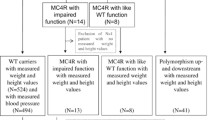
Aim: To screen mutations in the melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) in obese and normal-weight Chinese children and adolescents. Methods: Three hundred Chinese children and adolescents, including 200 obese and 100 healthy non-obese individuals, were evaluated. The coding region of the MC4R gene was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequenced. Results: In obese individuals, we detected two novel heterozygous non-synonymous mutations (c.496G>A, resulting in Val166Ile; c.929G>A, resulting in Arg310Lys) and a novel heterozygous non-sense mutation (c.831T>A, resulting in a premature stop codon Cys277Stop). In both obese individuals and controls, a novel heterozygous non-synonymous mutation (c.68T>G, resulting in Leu23Arg, 0.5 and 1%, respectively) and the Val103Ile polymorphism (c.307G>A, 3 and 2%, respectively) were found. There was no difference in alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), triglyceride (TG), cholesterol (CHOL) and whole body insulin sensitivity index (WBISI) between obese individuals with and without mutation. The prevalence for heterozygous MC4R mutations was 1.5% in the obese. Conclusions: Two novel heterozygous non-synonymous mutations (Val166Ile; Arg310Lys) and a novel heterozygous non-sense mutation (Cys277Stop) were detected in Chinese obese individuals. Leu23Arg variant might be a polymorphism in the Chinese population. There were no differences between clinical and biochemical profiles in the heterozygous mutations and the wild type.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ste Marie L, Miura GI, Marsh DJ, Yagaloff K, Palmiter RD. A metabolic defect promotes obesity in mice lacking melanocortin-4 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000, 97: 12339–44.
Farooqi IS, Yeo GS, Keogh JM, et al. Dominant and recessive inheritance of morbid obesity associated with melanocortin 4 receptor deficiency. J Clin Invest 2000, 106: 271–9.
Cone RD. The central melanocortin system and energy homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 1999, 10: 211–6.
Huszar D, Dynch CA, Fairchild-Huntress V, et al. Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell 1997, 88: 131–41.
Vaisse C, Clement K, Durand E, Hercberg S, Guy-Grand B, Froguel P. Melanocortin-4 receptor mutations are a frequent and heterogeneous cause of morbid obesity. J Clin Invest 2000, 106: 253–62.
Dubern B, Clement K, Pelloux V, et al. Mutational analysis of melanocortin-4 receptor, agouti-related protein, and α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone genes in severely obese children. J Pediatr 2001, 139: 204–9.
Lubrano-Berthelier C, Durand E, Dubern B, et al. Intracellular retention is a common characteristic of childhood obesity-associated MC4R mutations. Hum Mol Genet 2003, 12: 145–53.
Farooqi IS, Keogh JM, Yeo GS, Lank EJ, Cheetham T, O’Rahilly S. Clinical spectrum of obesity and mutations in the melanocortin 4 receptor gene. N Engl J Med 2003, 348: 1085–95.
Hinney A, Hohmann S, Geller F, et al. Melanocortin-4 receptor gene: case-control study and transmission disequilibrium test confirm that functionally relevant mutations are compatible with a major gene effect for extreme obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 4258–67.
Ma L, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C, Baier LJ. Melanocortin 4 receptor gene variation is associated with severe obesity in Pima Indians. Diabetes 2004, 53: 2696–9.
Ohshiro Y, Sanke T, Ueda K, Shimajiri Y, et al. Molecular scanning for mutations in the melanocortin-4 receptor gene in obese/diabetic Japanese. Ann Hum Genet 1999, 63: 483–7.
Kobayashi H, Ogawa Y, Shintani M, et al. A novel homozygous missense mutation of melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) in a Japanese woman with severe obesity. Diabetes 2002, 51: 243–6.
Cai SB, Jia WP, Fang QC, Shao XY, Zhang R, Xiang KS. F261S-A novel mutation of melanocortin 4 receptor gene in the obese patients. Chin J Endocrinol Metab 2004, 20: 372–5 (in Chinese).
Hu YM, Jiang ZF. ZHU Futang Textbook of Pediatrics. 7th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House. 2000, 27–9 (in Chinese).
Group of China Obesity Task Force. Body mass index reference norm for screening overweight and obesity in Chinese children and adolescents. Chin J Epidemiol 2004, 25: 97–102 (in Chinese).
Yeckel CW, Weiss R, Dziura J, et al. Validation of insulin sensitivity indices from oral glucose tolerance test parameters in obese children and adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 89: 1096–101.
Wang CL, Liang L, Fu JF, Hong F. Comparison of methods to detect insulin resistance in obese children and adolescents. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2005, 34: 316–9 (in Chinese).
Hinney A, Schmidt A, Nottebom K, et al. Several mutations in the melanocortin-4 receptor gene including a nonsense and a frameshift mutation associated with dominantly inherited obesity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999, 84: 1483–6.
Gotoda T, Scott J, Aitman TJ. Molecular screening of the human melanocortin-4 receptor gene: identification of a missense variant showing no association with obesity, plasma glucose, or insulin. Diabetologia 1997, 40: 976–9.
Yeo GS, Farooqi IS, Aminian S, Halsall DJ, Stanhope RG, O’Rahilly S. A frameshift mutation in MC4R associated with dominantly inherited human obesity. Nat Genet 1998, 20: 111–2.
Miraglia Del Giudice E, Cirillo G, Nigro V, et al. Low frequency of melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4RR) mutations in a Mediterranean population with early-onset obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002, 26: 647–51.
Jacobson P, Ukkola O, Rankinen T, et al. Melanocortin-4 receptor sequence variations are seldom a cause of human obesity: the Swedish Obese Subjects, the HERITAGE Family Study, and a Memphis cohort. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002, 87: 4442–4.
Tarnow P, Schoneberg T, Krude H, Gruters A, Biebermann H. Mutationally induced disulfide bond formation within the third extracellular loop causes melanocortin 4 receptor inactivation in patients with obesity. J Biol Chem 2003, 278: 48666–73.
Geller F, Reichwald K, Dempfle A, et al. Melanocortin-4 receptor gene variant I103 is negatively associated with obesity. Am J Hum Genet 2004, 74: 572–81.
Heid IM, Vollmert C, Hinney A, et al. Association of the 103I MC4R allele with decreased body mass in 7937 participants of two population based surveys. J Med Genet 2005, 42: e21.
Lubrano-Berthelier C, Le Stunff C, Bougneres P, Vaisse C. A homozygous null mutation delineates the role of the melanocortin-4 receptor in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 89: 2028–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C.L., Liang, L., Wang, H.J. et al. Several mutations in the melanocortin 4 receptor gene are associated with obesity in Chinese children and adolescents. J Endocrinol Invest 29, 894–898 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03349193
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03349193