Abstract
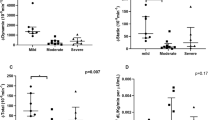
Aim of our study is to verify the association between the genetic predisposition to hyperinsulinism due to the presence of the insulin gene (INS) I/I genotype and the development of sleep-related breathing disorders (SRBD) in obese children and adolescents. Two hundred and fifty-six obese children and adolescents (125 girls) have been investigated. As initial screening all subjects’ mothers filled out the Sleep Disturbances Scale for Children (SDSC). The Sleep-Disordered Breathing (SDB) scale has been taken into account. Successively, a subgroup of 34 patients belonging to the first (14 children) and the last (20 children) SDB score quintiles underwent an overnight polysomnography and the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) was evaluated. All subjects were genotyped for the INS VNTR and fasting insulin levels were evaluated. The population was divided into two groups according to the genotype: the first group was comprehensive of patients homozygotes for class I allele and the second group was composed by class III allele heterozygotes and homozygotes patients. Subjects I/I showed statistically significant higher insulin levels (p<0.001) and SDB scores (p<0.001). Moreover, in the subgroup of patients investigated with polysomnography, class I homozygous subjects showed higher AHI compared to those patients carrying class III allele (p<0.001). Our data support the hypothesis that INS VNTR is associated with the development of SDB among obese children and adolescents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hasler G, Buysse DJ, Klaghofer R, et al. The association between short sleep duration and obesity in young adults: a 13-year prospective study. Sleep 2004, 27: 661–6.
Peltier AC, Consens FB, Sheikh K, Wang L, Song Y, Russell JW. Autonomic dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea is associated with impaired glucose regulation. Sleep Med 2007, 8: 149–55.
Makino S, Handa H, Suzukawa K, et al. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome, plasma adiponectin levels, and insulin resistance. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2006, 64: 12–9.
Alam I, Lewis K, Stephens JW, Baxter JN. Obesity, metabolic syndrome and sleep apnoea: all pro-inflammatory states. Obes Rev 2007, 8: 119–27.
McGarry JD. Banting lecture 2001: dysregulation of fatty acid metabolism in the etiology of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2002, 51: 7–18.
Bell GI, Horita S, Karam JH. Apolymorphic locus near the human insulin gene is associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1984, 33: 176–83.
Bennett ST, Wilson AJ, Cucca F, et al. IDDM2-VNTR-encoded susceptibility to type 1 diabetes: dominant protection and parental transmission of alleles of the insulin gene-linked minisatellite locus. J Autoimmun 1996, 9: 415–21.
Bennett ST, Todd JA. Human type 1 diabetes and the insulin gene: principles of mapping polygenes. Annu Rev Genet 1996, 30: 343–70.
Kennedy GC, German MS, Rutter WJ. The minisatellite in the diabetes susceptibility locus IDDM2 regulates insulin transcription. Nat Genet 1995, 9: 293–8.
Le Stunff C, Fallin D, Schork NJ, Bougneres P. The insulin gene VNTR is associated with fasting insulin levels and development of juvenile obesity. Nat Genet 2000, 26: 444–6.
Carotenuto M, Bruni O, Santoro N, Miraglia del Giudice E, Perrone L, Pascotto A. Waist circumference predicts the occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing in obese children and adolescents: a questionnaire-based study. Sleep Med 2006, 7: 357–61.
Cole TJ. The LMS method for constructing normalized growth standards. Eur J Clin Nutr 1990, 44: 45–60.
Tanner JM, Whitehouse RH. Clinical longitudinal standards for height, weight, height velocity, weight velocity, and stages of puberty. Arch Dis Child 1976, 51: 170–9.
Santoro N, Cirillo G, Amato A, et al. Insulin gene variable number of tandem repeats (INS VNTR) genotype and metabolic syndrome in childhood obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006, 91: 4641–4.
Bruni O, Ottaviano S, Guidetti V, et al. The Sleep Disturbance Scale for Children (SDSC). Construction and validation of an instrument to evaluate sleep disturbances in childhood and adolescence. J Sleep Res 1996, 5: 251–61.
Bruni O, Ferini-Strambi L, Russo PM, et al. Sleep disturbances and teacher ratings of school achievement and temperament in children. Sleep Med 2006, 7: 43–8.
Eitner S, Urschitz MS, Guenther A, et al. Sleep problems and daytime somnolence in a German population-based sample of snoring school-aged children. J Sleep Res. Mar 2007, 16: 96–101.
Spruyt K, Cluydts R, Verleye GB. Pediatric sleep disorders: exploratory modulation of their relationships. Sleep 2004, 27: 495–501.
American Thoracic Society. Standards and indications for cardiopulmonary sleep studies in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996, 153: 866–78.
Redline S, Budhiraja R, Kapur V, et al. Reliability and validity of respiratory event measurement and scoring. J Clin Sleep Med 2007: 3: 169–200.
Kalra M, Chakraborty R. Genetic susceptibility to obstructive sleep apnea in the obese child. Sleep Med 2007, 8: 169–75.
Redline S, Tishler PV, Tosteson TD, et al. The familial aggregation of obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995, 151: 682–7.
Bougneres P. Genotypic and phenotypic complexity at the insulin variable number of tandem repeats locus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006, 91: 4246–9.
Nakra N, Bhargava S, Dzuira J, Caprio S, Bazzy-Asaad A. Sleep-disordered breathing in children with metabolic syndrome: the role of leptin and sympathetic nervous system activity and the effect of continuous positive airway pressure. Pediatrics 2008, 122: e634–42.
Vgontzas AN, Bixler EO, Chrousos GP. Sleep apnea is a manifestation of the metabolic syndrome. Sleep Med Rev 2005, 9: 211–24.
Ip MS, Lam B, Ng MM, Lam WK, Tsang KW, Lam KS. Obstructive sleep apnea is independently associated with insulin resistance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002, 165: 670–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carotenuto, M., Santoro, N., Grandone, A. et al. The insulin gene variable number of tandem repeats (INS VNTR) genotype and sleep disordered breathing in childhood obesity. J Endocrinol Invest 32, 752–755 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346531
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346531