Abstract
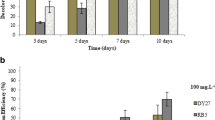
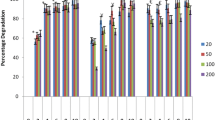
Detoxification of synthetic dyes is one of the main challenges in clearing textile industry wastes. Biodegradation of azo-dyes using Phanerochaete chrysosporium is one the most environmentally friendly methods available. The main enzymes responsible for mycodecolorization process are lignin and manganese peroxidases. Here, optimization of expression conditions has been carried out with manipulating culture condition and nutrient sources. Therefore, the effects of buffer and temperature as well as nitrogen source on lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase production were investigated at two levels and four levels, respectively. For this purpose, P. chrysosporium RP78 based on Taguchi design of experiment has been applied. Maximum lignin and manganese peroxidase activities of 182 ± 2.5 U/L and 850 ± 41 U/L were obtained under predicted optimum conditions, respectively. Thereby, about 100 % decolorization was achieved after 24 h for two most widely used groups of azo dyes in textile industry consisting reactive and acidic. The physical adsorption of the azo dyes by mycelia was not significant which indicated that the enzymatic degradation of the dyes was occurred. Time profile of these enzymes showed that manganese peroxidase was peaked on 9th day while lignin peroxidase peaked on 13th day and remained stable in the culture. The extracellular expression profiles of both were studied by 2 dimensional gel electrophoresis to partially characterize the enzymes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambròsio, S. T.; Campos-Takaki, G. M., (2004). Decolorization of reactive azo dyes by cunninghamella elegans UCP 542 under co-metabolic conditions. Bioresour. Tech., 91(1), 69–75 (7 pages).
Azmi, W.; Sani, R. K.; Banerjee, U. C., (1998). Biodegradation of triphenylmethane dyes. Enzyme Microb. Tech., 22(3), 185–191 (7 pages).
Bandyopadhyay, G.; Chattopadhyay, S., (2007). Single hidden layer artificial neural network models versus multiple linear regression model in forecasting the time series of total ozone. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(1), 141–150 (10 pages).
Beydilli, M. I.; Pavolsathis, S. G.; Tincher, W. C., (1998). Decolorization and toxicity screening of selected reactive azo dyes under methanogenic condition. Water Sci. Tech., 38(4–5), 225–232 (8 pages).
Chaudhry, G. R., (1994). Biological degradation and bioremediation of toxic chemicals. 1st. Ed., Chapman and Hall, 345–363 (19 pages).
Couto, S.; Moldes, D.; Sanromán, M., (2006). Optimum stability conditions of pH and temperature for ligninase and manganese-dependant peroxidase from phanerochaete chrysosporium. Application to in vitro decolorization of poly R-478 by MnP. World J. Microb. Biot., 22(6), 607–612 (6 pages).
Cripps, C.; Bumpus, J. A.; Aust, S. D., (1990). Biodegradation of azo and heterocyclic dyes by phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microb., 56(4), 1114–1118 (5 pages).
Dosoretz, C. G.; Grethlein, H. E., (1991). Physiological aspects of regulation of extracellular enzymes of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Biochem. Biotech., 28(29), 253–265 (12 pages).
Dosoretz, C. G.; Rothschild N.; Hard, Y., (1993). Overproduction of lignin peroxidase by phanerochaete chrysosporium (BKM-F-1767) under nonlimiting nutrient condition. Appl. Environ. Microb., 59(6), 1919–1926 (8 pages).
Gao, D.; Wen, X.; Zhou, X.; Qian, Y, (2006). Effect of trace element on the growth of white rot fungi and suppressing yeast in liquid medium. Environ. Sci., 27(8), 1623–1626 (5 pages).
Gharbani, P.; Tabatabaii, S. M.; Mehrizad, A., (2008). Removal of Congo red from textile wastewater by ozonation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(4), 495–500 (7 pages).
Goszczynski, S.; Paszczynski, A.; Basti-Gorigsby, M. B.; Crawford, R. L.; Crawford, D. L., (1994). New pathway for degradation of sulfonated azo dyes by microbial peroxidases of phanerochaete chrysosporium and Streptomyces chromofuscus. J. Bacteriol., 176(5), 1339–1347 (9 pages).
Gueu, S.; Yao, B.; Adouby, K.; Ado, G. (2007). Kinetics and thermodynamics study of lead adsorption on to activated carbons from coconut and seed hull of the palm tree. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(1), 11–17 (6 pages).
Heinfling, A.; Martinez, M. J.; Martinez, A. T.; Bergbauer, M.; Szewzyk, U., (1998). Transformation of industrial dyes by manganese peroxidase from Bjerkandera adusta and Pleurotus eryngii in a manganese-independent reaction. Appl. Environ. Microb., 64(8), 2788–2793 (6 pages).
Igbinosa, E. O.; Okoh, A. I., (2009). Impact of discharge wastewater effluents on the physico-chemical qualities of a receiving watershed in a typical rural community. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(2), 175–182 (8 pages).
Krishna Prasad, K.; Venkata Mohan, S.; Sreenivas Rao, R.; Ranjan Pati, B.; Sarma, P. N., (2005). Laccase production by pleurotus ostreatus 1804: Optimization of submerged culture condition by Taguchi DOE methodology. Biochem. Eng. J., 24(1), 17–26 (10 pages).
Laemmli, U., (1970). Cleavage of structural protein during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 277(5259), 680–685 (6 pages).
Leatham, G. F.; Crawford, R. L.; Kirk, T. K., (1983). Degradation of phenolic compounds and ring cleavage of catechol by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microb., 46(1), 191–197 (7 pages).
Minussi, R. C.; de Moraes, S. G.; Pastore, G. M.; Duran, N., (2001). Biodecolorization screening of synthetic dyes by four white-rot fungi in a solid medium: Possible role of siderophores. Lett. Appl. Microb., 33(1), 21–25 (5 pages).
Montgomery, D. C., (2001) Design and analysis of experiments. 5th. Ed., John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York.
Naidu, K. S. B; Reddy, N. S.; Rao G. V.; Rao, K. R. S. S., (2003). Biodegradation of textile dyes using Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Indian J. Ecol., 30(1), 268–270 (3 pages).
O’Farrells, P. H., (1975). High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J. Biol. Chem., 250(10), 4007–4021 (15 pages).
Okafor, E. Ch.; Opuene, K., (2007). Preliminary assessment of trace metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(2), 233–240 (9 pages).
Oyadomari, M.; Shinohara, H.; Johjima, T.; Wariishi, H.; Tanaka, H., (2003). Electrochemical characterization of lignin peroxidase from the white-rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J. Mol. Catal. B-enzymatic, 21(4–6), 291–297 (7 pages).
Paszczynski, A.; Crawford, R. L.; Huynh, V., (1988). Manganese peroxidase of phanerochaete chrysosporium: purification. Method. Enzymol., 161, 264–270 (7 pages).
Samarghandi, M. R.; Nouri, J.; Mesdaghinia, A. R.; Mahvi, A. H.; Nasseri, S.; Vaezi, F., (2007). Efficiency removal of phenol, lead and cadmium by means of UV/TiO2/H2O2 processes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(1), 19–25 (7 pages).
Sato, S.; Liu, F.; Koc, H.; Tien, M., (2007). Expression analysis of extracellular protein from Phanerochaete chrysosporium grown on different liquid and solid substrates. Microbiology, 153(9), 3023–3033 (11 pages).
Shah, V.; Nerud F., (2002). Lignin degrading system of white-rot fungi and its exploitation for dye decolorization. Can. J. Microbl., 48(10), 857–870 (4 pages).
Spadaro, J. T.; Gold, M. H.; Renganathan, V., (1992). Degradation of azo dyes by the lignin degrading fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microb., 58(8), 2397–2401 (5 pages).
Tien, M.; Kirk, K., (1988). Lignin peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Method. Enzymol., 161, 238–249 (12 pages).
Yadav, J. S.; Doddapaneni, H.; Subramanian, V., (2006). P450ome of the white-rot fungus phanerochaete chrysosporium: Structure, evolution and regulation of expression of genomic P450 Clusters. Biochem. Soc. T., 34(6), 1165–1169 (4 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi, F., Tabandeh, F., Bambai, B. et al. Decolorization of different azo dyes by Phanerochaete chrysosporium RP78 under optimal condition. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 457–464 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326155
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326155