Abstract
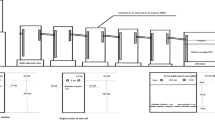
Polyvinyl alcohol-containing desizing wastewater discharged within final textile wastewater has a great impact to the environment due to its poor biodegradability. An improved lab-scale hybrid anaerobic baffled reactor was developed to treat desizing wastewater. The modification was achieved by increasing the height of hybrid anaerobic baffled reactor and application of proper effluent recycle enabled to increase the ability of entrapping microbe-rich small particles in the reactor and prompted the formation of granules. The significant difficulty in hybrid anaerobic baffled reactor operation is the slow start-up procedure, which is crucial to the overall polyvinyl alcohol-containing desizing wastewater treatment. Therefore, the ability of a hybrid anaerobic baffled reactor, treating desizing wastewater, to achieve a prompt start-up was studied at lab-scale. Results showed that inoculated with anaerobic granular sludge and adoption of effluent recycle during start-up, the system demonstrated a good performance of polyvinyl alcohol removal efficiency (above 17.2 %) and satisfactory stability of pH and alkalinity in effluent (range around 7.4–8.0 and 700–920 mg/L, respectively) and the sludge appeared obviously granulation. Thus, the prompt start-up was achieved after 60 days. The start-up strategy used for this process has achieved its goals by creating an active microbial population. The improved lab-scale hybrid anaerobic baffled reactor proved to be an efficient reactor configuration for the treatment of desizing wastewater, which favored the prompt start-up of hybrid anaerobic baffled reactor. The results also provide evidence to modify the design of anaerobic baffled reactor to improve reactor performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azbar, N.; Ursillo, P.; Speece, R. E., (2001). Effect of process configuration and substrate complexity on the performance of anaerobic processes. Water Res., 35 (3), 817–829 (13 pages).
Babel, S.; Tang, J.; Pecharaply, A., (2008). Anaerobic co-digestion of sewage and brewery sludge for biogas production and land application. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6 (1), 131–140 (10 pages).
Barber, W. P.; Stuckey, D. C, (1999). The use of the anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR) for wastewater treatment: A review. Water Res., 33 (7), 1559–1578 (20 pages).
Banu, J. R.; Kaliappan, S.; Yeom, I. T., (2007). Treatment of domestic wastewater using upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (3), 363–370 (7 pages).
Behera, S. K.; Rene, E. R.; Murthy, D. V. S., (2007). Performance of up - flow anoxic bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (2), 247–252 (6 pages).
Chen, G; Chai, X.; Yue, P. L.; Mi, Y., (1997). Treatment of textile desizing wastewater by pilot scale nanofiltration membrane separation. J. Membrane Sci., 127 (1), 93–99 (7 pages).
Dilallo, R.; Alberton, O. E., (1961). Volatile acids by direct titration. JWPCF., 33 (4), 356–365 (10 pages).
Dos Santos, A.B.; Bisschops, I. A. E.; Cervantes, F. J., (2006a). Closing process water cycles and product recovery in textile industry: Perspective for biological treatment. In: Cervantes, F. J.; Van Haandel, A. C, Pavlostathis, S.G. (Eds.), Advanced Biological Treatment Processes for Industrial Wastewaters,Vol. 1. International Water Association,London, 298.
EPA, (1997). Profile of the textile industry. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, USA.
Feitkenhauer, H., (2003). Anaerobic digestion of desizing wastewater: Influence of pretreatment and anionic surfactant on degradation and intermediate accumulation. Enzyme. Microb. Tech., 33 (2–3), 250–258 (9 pages).
Gharbani, P.; Tabatabaii, S. M.; Mehrizad, A., (2008). Removal of Congo red from textile wastewater by ozonation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5 (4), 495–500 (6 pages).
Gopala Krishna, G V. T.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, P., (2009). Treatment of low-strength soluble wastewater using an anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR). J. Environ. Manage., 90 (1), 166–176 (11 pages).
Hickmann, W., (1993). Environmental aspects of textile processing. J. Soc. Dyers Colour., 109 (1), 32–37 (6 pages).
Joseph, H. F., (1961). Spectrophotometric determination of polyvinyl alcohol in paper coatings. Anal. Chem., 33 (13), 1925–1927 (3 pages).
Juang, D. F.; Chiou, L. J., (2007). Microbial population structures in activated sludge before and after the application of synthetic polymer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (1), 119–125 (7 pages).
Kumar, P.; Prasad, B.; Chand, S., (2009). Treatment of desizing wastewater by catalytic thermal treatment and coagulation. J. Hazard. Mater., 163 (1), 433–440 (8 pages).
Matsumura, S.; Kurita, H.; Shimokobe, H., (1993). Anaerobic biodegradability of polyvinyl alcohol. Biotech. Lett., 15 (7), 749–754 (6 pages).
Ren, N.; Wang, B.; Huang, J. C, (1997). Ethanol type fermentation from carbohydrate in high rate acidogenic reactor. Biotech. Bioeng., 54 (5), 428–433 (6 pages).
Sallis, P. J.; Uyanik, S., (2003). Granule development in a split-feed anaerobic baffled reactor. Bioresour. Tech., 89 (3), 255–265 (11 pages).
Schlüter, K., (1990). Oekologische beurteilung von Schlichtemitteln. Melliand. Textil. Int., 71, 195–198 (4 pages).
Shin, H. S.; Han, S. K.; Song, Y. C; Lee, C. Y, (2001). Performance of UASB reactor treating leachate from acidogenic fermenter in the two-phase anaerobic digestion of food waste. Water Res., 35 (14), 3441–3447 (7 pages).
Skiadas, I. V.; Lyberatos, G., (1998). The periodic anaerobic baffled reactor. Water Sci. Tech., 38 (8–9), 401–408 (8 pages).
Tartakovsky, B.; Guiot, S. R., (1997). Modeling and analysis of layered stationary anaerobic granular biofilms. Biotech. Bioeng., 54 (2), 122–130 (9 pages).
Treffry Goatley, K.; Buckley, C.; Groves, G., (1983). Reverse osmosis treatment and reuse of textile dyehouse effluents. Desalination, 47(1–3), 313–320 (8 pages).
Wang, J. L.; Huang, Y. H.; Zhao, X., (2004). Performance and characteristics of an anaerobic baffled reactor. Bioresour. Tech., 93 (2), 205–208 (4 pages).
Wolfe, R. S., (1979). Methanogens, a surprising microbial group. Anton. Leeuw., 45, 353–364 (12 pages).
Yu, H.; Gu, G; Song, L., (1996). Degradation of polyvinyl alcohol in sequencing batch reactors. Environ. Sci. Tech., 17 (11), 1261–1267 (7 pages).
Zoetemeyer, R. J.; van den Heuvel, J. C; Cohen, A., (1982). pH influence on acidogenic dissimilation of glucose in an anaerobic digestor. Water Res., 16 (3), 303–311 (9 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R.R., Tian, Q., Yang, B. et al. Hybrid anaerobic baffled reactor for treatment of desizing wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 111–118 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326122
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326122