Abstract
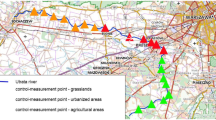
A study was carried out in a strip of a river in the dry and rainy seasons to assess the effect of farming along river banks on the quality of water in rivers. The results showed that there was an increase in the concentration of nitrate in the water downstream in both the rainy and dry seasons. In both rainy and dry seasons, the total nitrogen in the soil was highest (p<0.01) in the middle section. Significant seasonal differences (p<0.01) were observed for phosphate in water, being higher in the dry season. In the soil, the concentration of phosphate showed significant sectional differences (p<0.01) in the rainy season with the highest concentration observed in the lower section (1.74±0.01mg/l) and the least in the upper section (1.02±0.01g/l). However, in the dry season, the highest concentration was obtained in the middle section (1.69±0.01mg/l) and the least in the upper section (1.15±0.02 mg/l). The results suggest that the farms along the riverbanks have an impact on the water quality of the water in the river. It is therefore recommended that there should be close monitoring of the activities of the farms on riverbanks to minimise their impacts on the natural ecosystems that they interact with. Frequent monitoring of the water quality in the rivers relative to the farming estates should be done.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Association of Official American Chemists, (2002). Official methods of analysis, 17th. Ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Maryland, USA.
Altman, S. J. and Parizek, R. R., (1995). Dilution of non-point source nitrate in ground water. J. Environ. Qual., 24, 707–718.
Campbell, C. A., Lafond, G. P., Zentner, R. P. and Jame, Y. W., (1994). Nitrate leaching in udic haploboroll as influenced by fertilization and legumes. J. Environ. Qual., 23, 195–201.
Eana, G. R. E. and Sridhar, M. K. C., (2004). Soil quality near chemical fertilizer industry at Port Harcourt, Nigeria. African J. Environ. Ass. and Mgt. 8, 19–26.
Fakayode, S. O., (2005). Impact assessment of industrial effluent on water quality of the receiving Alaro River in Ibadan, Nigeria. African J. of Environ. Ass. Manag., 10, 1–13.
Jackson, M. H., Morris, P. G., Smith, P. G. and Crawford, J. F., (1989). Environmental health reference book, 9, 1–22.
Krantz, D. and Kifferstein, B., (2005). Water pollution and Society. Available at http://www.umich.edu
Malawi Bureau of Standards (MBS), (2000). MBS guidelines on constituents of health significance, MBS, Malawi.
Mahvi, A. H., Nouri, J., Babaei, A.A. and Nabizadeh, R.,(2005). Agricultural activities impact on groundwater nitrate pollution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 2(1), 30–35.
Mironga, J. M., (2005). Conservation related attitudes of wetland users in Kisii District, Kenya. African J. of Environ. Ass. Manag., 10, 14–25.
Mughogho, S., (2004). Personal communication, University of Malawi, Bunda College of Agriculture.
O’Neill, P., (1998). Environmental Chemistry, Blackie Academic and Professional Pub. London, UK.
Subramanian, V., (2004). Water quality in South Asia. Asian J. water, environ. pollut., 1(1-2), 41–54.
Weier, K. L., Doran, J. W., Mosier, A. R., Power, J. F. and Peterson, T. A., (1994). Potential for bioremediation of high nitrate irrigation water via denitrification. J. Environ. Qual., 23, 105–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chimwanza, B., Mumba, P.P., Moyo, B.H.Z. et al. The impact of farming on river banks on water quality of the rivers. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2, 353–358 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325896
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325896