Summary
In a fundamental study on the effect of probenecid on the plasma kinetics and the renal handling of some organic anions known to be transported by the tubular secretion mechanism in the mammalian kidney, we measured plasma levels and urinary excretion rates of salicyluric acid in male Beagle dogs, after intravenous application of salicyluric acid, with and without co-administration of probenecid.
The animals were anaesthetized with sodium pentobarbital (30 mg/kg) and provisions were made for blood and urine sampling. In order to obtain a sufficiently high and constant urine flow, an infusion of a solution containing 5% inulin (2 ml/min) was given throughout an experiment. Inulin was added for measurement of the glomerular filtration rate.
Linear plots of the urinary excretion rate against the average plasma concentration of each urine collection period were drawn as an illustrative way to depict the relation between plasma concentration and urinary excretion rate.
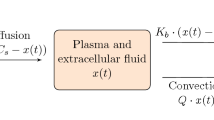
In order to quantify the effect of probenecid on the plasma kinetics and the renal handling of salicyluric acid, we conceived a dynamic model, able to describe changes in plasma kinetics as well as in urinary excretion. The effect of probenecid on the pharmacokinetics of salicyluric acid can be adequately described in terms of a non-competitive inhibition of the tubular secretory mechanism for salicyluric acid. Parameters for the description of this interaction were estimated by a simulation procedure with the aid of the computer program CSMP III.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hekman, P., Porskamp, P.A.T.W., Ketelaars, H.C.J. and Van Ginneken, C.A.M. (1980): Rapid high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of probenecid in biological fluids, J. Chrom. Biomed. Appl.182, 252–256.
Heyrovksy, A. (1956): A new method for the determination of inulin in plasma and urine, Clin. Chim. Acta1, 470–474.
Farmfit, a computer program for non-linear regression analysis, in use at the Computer Centre of the University of Nijmegen. Details available upon request from the present authors.
Van Ginneken, C.A.M., Van Rossum, J.M. and Fleuren, H.L.J.M. (1974): Linear and non-linear kinetics of drug elimination, J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm.2, 395–415.
Bekersky, I., Colburn, W.A., Fishman, L. and Kaplan, S.A. (1980): Metabolism of salicylic acid in the isolated perfused rat kidney, Drug Met. Disp.8, 319–324.
Ewald, B.H. (1967): Renal function tests in normal Beagle dogs, Am. J. Vet. Res.28, 741–749.
Chinard, F.B., Enns, T., Goresky, C.A. and Nolan, M.F. (1965): Renal transit times and distribution volumes of T-1824,creatinin and water, Am. J. Physiol.209, 243–252.
Bojesen, E. (1949): The function of the urinary tract as dead space in clearance experiments, Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest.1, 290–294.
Chinard, F.P. (1955): Comparative renal excretions of glomerular substances following instantaneous injection into a renal artery, Am. J. Physiol. 180, 617–619.
Smith, H.W. (1951): The Kidney, Structure and Function in Health and Disease, Oxford University Press, New York.
Braun, W. (1960): Zum Mechanismus des gegenseitigen Hemmung von Phenolrot, Para-amino-hippursäure und Probenecid, Arch. exp. Path. Pharmac.239, 400–409.
Kinsella, J.L., Holohan, P.D., Pessah, N.I. and Rose, C.R. (1979): Transport of organic ions in renal cortical luminal and anti-luminal membrance vesicles, J. Pharmacol, exp. Ther. 209, 443–450.
Knoefel, P.K., Huang, K.C and Jarboe, H. (1962): Renal disposal of salicyluric acid, Am. J. Physiol.203, 6–10.
Morales, P.A., Crowder, CH., Fishman, A.P., Max-well, M.H. and Gomez, D.M. (1950): Measurement and significance of urinary appearance time in the dog, Am. J. Physiol.163, 454–460.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herman, P., Van Ginneken, C.A.M. Simultaneous kinetic modelling of plasma levels and urinary excretion of salicyluric acid, and the influence of probenecid. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 8, 239–249 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03188754
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03188754