Abstract
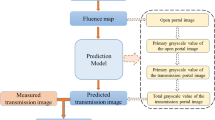
Patient dose verification is becoming increasingly important with the advent of new complex radiotherapy techniques such as conformal radiotherapy (CRT) and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT). An electronic portal imaging device (EPID) has potential application forin vivo dosimetry. In the current work, an EPID has been modelled using a treatment planning system (TPS) to predict transmitted dose maps. A thin slab of RW3 material used to initially represent the EPID. A homogeneous RW3 phantom and the thin RW3 slab placed at a clinical distance away from the phantom were scanned using a CT simulator. The resulting CT images were transferred via DICOM to the TPS and the density of the CT data corresponding to the thin RW3 slab was changed to 1 g/cm3. Transmitted dose maps (TDMs) in the modelled EPID were calculated by the TPS using the collapsed-cone (C-C) convolution superposition (C/S) algorithm. A 6 MV beam was used in the simulation to deliver 300 MU to the homogenous phantom using an isocentric and SSD (source-to-surface) technique. The phantom thickness was varied and the calculated TDMs in the modelled EPID were compared with corresponding measurements obtained from a calibrated scanning liquid-filled ionisation chamber (SLIC) EPID. The two TDMs were compared using the gamma evaluation technique of Lowet al. The predicted and measured TDMs agree to within 2 % (averaged over all phantom thicknesses) on the central beam axis. More than 90 % of points in the dose maps (excluding field edges) produce a gamma index less than or equal to 1, for dose difference (averaged over all phantom thicknesses), and distance-to-agreement criteria of 4 %, 3.8 mm, respectively. In addition, the noise level on the central axis in the predicted dose maps is less than 0.1 %. We found that phantom thickness changes of ≈1 mm, which correspond to dose changes on the central beam axis of less than 0.6 %, can be detected in the predicted transmitted dose distributions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louwe, R.J., Tielenburg, R., van Ingen, K.M., Mijnheer, B.J., van Herk, M.B.,The stability of liquid-filled matrix ionisation chamber electronic portal imaging devices for dosimetry purposes, Medical Physics. 31:819–827, 2004.
Nijsten, S.M., Minken, A.W., Lambin, P., Bruinvis, I.A.,Verification of treatment parameter transfer by means of electronic portal dosimetry, Medical Physics. 31: 341–347, 2004.
McDermott, L.N., Louwe, R.J.W., Sonke, J.-J., van Herk, M.B., and Mijnheer, B.J.,Dose—response and ghosting effects of an amorphous silicon electronic portal imaging device, Medical Physics. 31:285–295, 2004.
Chang, J., Mageras, G.S., Ling, C.C., and Lutz, W.,An iterative EPID calibration procedure for dosimetric verification that considers the EPID scattering factor, Medical Physics. 28:2247–2257, 2001.
Hansen, V.N., Evans, P.M. and Swindell, W.,The application of transit dosimetry to precision radiotherapy, Medical Physics. 23:63–73, 1996.
Hansen, V.N., Swindell, W. and Evans, P.M.,Extraction of primary signal from EPIDs using only forward convolution, Medical Physics. 24:1477–1484, 1997.
Wong, J.W., Slessinger, E.D., Rosenberger, F.U., Krippner, K. and Purdy, J.A.,The delta-volume method for 3-dimensional photon dose calculations, Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on the use of computers in radiation therapy. 8:26–30, 1984.
Wong, J.W., Slessinger, E.D., Hermes, R.E., Offutt, C.J., Roy, T.R. and Vanier, M.W.,Portal dose images I: Quantitative treatment plan verification, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 18:1455–1463, 1990.
Ying, X., Geer, L.Y. and Wong, J.W.,Portal dose images II: Patient dose estimation, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 18:1465–1475, 1990.
McNutt, T.R., Mackie, T.R., Reckwerdt, P. Papanikolaou, N. and Paliwal, B.R.,Calculation of portal dose using the convolution/superposition method, Medical Physics. 23:527–535, 1996.
McNutt, T.R., Mackie, T.R., Reckwerdt, P. and Paliwal, B.R.,Modelling dose distributions from portal dose images using the convolution/superposition method, Medical Physics.23:1381–1392, 1996.
McNutt, T.R., Mackie, T.R., and Paliwal, B.R.,Analysis and convergence of the iterative convolution/superposition dose reconstruction technique for multiple treatment beams and tomotherapy, Medical Physics.24:1465–1476, 1997.
Van Dyk, J., Barnett, R.B., Cygler, J.E., Shragge, P.C.,Commisioning and quality assurance of treatment planning computers, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 26:261–273, 1993.
Harms, W.B., Sr., Low, D.A., Wong, J.W. and Purdy, J.A.,A software tool for the quantitative evaluation of 3D dose calculation algorithms, Medical Physics. 25:1830–1836,1998.
Low, D.A., Harms, W.B., Mutic, S. and Purdy, J.A.,A technique for the quantitative evaluation of dose distributions, Medical Physics. 25:656–661, 1998.
Depuydt, T., Van Esch, A., Huyskens, D. P.,A quantitative evaluation of IMRT dose distributions: refinement and clinical assessment of the gamma evaluation, Radiotherapy and Oncology. 62:309–319, 2001.
Van Herk, M. and Meertens, H.,Physical aspects of a liquid-filled ionisation chamber with pulsed polarizing voltage, Medical Physics. 18:692–702, 1991.
Yin, F.-F., Schell, M.C. and Rubin, P.,Input/output characteristics of a matrix ion-chamber electronic portal imaging device, Medical Physics. 21:1447–1454, 1994.
Louwe, R.J.W., Tielenburg, R., van Ingen, K.M., Mijnheer, B.J. and van Herk, M.B.,The stability of liquid-filled matrix ionization chamber electronic portal imaging devices for dosimetry purposes, Medical Physics.31:819–827, 2004.
Mohammadi, M., Bezak, E. and Fog, L.Two dimensional transmitted dose measurements using a liquid ionization chamber EPID, submitted to Physics in Medicine and Biology (currently under review).
Essers, M., Boellaard, R., van Herk, M., Lanson, H., and Mijnheer, B.,Transmission dosimetry with a liquid-filled electronic portal imaging device, Int. J. Rad. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 34:931–941, 1996.
Van Esch, A., Depuyt, T., Huyskens, D.P.,The use of an aSi-based EPID for routine absolute dosimetric pre-treatment verification of dynamic IMRT fields. Rad. Oncol, 71:223–34, 2004.
Boellaard, R., van Herk, M., Mijnheer, B.J.,The dose response relationship of a liquid-filled electronic portal imaging device, Medical Physics, 23:1601–1611, 1996.
Keller, H., Fix, M., and Rüegsegger, P.,Calibration of a portal imaging device for high-precision dosimetry: A Monte Carlo study, Medical Physics, 25:1891–1902, 1998.
Essers, M., Hoogervorst, B.R., van Herk, M., Lanson, H., and Mijnheer, B.J.,Dosimetric characteristics of a liquid-filled electronic portal imaging device, Int. J. Rad. Oncol. Biol. Phys., 33:1265–1272, 1995.
Chang, J., Mageras, G., Chui, C.S., Ling, C.C., and Lutz, W.,Relative profile and dose verification of intensity-modulated radiation therapy, Int. J. Rad. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 47:231–240, 2000.
Zhu, Y., Jiang, X., and Dyk, J.,Portal dosimetry using a liquid ion chamber matrix: Dose response studies, Medical Physics, 22:1101–1106, 1995.
Low, D.A. and Dempsey, J.F.,Evaluation of the gamma dose distribution comparison method, Medical Physics, 30:2455–2464, 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reich, P., Bezak, E., Mohammadi, M. et al. The prediction of transmitted dose distributions using a 3D treatment planning system. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 29, 18 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178824
Received:
Accepted:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178824