Abstract
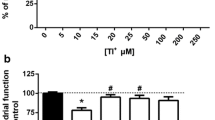
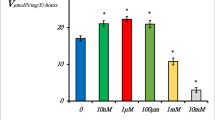
The (Na+ + K+)-ATPase is responsible for maintenance of the ionic milieu of cells. The objective of this study is to investigate the effect of aluminum, an ion implicated in several neurological disorders, on ATP hydrolysis catalyzed by the rat brain synaptosomal (Na+ + K+)-ATPase and on the binding of [3H]ouabain to this enzyme. AlCl3 (25–100 μM) inhibits the phosphatase activity of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in a dose-dependent manner. AlCl3 appears to act as a reversible, noncompetitive inhibitor of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity by decreasing the maximum velocity of the enzyme without significantly affecting the apparent dissociation constant with respect to ATP. AlCl3 may affect Mg2+ sites on the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase but does not appear to interact with Na+ or K+ sites on the enzyme. In contrast to this inhibitory effect on the phosphatase function of the enzyme, AlCl3 (1–100 μM) stimulates the binding of [3H]ouabain to the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. This effect is due to an increase in the maximum [3H]ouabain binding capacity of the enzyme with no change in the [3H]ouabain binding affinity. These data support the hypothesis that AlCl3 may stabilize the phosphorylated form of the synaptosomal (Na+ + K+)-ATPase which increases [3H]ouabain binding while inhibiting the phosphatase activity of the enzyme.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anner B. M. (1985) The receptor function of the Na+ + K+-activated adenosine triphosphatase system.Biochem. J. 227, 1–11.
Berrebi-Bertrand I., Maixent J. M., Christe G., and Lelievre L. G. (1990) Two active Na+/K+-ATPases of high affinity for ouabain in adult rat brain membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1021, 148–156.
Bonting S. L. (1970) Sodium-potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase and and cation transport, inMembranes and Ion Transport, vol. 1 (Bittar E. E., ed.) pp. 257–363, Wiley-Interscience, London.
Brodsky J. L. (1990) Insulin activation of brain Na+−K+-ATPase is mediated by α2-form of enzyme.Am. J. Physiol. 258, C812-C817.
Caspers M. L. and Siegel G. J. (1980) Inhibition by lead of human erythrocyte (Na++K+)-adenosine triphosphatase associated with binding of210Pb to membrane fragments.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 600, 27–35.
Caspers M. L. and Grammas P. (1988) Effect of fatty acids on [3H]ouabain binding to cerebromicrovascular (Na+ + K+-ATPase.J. Neurochem. 50, 1215–1219.
Caspers M. L., Schwartz R. D., Labarca R., and Paul S. M. (1987) Autoradiographic visualization and characterization of [3H]ouabain binding to the Na+, K+-ATPase of rat brain and pineal.Brain Res. 409, 335–342.
Caspers M. L., Kwaiser T. M., and Grammas P. (1990) Control of [3H]ouabain binding to cerebromicrovascular (Na+ + K+)-ATPase by metal ions and proteins.Biochem. Pharmacol. 39, 1891–1895.
Caspers M. L., Kwaiser T. M., Dow M. J., Fu M. J., and Grammas P. (1993) Control of the Na+, K+-ATPase under normal and pathological conditions.Molec. Chem. Neuropathol. 19, 65–81.
Cochran M., Elliott D. C., Brennan P., and Chawtur V. (1990) Inhibition of protein kinase C activation by low concentrations of aluminum.Clin. Chim. Acta 194, 167–172.
Crapper McLachlan D. R., Lukiw W. J., and Kruck T. P. A. (1989) New evidence for an active role of aluminum in Alzheimer’s disease.Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 16, 490–497.
Crapper McLachlan D. R., Dalton A. J., Kruck T. P. A., Bell M. Y., Smith W. L., Kalow W., and Andrews D. F. (1991) Intramuscular desferrioxamine in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.Lancet 337, 1304–1308.
DeLeers M. (1985) Cationic atmosphere and cation competition binding at negatively charged membranes: Pathological implications of aluminum.Res. Commun. Chem. Path. Pharmacol. 49, 277–292.
Erdmann E. and Schoner W. (1973) Ouabain-receptor interactions in (Na+ + K+)-ATPase preparations from different tissues and species. Determination of kinetics constants and dissociation constants.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 307, 386–398.
Ganrot P. O. (1986) Metabolism and possible health effects of aluminum.Environ. Healhh Perspec. 65, 363–441.
Good P. F., Perl D. P., Bierer L. M., and Schmeidler J. (1992) Selective accumulation of aluminum and iron in the neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer’s disease: A laser microprobe (LAMMA) study.Ann. Neurol. 31, 286–292.
Grammas P. and Caspers M. L. (1991) The effect of aluminum on muscarinic receptors in isolated cerebral microvessels.Res. Comm. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 72, 69–79.
Hajos F. (1975) An improved method for the preparation of synaptosomal fractions in high purity.Brain Res. 93, 485–489.
Hauger R., Luu H. M. D., Meyer D. K., Goodwin F. K., and Paul S. M. (1985) Characterization of “high-affinity” [3H]ouabain binding in the rat central nervous system.J. Neurochem. 44, 1709–1715.
Hsu Y. M. and Guidotti G. (1989) Rat brain has the α3 form of the (Na+, K+)-ATPase.Biochemistry 28, 569–573.
Jacobs R. W., Duong T., Jones R. E., Trapp G. A., and Scheibel A. B. (1989) A reexamination of aluminum in Alzheimer’s disease: Analysis by energy dispersive X-ray microprobe and flameless atomic absorption spectrophotometry.Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 16, 498–503.
Johnson G. V. W. and Jope R. S. (1987) Aluminum alters cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP levels but not presynaptic cholinergic markers in rat brain in vivo.Brain Res. 403, 1–6.
Johnson G. V. W. and Jope R. S. (1988) Phosphorylation of rat brain cytoskeletal proteins is increased after orally administered aluminum.Brain Res. 456, 95–103.
Johnson G. V. W., Cogdill K. W., and Jope R. S. (1990) Oral aluminum alters in vitro protein phosphorylation and kinase activity in rat brain.Neurobiol. Aging 11, 209–216.
Lai J. C. K., Guest J. F., Leung T. K. C., Lim L. and Davison A. N. (1980) The effects of cadmium, manganese and aluminum on sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase activity and choline uptake in rat brain synaptosomes.Biochem. Pharmacol. 29, 141–146.
Landsberg J. P., McDonald B., and Watt F. (1992) Absence of aluminum in neuritic plaque cores in Alzheimer’s disease.Nature 360, 65–68.
Lowry O. H., Rosebrough N. J., Farr A. L., and Randall R. J. (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Lytton J. (1985) Insulin effects the sodium affinity of the rat adipocyte (Na+, K+)-ATPase.J. Biol. Chem. 260, 10,075–10,080.
Macdonald T. L. and Martin R. B. (1988) Aluminum ion in biological systems.Trends Biochem. Sci. 13, 15–19.
Martin R. B. (1986) The chemistry of aluminum as related to biology and medicine.Clin. Chem. 12, 1797–1806.
Miller J. L., Hubbard C. M., Litman B. J., and Macdonald T. L. (1989) Inhibition of transducin activation and guanosine triphosphatase activity by aluminum ion.J. Biol. Chem. 264, 243–250.
Missiaen L>, Wuytack F., DeSmedt H., Vrolix M., and Casteels R. (1988) AlF4-reversibly inhibits “P”-type cation-transport ATPases, possibly by interacting with the phosphate-binding site of the ATPase.Biochem. J. 253, 827–833.
Perl D. P. (1985) Relationship of aluminum to Alzheimer’s disease.Environ. Health Perspec. 63, 149–153.
Post R. L., Merritt C. R., Kinsolving C. R., and Albright C. D. (1960) Membrane adenosine triphosphatase as a participant in the active transport of sodium and potassium in the human erythrocyte.J. Biol. Chem. 235, 1796–1802.
Segel I. H. (1975)Enzyme Kinetics, pp. 127–128. Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Siegel G. J. and Fogt S. K. (1976) Lead ion activates phosphorylation of Electroplax Na+- and K+-dependent adenosine triphosphatase [(NaK)-ATPase] in the absence of sodium ion.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 174, 744–746.
Swarts H. G. P., Schuurmans Stekhoven F. M. A. H., and DePont J. J. H. H. M. (1990) Binding of unsaturated fatty acids to Na+, K+-ATPase leading to inhibition and inactivation.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1024, 32–40.
Sweadner K. J. (1979) Two molecular forms of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated ATPase in brain: separation and difference in affinity for strophanthidin.J. Biol. Chem. 254, 6060–6067.
Urayama O. and Sweadner K. J. (1988) Ouabain sensitivity of the alpha 3 isozyme of rat Na, K-ATPase.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 156, 796–800.
Whittam R. (1962) The dependence of the respiration of brain cortex on active cation transport.Biochem. J. 82, 205–212.
Wills M. R. and Savory J. (1983) Aluminum poisoning: Dialysis encephalopathy, osteomalacia and anaemia.Lancet ii, 29–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caspers, M.L., Dow, M.J., Fu, MJ. et al. Aluminum-induced alterations in [3H]Ouabain binding and ATP hydrolysis catalyzed by the rat brain synaptosomal (Na+ + K+)-ATPase° . Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 22, 43–55 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160093
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160093