Abstract
An attempt was made to investigate the effect of TMB-8 [3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate-8 (N,N-diethylamino) octyl ester], which is known to be an inhibitor of intracellular Ca2+ release, on catecholamines (CA) secretion evoked by Ach, excess K+, DMPP, McN-A-343 and caffeine from the isolated perfused rat adrenal glands and to clearify its mechanism of action.
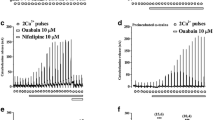
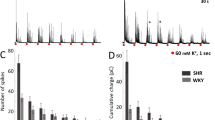
The pretreatment with a low dose of TMB-8 (10 μM) for 20 min led to marked inhibition in CA secretion evoked by Ach (5.32 mM), excess K+ (56 mM), DMPP (100 μM), McN-A-343 (100 μM) and BAY-K 8644 (10−5M). Caffeine-induced CA secretion was similar to that of control only during the first periods (0–3 min) but thereafter marked inhibition in CA secretion evoked by caffeine was observed during the rest periods up to 30 min. The increased moderate concentration of TMB-8 (30 μM) caused the result similar to that of 10 μM TMB-8. However, in adrenal glands preloaded with a high dose of TMB-8 (100 μM), CA releases evoked by Ach, excess K+, DMPP, McN-A-343 and caffeine were almost completely blocked by the drug.
These experimental data demonstrate that TMB-8 may inhibit cholinergic receptor-mediated and also depolarization-dependent CA secretion, suggesting that these TMB-8 effects seem to be mediated through inhibiting influx of extracellular calcium into the rat adrenal medullary chromaffin cells as well as reducing the release of calcium from intracellular sources.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Charo, I. F., Feinman and Detwiler, T. C.: Inhibition of platelet secretion by an antagonist of intracellular calcium.Biochim. Biophys. Res. Commun. 72, 1462 (1976).
Chiou, C. Y. and Malagodi, M. H.: Studies on the mechanism of action of a new antagonist-(N,N-diethylamino-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate hydrochloride in smooth and skeletal muscles.Br. J. Pharmacol. 53 279 (1975).
Rubin, R. P., Shen, J. C. and Laychock, S. G.: Evidence for the mobilization of cellular calcium by prostacyline in cat adrenocortical cells. The effect of TMB-8.Cell Calcium.11, 391 (1980).
Smith, R. J. and Iden, S. S.: Phorbol myristate acetate-induced release of granule enzymes form human neutrophils inhibition by the calcium antagonist, 8-(N,N-diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate hydrochloride.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 91, 263 (1979).
Wiedenkeller, D. E. and Sharp, G. W. G.: Unexpected potentiation of insulin release by the calcium store blocker TMB-8,Endocrinology.114, 116 (1984).
Misbahuddin, M., Isosaki M., Houchi, H. and Oka, M.: Muscarinic receptor-mediated increase in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells. Effects of TMB-8 and phorbor ester TPA.FEBS Lett.,190, 25 (1985).
Sasakawa, N., Yamamoto, S., Ishii, K. and Kato, R.: Inhibition of calcium uptake and catecolamine release by 8-(N,N-diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxy benzoate hydrochloride (TMB-8) in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells.Biochem. Phamacol. 33, 4063 (1984).
Poisner, A. M.: Direct stimulant effect of aminophilline on catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla.Biochem. Pharmacol. 22, 469 (1973).
Lim, D. Y., Lee, J. H., Kim, W. S., Lee, E. H., Kim, S. P., Lee, B. J. and Koh, S. T.: Studies on secretion of catecholamines evoked by caffeine from the isolated perfused rat adrenal glands.Arch. Pharmac. Res. 14, 55 (1991).
Yamada, Y., Teraoka, H., Nakazato, Y. and Ohga, A.: Intracellular Ca2+ antagonist TMB-8 blocks catecholamine secretion evoked by caffeine and acetylcholine from perfused cat adrenal glands in the absence of extracellular Ca2+.Neurosci. Lett. 90, 338 (1988).
Nakazato, Y., Yamada, Y., Tomita, U. and Ohga, A.: Muscarinic agonists release adrenal catecholamines by mobilizing intracellular Ca2+ Proc. Jpn. Acad. 60, 314 (1984).
Nakazato, Y., Ohga, A., Oleshansky, M., Tomita, U. and Yamada, Y.: Voltage-independent catecholamines release mediated by the activation of muscarinic receptors in guinea-pig adrenal glands.Br. J. Pharmacol. 93, 101 (1988).
Donowitz, M., Cusolito, S. and Sharp, G. W. G.: Effects of calcium and Cl transport in rabbit ileum.Am. J. Physiol. 250, G691 (1986).
Takahara, A., Suzuki-Husaba, M., Hisa, H. and Satoh, S.: Effects of a novel Ca2+ entry blocker, CD-349, and TMB-8 on renal vasoconstriction induced by angiotensin II and vasopressin in dogs.J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 16, 966 (1990).
Malagodi, M. H. and Chiou, C. Y.: Pharmacological evaluation of a new Ca2+ antagonist, 8-(N, N-diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,6-trimethoxybenzoate hydrochloride) (TMB-8): Studies in smooth muscle.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 27, 25 (1974).
Kojima, I., Kojima, K. and Rasmussen, H.: Effects of ANG 2 and K+ on Ca2+ efflux and aldosterone production in adrenal glomerulosa cells.Am. J. Physiol. 248, E36 (1985).
Ogawa, N. and Ono, H.: Effect of 8-(N, N-diethylamino) octyl 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate (TMB-8), an inhibitor of intracellular Ca2+ release. On autoregulation of renal blood flow in the dog.Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 338, 293 (1988).
Wakade, A. R.: Studies on secretion of catecholamines evoked by acetylcholine or transmural stimulation of the rat adrenal gland.J. Physiol. 313, 463 (1981).
Anton, A. H. and Sayre, D. F.: A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxide-trihydroxy indole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.,138, 360 (1962).
Tallarida, R. J. and Murray R. B.: Manual of pharmacologic calculation with computer programs. 2nd ed. Springer-Verlag, New York. p. 132 (1987).
Schramm, M., Thomas, G., Towart, R. and Franckowiak, G.: Novel dihydropyridines with positive inotropic action through activation of Ca2+ channels.Nature.303, 535 (1982).
Wada, Y., Satoh, K., Taira, N.: Cardiovascular profile of Bay-k 8644, a presumed calcium channel activator in the dog. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs.Arch. Pharmacol. 328, 382 (1985).
Hammer, R. and Giachetti, A.: Muscarinic receptor subtypes: M1 and M2 biochemical and functional characterization.Life Sci.31, 2991 (1982).
Peach, M. J.: Stimulation of release of adrenal catecholamine by adenosine 3,5-cycle monophosphate and theophylline in the absence of extracellular Ca2+.Pro. Natl. Aca. Sci. USA. 69, 834 (1972).
Yamata, Y., Nakazato, Y. and Ohga, A.: Ouabain distinguishes between nicotinic and muscarinic receptor-mediated catecholamines secretions in perfused adrenal glands of cat.Br. J. Pharmacol. 96, 470 (1989).
Poisner, A. M.: Caffeine-induced cathecholamine secretion similarity to caffeine-induced muscle contration.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 142, 103 (1973).
Morita, K., Dohi, T., Kitayama, S., Koyama, Y. and Tsujimoto, A.: Enhancement of stimulation-evoked catecholamine release from cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by forskolin.J. Neurochem. 48, 243 (1987).
Morita, K., Dohi, T., Kitayama, S., Koyama, Y. and Tsujimoto, A.: Simulation-evoked Ca2+ fluxes in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells are enhanced by forskolin.J. Neurochem. 48, 248 (1987).
Baker, D. F. and Knight, D. E.: Calcium-dependent exocytosis in bovine adrenal medullary cells with leaky plasma membrane.Nature.276, 620 (1978).
Ohashi, H., Takewaki, T. and Okada, T.: Calcium and the contractile effect of carbachol in the depolarized guinea pig taenia caecum.Jap. J. Pharmacol. 24, 601 (1974).
Casteel, R. and Raemaeker, L.: The action of acetylcholine and catecholamines on an intracellular calcium store in the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli.J. Physiol. 294, 51 (1979).
Cheek, T. R. and Burgoyne, R. F.: Effect of activation of muscarinic receptors on intracellular free calcium and secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells.Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 846, 167 (1985).
Kao, L. S. and Schneider, A. S.: Muscarinic receptors on bovine chromaffin cells mediated a rise in cytosolic calcium that is independent of extracellular calcium.J. Biol. Chem. 260, 2019 (1985).
Kao, L. S. and Schneider, A. S.: Calcium mobilization and catecholamine secretion in adrenal chromaffin cells.J. Biol. Chem. 261, 4881 (1986).
Harish, O. E., Kao, L. S., Raffaniello, R., Wakade, A. K. and Schneider, A. S.: Calcium dependence of muscarinic receptor-mediated catecholamine secretion from the perfused rat adrenal medulla.J. Neurochem. 48, 1730 (1987).
Wakade, A. R. and Wakade, T. D.: Contribution of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in the secretion of catecholamines evoked by endogenous an exogenous an exogenous acetylcholine.Neuroscience.10, 973 (1983).
Kilpatrick, D. L., Slepepis, R. J., Corcoran, J. J. and Kirshner, N.: Calcium uptake and catecholamine secretion by cultured bovine adrenal medulla cells.J. Neurochem. 38, 427 (1982).
Kilpatrick, D. L., Slepetis, R. and Kirshner, N.: Ion channels and membrane potential in stimulus-secretion coupling in adrenal medulla cells.J. Neurochem. 36, 1245 (1981).
Knight, D. E. and Kesteven, N. T.: Evoked transient intracellular free Ca2+ changes and secretion in isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 218, 177 (1983).
Kojima, I., Kojima, K. and Rasmussen, H.: Mechanism of inhibitory action of TMB-8 (8-(N,N-diethylamino) octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate hydrochloride) on aldosterone secretion in adrenal glomerulosa cells.Biochem. J. 232, 87 (1985).
Yamamoto, H., Hwang, O. and Van Breeman, C.: Bay-k 8644 differentiates between potential and receptor operated Ca2+ channels.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 102, 555 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, DY., Kim, CD. & Ahn, GW. Influence of TMB-8 on secretion of catecholamines from the perfused rat adrenal glands. Arch. Pharm. Res. 15, 115–125 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974085
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974085