Abstract
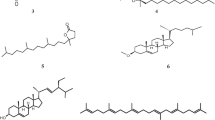
A new naturally occurring sterol, compound5, and six known stigmasterols were isolated from fruits ofAilanthus altissima Swingle by repeated column chromatography and RP-HPLC. Their structures were identified as, 5α-stigmastane-3,6-dione (1), 3β-hydroxystigmast-5-en-7-one (2), stigmast-5-ene-3β, 7α-diol (3), 6α-hydroxystigmast-4-en-3-one (4), 5α-stigmastane-3β, 6β-diol (5), stigmast-4-ene-3β, 6α-diol (6), stigmast-5-ene-3β, 7α,20ζ-triol (7) by spectral analysis and comparison with the published data. These compounds have not been reported from genusAilanthus, whereas compound7 was identified by NMR for the first time. In addition, the 95% ethanol extract and compounds from the fruits of Ailanthus altissima SWINGLE were assayed forin vitro antimicrobial activity. The extract was potent active against the assayed bacteria while compounds3 and7 exhibited moderate activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greca, M. D., Monaco, P., and Previtera, L., Stigmasterols fromTypha Latifolia.J. Nat. Prod., 53, 1430–1435 (1990).
Kimura, Y., Akihisa, T., Yasukawa, K., Takido, M., and Tamura, T., Structures of five hydroxylated sterols from the seeds of Trichosanthes kirilowii MAXIM.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 43, 1813–1817 (1995).
Pardo, F., Perich, F., Torres, R., and Monache, F. D., Stigmast-4-ene-3,6-dione an unusual phytotoxic sterone from the roots ofEchium vulgare L.Biochem. Sys. Ecol., 28, 911–913 (2000).
Pierre, L., Andre, G., Stephane, G., Pierre, J., Jean-Louis, S., and Constantin, B., Formation of modified fatty acids and oxyphytosterols during refining of low erucic acid rapessed oil.J. Agric. Food. Chem., 51, 4284–4290 (2003).
Shin, Y., Masami, I., Takakiko, T., Takahashi, T., and Matsushita, K., Constituents ofAilanthus altissima Swingle. Isolation and Structures of Shin Juglycosides A, B, C, and D.Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 57, 2496–2501 (1984).
Zhao, C. C., Wang, J. H., Li, W., Sha, Y., and Li, X., Studies on the chemical constituents of Fructus Ailanthi altissimae.Clin. J. Med. Chem., 13, 211–214 (2003).
Zheng, J. P., Wang, G. B., Yao Pin Wei Sheng Wu Xue Ji Jian Yan Ji Shu [M]. Bei Jing: People's Medical Publishing House. (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, CC., Shao, JH., Li, X. et al. Antimicrobial constituents from fruits ofAilanthus altissima SWINGLE. Arch Pharm Res 28, 1147–1151 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02972977
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02972977