Abstract
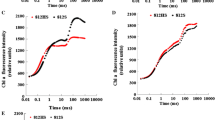
This investigation was performed to study the influence of benomyl on photosynthetic pigments and enzymes in soybean leaves. Chlorophyll and pheophytin levels were reduced by benomyl 45 days after greening. These results indicate that chlorophylla andb, and pheophytin must be controlled by benomyl. SDS-PAGE analysis showed that 50 and 14.5 kD polypeptides represented as the large and small subunits of rubisco. In the both of these subunits, the band intensity of the control was significantly higher than that after benomyl treatment, indicating that these two subunits are affected by benomyl. Benomyl strongly inhibited both the activity and content of rubisco as its concentration was gradually increased. However, it remains unclear whether this reduction of rubisco level was due to a reduced level of rubisco activase. Two major polypeptides of 46 and 42 kD were identified as rubisco activase subunits by SDS-PAGE. The intensity of these two bands was shown to be higher in the control than after benomyl treatment. These results indicate that the rubisco decrease resulting from increased benomyl concentrations was caused by rubisco activase. A significant decrease in both the activity and content of rubisco activase by benomyl was also observed. These results suggest that the decrease in rubisco level caused by benomyl is accompanied by a decrease in both the activity and content of rubisco activase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BTP:
-
Bis-tris propane
- DMF:
-
N,N-Dimethylformamide
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- MBT:
-
Mercaptobenzothiazole
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonylfluoride
- PSII:
-
Photosystem II
- PVPP:
-
Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone
References
Chiba, M. and R. P. Singh (1986) High-performance liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of benomyl and carbendazim in aqueous media.J. Agric. Food Chem. 34: 108–112.
Cano, P., J. L. De la Plaza, and L. Munoz-Delgado (1987) Determination and persistence of several fungicides in postharvest-treated apples during their cold storage.J. Agric. Food Chem. 35: 144–147.
Delp, C. J. (1987) Benzimidazole and related fungicides. pp. 233–244. In: H. Lyr (ed.).Modern Selective Fungicides-Properties Applications, Mechanisms of Action. Longman Group, London, UK.
Liu, C-H., G. C. Mattern, X. Yu, and J. D. Rosen (1990) Determination of benomyl by high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry/selected ion monitorning.J. Agric. Food Chem. 38: 167–171.
Paul, N. D., P. G. Ayres, and L. E. Wyness (1989) On the use of fungicides for experimentation in natural vegetationFunctional Ecol. 3: 759–769.
Sukarno, N., S. E. Smith, and E. S. Scott (1993) The effect of fungicides on vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. I. The effects on vesicular arbuscular mycorhizal fungi and plant growth.New Phytologist 25: 139–147.
Newsham, K. K., A. H. Fitter, and A. R. Watkinson (1994) Root pathogenic and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi determine fitness in asymptomatic plant in the field.J. Ecol. 82: 805–814.
Bardalaye, P. C. and W. B. Wheeler (1985) Simplified method for the clean-up and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of benomyl in mangoes.J. Chromatogr. 330: 403–407.
Davidse, L. C. (1986) Senzimidazole fungicides: Mechanism of action and biological impact.Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 24: 43–65.
Ramanayake, S. M. S. D. and K. Yakandawala (1997) Micropropagation of giant bamboo (Dendrocalamus giganteus Munro) from nodal explants of field grown culms.Plant Sci. 129: 213–223.
Aragaki, M., J. Y. Uchida, and C. Y. Kadooka (1994) Toxicity of benlate to cucumber and evidence for a volatile phytotoxic decomposition product.Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 27: 121–125.
Hale, K. A. and F. E. Sanders (1982) Effects of benomyl on vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection of red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) and consequences for phosphorus inflow.J. Plant Nutrition 5: 1355–1367.
Thringstrup, I. and S. Rosendahl (1994) Quantification of fungal activity in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis by polyacrylamide gel eletrophoresis and densitometry of malate dehydrogenase.Soil Biol. Biochem. 26: 1483–1489.
Weissbach, A., B. L. Horeckere, and J. Hurwitz (1956) The enzymatic formation of phosphoglyceric acid from ribulose diphophate and carbon dioxide.J. Biol. Chem. 218: 795–810.
Bowes, G., W. L. Ogren, and R. H. Hageman (1971) Phosphoglycolate production catalyzed by ribulose diphosphate carboxylase.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 45: 716–722.
Badger, M. R. and G. H. Lorimer (1976) Activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. The role of Mg2+, CO2 and pH.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 175: 723–729.
Lorimer, G. H. and H. M. Miziorko (1980) Carbamate formation on the amino group of a lysyl residue as the basis for the activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by CO2 and Mg2+.Biochemistry 19: 5321–5328.
Salvucci, M. E., A. R. Portis, Jr., and W. L. Ogren (1985) A soluble chloroplast protein catalyzes ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activationin vivo, Photosynth. Res. 7: 191–203.
Robinson, S. P. and A. R. Portis, Jr. (1989b) Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase protein prevents thein vitro decline in activity of ribulose-1,5-bis-phosphate carboxylase/oxygenase.Plant Physiol. 90: 968–971.
Portis, A. R. Jr. (1990) Rubisco activase.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1015: 15–28.
Salvucci, M. E., J. M. Werneke, W. L. Ogren, and A. R. Portis, Jr. (1987) Puritication of species distribution of rubisco activase.Plant Physiol. 84: 930–936.
Roh, K. S., J. K. Kim, S. D. Song, H. S. Chung, and J. S. Song (1996) Decrease of the activation and carbamylation of rubisco by high CO2 in kidney bean.Kor. J. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 11: 295–302.
Roh, K. S., I. S. Kim, B. W. Kim, J. S. Song, H. S. Chung, and S. D. Song (1997) Decrease in carbamylation of rubisco by high CO2 concentration is due to decrease of rubisco activase in kidney bean.J. Plant Biol. 40: 73–79.
Inskeep, W. P. and P. R. Bloom (1985) Extinction coefficients of chlorophylla andb inN,N-dimethylformamide and 80% acetone.Plant Physiol. 77: 483–485.
Vernon, L. P. (1960) Spectrophotometric determination of chlorophylls and pheophytins in plant extracts.Anal. Chem. 32: 1144–1150.
Wang, Z. Y., G. W. Snyder, B. D. Esau, A. R. Portis, Jr., and W. L. Ogren (1992) Species-dependent variation in the interaction of substrate-bound ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco) and rubisco activase.Plant Physiol. 100: 1858–1862.
Racker E. (1962) Ribulose diphosphate carboxylase from spinach leaves.Methods Enzymol. 5: 266–270.
Robinson, S. P. and A. R. Portis, Jr. (1989) Adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis by purified rubisco activase.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 268: 93–99.
Wishnick, M. and M. D. Lane (1971) Ribulose disphosphate carboxylase from spinach leaves.Methods Enzymol. 23: 570–577.
Bradford, M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4.Nature 227: 680–685.
Leong, T.-Y. and J. Anderson (1984) Adaptation of the thylakoid membranes of pea chloroplasts to light intensities. I. Study on the distribution of chlorophyll-protein complexes.Pirotosynth. Res. 5: 105–115.
Leong, T.-Y. and J. Anderson (1984) Adaptation of the thylakoid membranes of pea chloroplasts to light intensities. II. Regulation of electron transport capacities, election cariers, coupling factor (CF1) activity and rates of photosynthesis.Photosynth. Res. 5: 117–128.
Camp, P. J., S. C. Huber, J. J. Burke, and D. E. Moreland (1982). Biochemical changes that occur during senescence of wheat leaves. I. Basis for the reduction of photosynthesis.Plant Physiol. 70: 1641–1646.
Quick, W. P., U. Schurr, R. Scheibe, E.-D. Schulze, S. R. Rodermel, L. Bogorad, and M. Stitt (1991) Decreased ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in transgenic tobacco transformed with “antisense” rbcS. I. Impact on photosynthesis in ambient growth conditions.Planta 188: 542–554.
Andersson, B. and S. Styring (1991) Photosystem II: Molecular organization, function, and acclimation.Curr. Topics Bioenergetics 16: 1–81.
Kough, J. L., V. Gianinazzi-Pearson, and S. Gianinazzi (1987) Depressed metabolic activity of vesicular-arbuscular: mycorrhizal fungi after fungicide applications.New Phytologist 106: 707–715.
Downton, W. J. S., O. Bjorkman, and C. S. Pike (1980) Consequences of increased atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide for growth and photosynthesis of higher plant. pp. 143–151. In: G. I. Pearman (ed.).Carbon Dioxide and Climate: Australian Research. Australian Academy of Science, Canberra, Australia.
Makino, A., T. Mae, and K. Ohira (1983) Photosynthesis and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in rice leaves. Changes in photosynthesis and enzymes involved in carbon assimilation from leaf development through senescence.Plant Physiol. 73: 1002–1007.
Lilley, R. McC. and A. R. Portis, Jr. (1990) Activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco) by rubisco activase. Effects of some sugar phosphates.Plant Physiol. 94: 245–250.
Portis, A. R. Jr. (1992) Regulation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activity.Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 43: 415–437.
Wang, Z. Y. and A. R. Portis, Jr. (1992) Dissociation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate bound to ribulose-1,5-bisphossphate carboxylase/oxygenase and its enhancement by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase-mediated hydrolysis of ATP.Plant Physiol. 99: 1348–1353.
Roh, K. S., M. S. Kwan, Y. H. Do, J. S. Song, H. S. Chung, and S. D. Song (1998) Immunoblot analysis of the expression of genes for barley rubisco activase inE. coli.J. Plant Biol. 41: 288–289.
Sharkey, T. D., L. V. Savitch, and N. D. Butz (1991) Photometric method for routine determination of Keat and carbamylation of rubisco.Photosynth. Res. 28: 41–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roh, K.S., Oh, M.J., Song, S.D. et al. Influence of benomyl on photosynthetic capacity in soybean leaves. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 6, 100–106 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931954
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931954