Summary
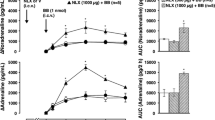
Since opioid peptides and opiate receptors have been demonstrated in the pancreatic islets, we investigated the effects of β-endorphin, metenkephalin, and dynorphin A, on basal and stimulated insulin secretion in the mouse. Each of the three opioid peptides was injected intravenously (0.06-64 nmol/kg) alone or together with each of the three insulin releasing agents glucose (2.8 mmol/kg), carbachol (cholinergic agonist, 0.16 µmol/kg), or terbutaline (β2-adrenoceptor agonist, 3.6 µmol/kg). It was found that β-endorphin, met-enkephalin, and dynorphin A were all without effect on basal plasma insulin levels, except a slight elevation by β -endorphin induced at 2 min after its injection at 64 nmol/kg (to 41 ±2 µU/mL vs 28±4 µU/mL in controls; p<0.05). Glucose- and terbutaline-induced insulin secretion were inhibited by µ-endorphin at the lower dose levels of 0.25 (p<0.01) and 1 nmol/kg (p<0.05). This effect was counteracted by the opiate receptor antagonist naloxone (500 µg/kg). In contrast, β-endorphin at the high dose levels of 16 and 64 nmol/kg augmented the glucose- and terbutaline-induced insulin secretion (p<0.05). Carbacholinduced insulin secretion was not affected by β-endorphin at the lower dose levels but augmented by the peptide at 64 nmol/kg (p<0.01). Metenkephalin inhibited glucose- (p<0.01) and terbutaline- (p<0.05) induced insulin secretion at the high dose rates of 16 and 64 nmol/kg, but the peptide was without effect on carbachol-induced insulin secretion. The inhibitory effects were counteracted by naloxone. Dynorphin A did not affect stimulated insulin secretion at any of the dose levels tested. In summary, in the mouse
-
1.
β-Endorphin at low dose levels inhibits and at high dose levels augments stimulated insulin secretion;
-
2.
Met-enkephalin inhibits stimulated insulin secretion; and
-
3.
Dynorphin A does not affect insulin secretion.
It is suggested that the main influence of β-endorphin and met-enkephalin under in vivo conditions in the mouse is to inhibit stimulated insulin secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roussier J. Opioid peptides have found their roots. Nature 1982; 298: 221–222.
Noda M, Teranishi Y, Takahashi H, Furatani Y, Hirose T, Inayama S, Nakanishi S, Numa S. Isolation and structural organisation of the human preproenkephalm gene. Nature 1982; 297: 431–434.
Kadikani H, Furatani Y, Takahoshi H, Noda M, Morimoto Y, Hirose T, Asai M, Inayama S, Nakanishi S, Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for porcine B-neo-endorphin-dynorphin precursor. Nature 1982; 298: 245–249.
Giugliano D, Torella R, Lefebvre, PJ, D’Onofrio F. Opioid peptides and metabolic regulation. Diabetologia 1988; 31: 3–15.
Akil H, Watson SJ, Young E, Lewis ME, Khachaturian H, Walker JM. Endogenous opioids: Biology and function. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 1984; 7: 223–255.
Smyth DG. β-Endorphin and related peptides in pituitary, brain, pancreas, and antrum. Br. Med. Bull. 1983; 39: 25–30.
Houck JC, Chang CM, Kimball CD. Pancreatic beta-endorphin-like polypeptides. Pharmacology 1981; 23: 14–23.
Bruni JF, Watkins WB, Yen SSC. B-endorphin in the human pancreas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1979; 49: 649–661.
Feurle GE, Weber U, Helmstaedter V. B-lipotropin-like material in human pancreas and pyloric antral mucosa. Life Sci. 1980; 27: 467–473.
Feurle GE, Helmstaedter V, Weber V. Met- and leu-enkephalin immuno- and bioreactivity in human stomach and pancreas. Life Sci. 1982; 31: 2961–2969.
Stern AS, Wurzbuger RJ, Barkey R, Spector S. Opioid polypeptides in guinea pig pancreas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982; 79: 6703–6706.
Grube D, Voigt KH, Weber E. Pancreatic glucagon cells contain endorphin-like immuno- reactivity. Histochemistry 1978; 59: 75–79.
Watkins WB, Bruni JF, Yen SSC. B-endorphin and somatostatin in the pancreatic D-cell colocalization by immunocytochemistry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1980; 28: 1170–1174.
Timmers KI, Voyles NR, King C, Wells M, Fairtile R, Recant L. Opioid peptides in rat islets of Langerhans. Immunoreactive met- and leu-enkephalins and BAM-22P. Diabetes 1986; 35: 52–57.
Cetin Y. Immunohistochemistry of β-neoendorphin and dynorphin in the endocrine pancreas of rat and man. Histochemistry 1985; 83: 369–373.
Cetin Y. Enterochromaffin (EC)- cells of the mammalian gastro-entero-pancreatic (GEP) endocrine system: cellular source of pro-dynorphin-derived peptides. Cell Tissue Res. 1988; 253: 173–179.
Larsson LI. Innervation of the pancreas by substance P, enkephalin, vasoactive intestinal peptide and gastrin/CCK immunoreactive nerves. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1979; 27: 1283–1284.
Verspohl EJ, Berger U, Ammon HPT. The significance of µ- and δ-receptors in rat pancreatic islets for the opioid-mediated insulin release. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1986; 888: 217–224.
Khawaja X, Titheradge M, Green IC. Opiate receptor binding sites in rat islets of Langerhans and liver membranes. Diabet. Med. 1987; 4: 387.
Zukin RS, Zukin SR. Multiple opiate receptors: emerging concepts. Life Sci. 1981; 29: 2681–2690.
Wuster M, Schulz R, Herz A. Specificity of opioids towards the mu-, delta- and epsilon-opiate receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 1979; 15: 193–198.
Wolozon BL, Pasternak GW. Classification of multiple morphine and enkephalin binding sites in the central nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981; 78: 6181–6185.
Paterson SJ, Robson LE, Kosterlitz HW. Classification of opioid receptors. Br. Med. Bull. 1983; 39: 31–36.
Knudtzon J. Effects of proopiomelanocortin-derived peptides on plasma levels of glucagon, insulin and glucose. Horm. Metab. Res. 1986; 18: 579–583.
Ehrenreich H, Goebel FD. The role of opioids in the endocrine function of the pancreas. Diab. Res. 1986; 3: 59–66.
Lala A, Bouloux P, Tamburrano G, Gale E. Opioid peptides and glucose metabolism. J. Endocrinol, invest. 1987; 10: 95–104.
Ahrén B, Lundquist I. Effects of naloxone on basal and stimulated insulin secretion in the mouse. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1984; 102: 135–139.
Reid RL, Sandler JA, Yen SSC. β-Endorphin stimulates the secretion of insulin and glucagon in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1981; 52: 592–594.
Feldman M, Kisel RS, Unger RH, Li CH. Beta-endorphin and the endocrine pancreas. Studies in healthy and diabetic human beings. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983; 308: 349–353.
Paolisso G, Giugliano D, Scheen AJ, Franchimont P, D’Onofrio F, Lefébvre PJ. Primary role of glucagon release in the effect of β-endorphin on glucose homeostasis in normal man. Acta Endocrinol. 1987; 115: 161–169.
Giugliano D, Cozzolino D, Salvatore T, Ceriello A, Torella R. Dual effect of beta-en- dorphin on insulin secretion in man. Horm. Metab. Res. 1987; 19: 502–503.
Matsumura M, Fukushima T, Saito H, Saito S. In vivo and in vitro effects of β-endorphin on glucose metabolism in the rat. Horm. Metab. Res. 1984; 16: 27–31.
Schleicher RL, Chawla RK, Coan PA, Martino-Saltzman D, Collins DC. β-Endorphin- induced hyperglycemia in rabbits: effects of a glucose or arginine challenge. Am, J. Physiol. 1987; 252: E255-E259.
Knudtzon J. Hyperinsulinaemic and hyperglycaemic effects of beta-endorphin in rabbits. Horm. Metab. Res. 1986; 18: 505–509.
Rudman D, Berny CJ, Riedeburg CH, Hollins BM, Kutner MH, Lynn MJ, Chawla RK. Effects of opioid peptides and opiate alkaloids on insulin secretion in the rabbit. Endo- crinology 1983; 112: 1702–1710.
Hart IC, Cowie AT. Effect of morphine, naloxone, and an enkephalin analogue on plasma prolactin, growth hormone, insulin and thyroxine in goats. J. Endocrinol. 1978; 77: 16–17.
Giugliano D, Quatrano A, Consoli G, Ceriello A, Torella R, D’Onofrio F. Inhibitory effect of enkephalin on insulin secretion in healthy subjects and in non-insulin-dependent, diabetic subjects. Metabolism 1987; 36: 286–289.
Jeanrenaud X, Maeder E, Del Pozo E, Felber JP. Effect of an enkephalin analogue (FK 33-824) on glucose tolerance in man. Acta Endocrinol. 1983; 104: 85–90.
Celotti F, Farina JMS, Motta M, Martini L. Effect of met-enkephalin on portal insulin and glucose in the rat. Horm. Metab. Res. 1980; 12: 125–126.
Ahrén B, Lundquist I. Effects of selective and non-selective β-adrenergic agents on insulin secretion in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1981; 71: 93–104.
Heding LG. A simplified insulin radioimmunoassay method.In: Donato L, Sirchis J, Milhaud G. Labelled Proteins in Tracer Studies. 1966; Euratom, Brussels, pp. 345–350.
Bruss ML, Black AL. Enzymatic microdetermination of glycogen. Anal. Biochem. 1978; 84: 309–312.
Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Di Pinto P, Saccomanno F, Gentile S, Cacciapuoti F. Impaired insulin secretion in human diabetes mellitus. The effect of naloxone-induced opiate receptor blockade. Diabetes 1982; 31: 367–370.
Morley JE. The endocrinology of the opiates and opioid peptides. Metabolism 1981; 30: 195–208.
El-Tayeb KMA, Vranic M, Brubaker PL, Lickley HLA. Beta endorphin modulation of the glucoregulatory effects of repeated epinephrine infusion in alloxan-diabetic and normal dogs. Diabetologia 1987; 30: 745–754.
Schleicher RL. The effect of β-endorphin (BE) on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from isolated rabbit pancreatic islets. Proc. 70th Ann. Meet. Endocr. Soc. Proc. 1988; p. 339.
Ipp E, Dobbs R, Unger RH. Morphine and β-endorphin influence the secretion of the endocrine pancreas. Nature 1978; 276: 190–191.
Curry DL, Bennett LL, Li CH. Stimulation of insulin secretion by beta-endorphin (1–27 & 1–31). Life. Sci. 1987; 40: 2053–2058.
Ahrén B, Lundquist I. Effects of α- and β-adrenoceptor stimulation on45Ca+ + efflux and insulin secretion from perfused rat islets. Acta. Physiol. Scand. 1985; 124: 381–389.
Ahrén B, Schersteén B. β2-Adrenoceptor induced increase of plasma insulin levels in man: Evidence of direct and indirect B-cell stimulation and liver effects. Diab. Res. 1986; 3: 443–445.
Ahrén B, Lundquist I. α-Adrenoceptor blockade by phentolamine inhibits β-adrenergi- cally and cholinergically induced glucagon secretion in the mouse. Horm. Metab. Res. 1987; 19: 600–604.
Green IC, Perrin D, Pedley KC, Leslie RDG, Pyke DA. Effects of enkephalins and morphine on insulin secretion from isolated rat islets. Diabetologia 1980; 19: 158–161.
Toyota T, Ishizuka J, Nagaoka J, Goto Y. Effects of met-enkephalin and dynorphin (1–17) on the secretion of insulin and glucagon from the isolated perfused pancreas. In: Sakamoto N, Min HK, Baba S (eds.) Current Topics in Clinical and Experimental Aspects of Diabetes Mellitus. 1985; Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 86–90.
Hermansen K. Enkephalins and the secretion of pancreatic somatostatin and insulin in the dog: studies in vitro. Endocrinology 1983; 113: 1149–1154.
Bailey CJ, Flatt PR. Increased responsiveness to glucoregulatory effect of opiates in obese diabetic ob/ob mice. Diabetologia 1987; 30: 33–37.
Simonds WF. The molecular basis of opioid receptor function. Endocr. Rev. 1988; 9: 200–212.
Klee WA, Koski G, Tocque Simonds WF. On the mechanism of receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Adv. Cyclic Nucleot. Prot. Phosph. Rec. 1984; 17: 153–159.
Hescheler J, Rosenthal W, Trautwein W, Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. Nature 1987; 325: 445–447.
Prentki M, Matschinsky FM. Ca2 +, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol. Rev. 1987; 67: 1185–1248.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahrén, B. Effects of β-endorphin, met-enkephalm, and dynorphin a on basal and stimulated insulin secretion in the mouse. Int J Pancreatol 5, 165–178 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02924417
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02924417