Abstract
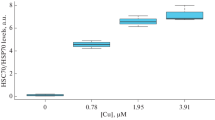
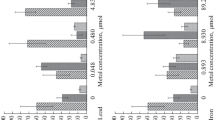
The changes in heme (associated with hemoglobin), hemoglobin and hematin in the coelomic fluid of marine worm,Urechis unicinctus, exposed to different concentrations of sulfide, were investigated using biochemical techniques. When exposed to different sulfide concentrations for up to 96 h, the relative amounts of the three components changed in a regular pattern suggesting that the coelomocytes play an important role in the worm's tolerance to sulfide. The possible roles of heme compounds in sulfide tolerance of this species are discussed on the basis of our experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arp, A. J. and J. J. Childress, 1983. Sulfide binding by the blood of the hydrothermal vent worm.Riftia pachyptila.Science 219: 295–297.
Arp, A. J., J. J. Childress and R.D. Vetter, 1987. The sulfide-binding protein in the blood of the vestimentiferan tubewormRiftia pachyptila is the extracellular hemoglobin.J. Exp. Biol. 128: 139–158.
Arp, A. J., B. M. Hansen and D. Julian, 1992. Burrow environment and coelomic fluid characteristics of the echiuran wormUrechis caupo from populations at three sites in northern California.Mar. Biol. 113: 613–623.
Arp, A.J., J. G. Menon and D. Julian, 1995. Multiple mechanisms provide tolerance to environmental sulfide inUrechis caupo.Am. Zool. 35: 132–144.
Bonaventura, J. and G. B. Kitto, 1973. Ligand-linked dissociation of some invertebrate hemoglobins.In: L. Bolis, N. K. Schmidt and S. H. P. Maddress eds Comp. Physiol. North-Holland, Amsterdam, p. 216–218.
Cline, J. D., 1969. Spectrophotometer determination of hy drogen sulfide in natural waters.Limnol. Oceanogr. 14: 454–458.
Doeller, J. E., D. W. Kraus, J. M. Colacino et al., 1998. Gill hemoglobin may deliver sulfide to bacterial symbionts ofSolemy velum (Bivalvia, Mollusca).Biol. Bull. Mar. Boil. Lab., Woods Hole 175: 388–396.
Falk, J. E., 1964. Porphyrins and Metalloporphyrins.In: Elsevier, Amsterdam, p.266.
Garey, J. R., A. F. Riggs, 1986. The hemoglobin ofUrechis caupo.J. Biol. Chem. 261: 16446–16450.
Johnson, K. S., C.L. Beehler and A. Sakamoto 1986. In situ measurement of chemical distributions in deep-sea hydrothermal vent field.Science 231: 1139–1141.
Julian, D., E. D. Wendy and A.J. Arp, 1998. Neuromuscular sensitivity to hydrogen sulfide in the marine invertebrateUrechis caupo.J. Exp. Biol. 201:1393–1403.
Kang, K. H., 1999. Sediment preference and burrow shape of Spoon worm,Urechis unicinctus in laboratory culture.Korea J. Aquaculture 12(3): 193–196.
Keilin, D. 1933. On the combination of methemoglobin with H2S.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 113B: 393–404.
Kraus, D. W., J. E. Doeller and C. S. Powell, 1996. Sulfide may directly modify cytoplasmic hemoglobin deoxygenation inSolemys Reidi Gills.J. Exp. Biol. 199:1343–1352.
Li, N., S. L. Song and Y. Z. Tang, 1997. Reproductive biology ofUrechis unicinctus along the coast of Shandong province.Acta Zool. Sini. 43(4): 433–435. (in Chinese)
Li, N., S. L. Song and Y. Z. Tang, 1998.Urechis unicinctus.Biol. Bull. 33(8): 12–14. (in Chinese)
Lijana, R. C. and M. C. Williams, 1979. Tetramethylbenzidine —A substitute for benzidine in hemoglobin analysis.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 94: 266.
Mangum, P. C., R. T. Terwilliger, N. B. Terwilliger et al. 1983. Oxygen binding of intact coelomic cells and extracted hemoglobin of the EchiuranUrechis caupo.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 76A: 253–257.
Powell, M. K. and A. J. Arp, 1989. Hydrogen sulfide oxidation by abundant nonhemoglobin heme compounds in marine invertebrates form sulfide-rich habitats.J. Exp. Zool. 249: 121–132.
Standefer, J. C. and D. Vanderjagt, 1977. Use of tetramethylbenzidine in plasma hemoglobin assay.Clin. Chem. 23: 749.
Somero, G. N., J. J. Childress and A. E. Anderson, 1989. Transport, metabolism and detoxification of hydrogen sulfide in animals from sulfide-rich marine environment.Crit. Rev. Aquat. Sci. 1: 591–614.
Well, R. M. G., N.W. Pankhust, 1980. An investigation into the formation of sulphide and oxidation compounds from the hemoglobin of the lugwormAbarenicola affinis (Ashworth).Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 66C: 255–259.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by the NSFC-KOSEF scientific cooperation program and NSFC (No. 30271039)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuojun, M., Zhenmin, B., Kyuoung-Ho, K. et al. The changes of three components in coelomic fluid ofUrechis unicinctus exposed to different concentrations of sulfide. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 23, 104–109 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02845150
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02845150