Abstract
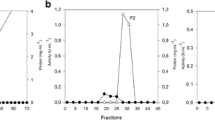
Butyrivibrio sp. Mz 5 with a high xylanolytic activity was isolated. Four major xylanases were detected in the cell-associated fraction using the zymogram technique. The xylanolytic activity was inducible with the oat spelts xylan; two endoxylanases (51 and 145 kDa) were formed constitutively. The bulk of the xylanolytic activity was cell-bound and growth-phase dependent; the maximum activity in the cell-associated fraction was achieved after 16 h of incubation. The highest xylanolytic activity was determined in a medium with 0.5% oat spelts xylan. Under optimum conditions (the highest xylanolytic activity produced), the two cell-bound xylanases (51 and 58 kDa) were isolated by anion exchange chromatography on CIM DEAE 8 tubes attached to a MPLC system, and gel filtration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ha Y.W., Stack R.J., Hespell R.B., Gordon S.H., Bothast R.J.: Some chemical and physical properties of extracellular polysaccharides produced byButyrivibrio fibrisolvens strains.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.57, 2016–2020 (1991).
Hespell R.B., Wolf R., Bothast R.J.: Fermentation of xylans byButyrivibrio fibrisolvens and other ruminal bacteria.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.53, 2849–2853 (1987).
Lin L.L., Thompson J.A.: An analysis of extracellular xylanases and cellulases ofButyrivibrio fibrisolvens H17c.FEMS Microbiol. Lett.68, 197–203 (1991).
Laemmli U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature227, 680–685 (1970).
Lever M.: Carbonydrate determination with 4-hydroxybenzoic acid hydrazide (PAHBAH): effect of bismuth on the reaction.Anal. Biochem.81, 21–27 (1977).
Mannarelli B.M.: Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness among strains of the speciesButyrivibrio fibrisolvens.Internat. J. Syst. Bacteriol.38, 340–347 (1988).
Marinšek Logar R., Zorec M., Nekrep F.V.: Isolation and characterization ofButyrivibrio-like rumen bacteria possessing high xylanolytic activity.Reprod. Nutr. Dev.40, 191–192 (2000).
Štrancar A., Barut M., Podgornik A., Koselj P., Schwinn H., Raspor P., Josić D.: Application of compact porous tubes for preparative isolation of clotting factor VIII from human plasma.J. Chromatogr. A760, 117–123 (1997).
Williams A.G., Withers S.E.: Induction of xylan-degrading enzymes inButyrivibrio fibrisolvens.Curr. Microbiol.25, 297–303 (1992a).
Williams A.G., Withers S.E.: The regulation of xylanolytic enzyme formation byButyrivibrio fibrisolvens NCFB 2249.Lett. Appl. Microbiol.14, 194–198 (1992b).
Wong C., Sridhara S., Bardwell J.C.A., Jakob U.: Heating greatly speeds Coomassie Blue staining and destaining.Biotechniques28, 426–432 (2000).
Wong K.K.Y., Tan L.U.L., Saddler J.N.: Multiplicity of β-1,4-xylanase in microorganisms: functions and applications.Microbiol. Rev.52, 305–317 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zorec, M., Čepeljnik, T., Nekrep, F.V. et al. Multiple endoxylanases ofButyrivibrio sp.. Folia Microbiol 46, 94–96 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02825897
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02825897