Abstract
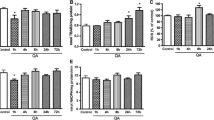
The excitatory amino acids (EAA) are involved in the pathogenesis of the cerebral ischemia. Moreover, several investigators have demonstrated that a considerable amount of dopamine (DA) is released in the striatum after ischemia reperfusion/insult (IRI). Recently, studies have demonstrated in vitro, that D-2 agonist, at the level of striatum and retina, may represent a powerful signal to inhibit release of excitatory amino acids implicated in cerebral ischemia. Therefore we have been incited to test, in vivo, the action of a D-2 agonist, piribedil, on gerbil brain after IRI. We have used the Stroke Index (SI); then to precise the mechanism of action, we have determined the levels of dopamine, EAA, and hydroxyl-free radicals (·OH), in striatum, hippocampus, and hemisphere. Piribedil, administered at dose of 10 mg/kg, per os, 60 min before induction of transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils, presents a neuroprotective effect, as measured by SI and significantly reverses the increase of DA, EAA, and ·OH induced by IRI. The mechanism of action of piribedil could be related to its D-2 agonist property.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama Y., Ito A, Koshimura K, Ohue T., Yagamata S., Miwa S., and Kikuchi H. (1991) Effects of transient forebrain ischemia and reperfusion on function of dopaminergic neurons and dopamine reuptake in vivo in rat striatum.Brain Res. 561, 120–127.
Baker A. J., Zornow M. H., Scheller M. S., Yaksh T. L., Skilling S. R., Smullin D. H., Larson A. A., and Kuczenski R. (1991) Changes in extracellular concentrations of glutamate, aspartate, glycine, dopamine, serotonin, and dopamine metabolites after transient global ischemia in the rat brain.J Neurochem. 57, 1370–1379.
Cao W., Carney J. M., Duchon A., Floyd R. A., and Chevion M. (1988) Oxygen free radical involvement in ischemia and reperfusion injury to brain.Neurosci. Lett. 88, 233–238.
Carney J. M., Starke-Reed P. E., Oliver C. N., Landum R. W., Cheng M. S., Wu J. F., and Floyd R. A. (1991) Reversal of age-related increase in brain protein oxidation, increase in enzyme activity, and loss in temporal and spatial memory by chronic administration of the spin-trapping compoundN-tert-butyl-α-phenylnitrone.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 88, 3633–3636.
Chang C. J., Ishii H., Yamamoto H., and Spatz M. (1993) Effects of cerebral ischemia on regional dopamine release and D-1 and D-2 receptors.J. Neurochem. 60, 1483–1490.
Chiueh C. C., Miyake H, and Peng M-T. (1993) Role of dopamine autoxidation, hydroxyl radical generation, and calcium overload in under lying mechanisms involved in MPTP-Induced parkinsonism, inAdvances in Neurology, vol. 60 (Narabayashi H., ed.), pp. 251–257, Raven, New York.
Delbarre G., Delbarre B., and Barrau Y. (1988) A suitable method to select gerbils with incomplete circle of Willis.Stroke 19, 126.
Delbarre B., Delbarre G., and Calinon F. (1992) Free radicals, glutamate, dopamine, and serotonin after ischemia reperfusion insult (IRI) in aging gerbil brain.Drug Dev. Res. 26, 1992.
Demopoulos H. B. (1973) The basis of the free radical pathology.Fed. Proc. 32, 1859–1861.
Floyd R. A. (1990) Role of oxygen free radicals in carcinogenesis and brain ischemia.FASEB J 4, 2587–2597.
Floyd R. A., Henderson R., Watson J. J., and Wong P. K. (1986) Use of salicylate with high pressure liquid chromatography and electrochemical detection (LCED) as a sensitive measure of hydroxyl free radicals in adriamycin treated rats.Free Radicals Biol. Med. 2, 13–18.
Ginsberg M. D., Graham D. I., and Busto R. (1985) Regional glucose utilization and blood flow following graded forebrain ischemia in the rat: correlation with neuropathology.Ann. Neurol. 18, 470–481.
Globus M. Y. T., Busto R., Dietrich W. D., Martinez E., Valdes I., and Ginsberg M. D. (1988) Effect of ischemia on the in vivo release of striatal dopamine, glutamate, and γ-aminobutyric acid studied by intracerebral microdialysis.J. Neurochem. 51, 1455–1464.
Granger D. N., Rutili G., and McCord J. M. (1981) Superoxide radicals in feline intestinal ischemia.Gastroenterology 81, 22–29.
Granger D. N., McCord J. M., Parks D. A., and Hollwarth M. E. (1986) Xanthine oxidase inhibitors attenuate ischemia-induced vascular permeability changes in the cat intestine.Gastroenterology 90, 80–84.
Hadberg H., Andersson P., Kjellmer I., Thiringer K., and Thordstein M. (1987) Extracellular overflow of glutamate, aspartate, GABA and taurine in the cortex and basal ganglia of fetal lambs during hypoxia-ischemia.Neurosci. Lett. 78, 311–317.
Hansson R., Gustafsson B., Jonsson O., Lundstom S., Petterson S., Schersten T. and Waldenstrom J. (1982) Effect of xanthine oxidase inhibition on renal circulation after ischemia.Transplant. Proc. 14, 51–58.
Kim J. S., Kornhuber H. H., Schmid-Burgk W., and Holzmuller B. (1980) Low cerebrospinal fluid glutamate in schizophrenic patients and a new hypothesis on schizophrenia.Neurosci. Lett. 20, 379–382.
Kornhuber J. and Kornhuber M. E. (1986) Presynaptic dopaminergic modulation of cortical input to the striatum.Life Sci. 39, 669–674.
Leach M. J., Swan J. H., Eisenthal D., Dopson M., and Nobbs M. (1993) BW619C89, a glutamate release inhibitor, protects against focal cerebral ischemic damage.Stroke 24, 1063–1067.
MacGraw C. P. (1977) Experimental cerebral infarction effects of pentobarbital in mongolian gerbils.Arch. Neurol. 34, 334–336.
Makwell M. A. K., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., and Tolbert N. E. (1978) A modification of the Lowry procedures to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples.Anal. Biochem. 87, 206–210.
Maura G., Giardi A., and Raiteri M. (1988) Release-regulating D-2 dopamine receptors are located on striatal glutamatergic nerve terminals.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 247–252, 680–684.
Maura G., Carbone R., and Raiteri M. (1989) Aspartate-releasing nerve terminals in rat striatum possess D-2 dopamine receptors mediating inhibition of release.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 251–253, 1142–1146.
Meldrum B. (1990) Protection against ischaemic neuronal damage by drugs acting on excitatory neurotransmission.Cerebrovasc. Brain Metab. Rev. 2, 27–57.
Olney J. W. (1989) Excitotoxicity and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.Drug Dev. Res. 17, 299–319.
Pulsinelli W. A., Brierley J. B., and Plum F. (1982) Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia.Ann. Neurol. 11, 491–498.
Rips R. and Morier E. (1986) Automatic assay of biogenic amines and their metabolites in mice using high pressure liquid chromatography and electrochemical detection LCED.Prog. in HPLC 2, 375–394.
Rothman S. V. and Olney J. W. (1987) Excitotoxicity and the NMDA receptor.Trends Neurol. Sci. 10, 7.
Seeman P. (1980) Brain dopamine receptors.Pharmacol. Rev. 32, 229–313.
Siesjo B. K. (1984) Cerebral circulation and metabolism.J. Neurosurg. 60, 883–908.
Slivka A. and Cohen G. (1985) Hydroxyl radical attack on dopamine.J. Biol. Chem. 260, 15,466–15,472.
Slivka A., Brannan T. S., Weinberger J., Knott P. J., and Cohen G. (1988) Increase in extracellular dopamine in the striatum during cerebral ischemia: a study utilizing cerebral microdialysis.J. Neurochem. 50, 1714–1718.
Smith M. L., Aller R. N., and Siesjo B. K. (1984) The density and distribution of ischemic brain injury in the rat following 2–10 min. of forebrain ischemia.Acta Neuropathol. 64, 319–332.
Upchurch M. (1985) Evidence for species differences between rats and gerbils in striatal dopamine content and dopamine metabolism.Neurosci. Lett. 59–61. 59–163.
Xu X., L’Helgoualc’h A., Morier-Teissier E., and Rips R. (1986) Determination of γ-aminobutyric acid in the mouse hypothalamus and hippocampus using liquid chromatography/electrochemistryJ. Liquid Chromatogr. 9–10, 2253–2267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delbarre, B., Delbarre, G., Rochat, C. et al. Effect of piribedil, a D-2 dopaminergic agonist, on dopamine, amino acids, and free radicals in gerbil brain after cerebral ischemia. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 26, 43–52 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814940
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814940