Abstract
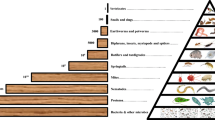
Studies on the ecotoxicology of soil organisms have led to the revision of views on the trophic structure of ecosystems. It was found that the microbial link is obligatory and controls the migration of toxicants and their effects in the food chain. Differences in effects are accounted for by both the physiological stability of organisms and their affliation with relatively independent and biogeochemically closed ecosystems differing in their spatiotemporal scales. The latter form a hierarchical three-level structure: ecosystems of unicellular organisms—ecosystems of small multicellular organisms—the ecosystem of large multicellular organisms, or of biogeocenosis. Trophic networks within the structure are united by ecosystemophagy as the type of feeding of large multicellular organisms, and this accounts for the importance of the latter as indicators of long-term changes in a biogeocenosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho, P.E., Seidler, R.J., Evans, H.J., and Raju, P.N., Distribution, Enumeration, and Identification of Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria Associated with Decay in Living White Fir Trees,Phytopathology, 1974, vol. 64, pp. 1413–1420.
Alexander, M.,Introduction in Soil Microbiology, New York: Wiley, 1977, 2nd ed.
Barber, S.A.,Biologischeskaya dostupnost' pitatel'nykh veshchestv v pochve (Biological Accessibility of Nutrients in the Soil), Moscow: Agropromizdat, 1988.
Barnes, R.S.K., Calow, P., and Olive, P.J.W.,The Invertebrates, Oxford: Blackwell, 1988.
Bengtsson, G., Dispersal, Heterogeneity, and Resistance: Challenging Soil Quality Assessment, in:Ecological Risk: Assessment of Contaminants in Soil, London: Chapman and Hall, 1997, pp. 191–212.
Bengtsson, G., Gunnarsson, T., and Rundgren, S., Growth Changes Caused by Metal Uptake in a Population ofOnichiurus armatus (Collembola) Feeding on Metal Pollution Fungi,Oikos, 1983, vol. 40, pp. 216–225.
Bengtsson, G., Ohlsson, L., and Rundgren, S., Influence of Fungi on Growth and Survival ofOnychiurus armatus (Collembola) in a Metal Polluted Soil,Oecologia, 1985, vol. 68, pp. 63–68.
Bengtsson, G., Gunnarsson, T., and Rundgren, S., Effects of Metal Pollution on EarthwormDendrobaena rubida (Sav.) in Acidified Soil.Water, Air, Soil Pollut., 1986, vol. 28, pp. 361–383.
Blanchette, R.A. and Shaw, C.G., Assotiations among Bacteria, Yeasts, and Basidiomycetes during Wood Decay.Phytopathology, 1978, vol. 65, pp. 631–637.
Byazrov, L.G., Medvedev, L.N., and Chernova, N.M., Lichen Consortia in Broadleaved-Coniferous Forests of the Moscow Region, inBiogeotsenotischeskie issledovaniya v shirokolistvenno-khvoinykh lesakh (Biocenological Studies in Broadleaved-Coniferous Forests), Moscow: Nauka, 1971, pp. 252–272.
Byzov, B.A., Kurakov, A.V., Tretyakova, E.V., Thanh, V.N., Luu, N.D.T., and Rabinovich, Y.M., Principles of the Digestion of Microorganisms in the Gut of Soil Millipedes: Specificity and Possible Mechanisms.Appl. Soil Ecol., 1999, vol. 9, pp. 145–151.
Coughtrey, P.J., Martin, M.H., Chard, J., and Shales, S.W., Microorganisms and Metal Retention in the WoodlouseOniscus assellus, Soil Biol. Biochem, 1980, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 23–27.
Cummins, K.W., Structure and Function of Stream Ecosystems.BioScience, 1974, vol. 24, pp. 631–641.
Dix, N.J. and Webster, J.,Fungal Ecology, London: Chapman and Hall, 1995.
Eijsackers, H., Ecotoxicology of Soil Organisms: Seeking the Way in a Pitch Dark Labyrinth, inEcotoxicology of Soil Organisms, Boca Raton: Lewis, 1994, pp. 3–32.
Faber, J.H., Functional Classification of Soil Fauna: A New Approach.Oikos, 1991, vol. 62, pp. 110–117.
Fagerström, T., Biomagnification in Food Chains and Related Concepts.Oikos, 1991, vol. 62, pp. 257–260.
Fermor, T.R. and Wood, D.A., Degradation of Bacteria byAgaricus bisporus and Other Fungi.J. Gen. Microbiol., 1981, vol. 126, pp. 377–387.
Gilyarov, M.S., The Ratio of Size and Number of Soil Invertebrates,Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1944, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 283–285.
Gilyarov, M.S.,Zoologicheskii metod diagnostiki pochv (A Zoological Method of Soil Diagnosis), Moscow: Nauka, 1965.
Guzev, V.S., Levin, S.V., and Bab'eva, I.P., Heavy Metals as a Factor Affecting the Microbial System of Soils, inEkologicheskaya rol'mikrobnykh metabolitov (The Ecological Role of Microbial Metabolites), Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1986, pp. 82–104.
Hopkin, S.P.,Ecophysiology of Metals in Terrestrial Invertebrates, London: Elsevier, 1989.
Hyvönen, R. and Persson, T., Effects of Fungivorous and Predatory Arthropods on Nematodes and Tardigrades in Microcosms with Coniferous Forest Soil,Biol. Fertil. Soils, 1987, vol. 21, pp. 121–127.
Klein, S., Transformation Reactions of Selected Heavy Metals (Hg and Sn),Spurenelement-Symp. New Trace Element. Leipzig, Jena: Karl Marx Univ. Verlag, 1986, pp. 1099–1110.
Krivolutskii, D.A.,Pochvennaya fauna v ekologicheskom kontrole (The Soil Fauna in Ecological Control), Moscow: Nauka, 1994.
Krivolutskii, D.A. and Pokarzhevskii, A.D., The Microbial Link in Trophic Chains.Ekologiya, 1988, no. 5, pp. 10–20.
Marinussen, M., Heavy Metal Accumulation in Earthworms Exposed to Spatially Variable Soil Contamination,Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen: Agricultural University, 1997.
Moore, J.C., Walter, D.E., and Hunt, H.W., Arthropod Regulation on Micro- and Mesobiota in Below-Ground Detritial Food Webs.Ann. Rev. Entomol., 1988, vol. 33, pp. 419–439.
Müller, E. and Loeffler, W.,Mykologie, Stuttgart: G Thieme, 1971, 2 Aufl. Translated under the titleMikologiya (Mycology), Moscow: Mir, 1995.
O'Neill, R.V., De Angelis, D.L., Wajde, J.B., and Allen, T.F.N.,A Hierarchical Concept of Ecosystems, Princeton: Princeton Univ. Press, 1986.
Pokarzhevskii, A.D.,Geokhimicheskaya ekologiya nazemnykh zhivotnykh (The Geochemical Ecology of Terrestrial Vertebrates), Moscow: Nauka, 1985.
Pokarzhevskii, A.D., The Problem of Scale in Bioindication of Soil Contamination,Bioindicator System of Soil Pollution, Dordrecht: Kluwer, 1996, pp. 111–121.
Pokarzhevskii, A.D. and Usachev, V.L., Animals and Migration of Artificial Radionuclides in Natural Ecosystems, inEkologicheskie posledstviya radioaktivnogo zagryazneniya na Yuzhnom Urale (Ecological Consequences of Radioactive Contamination in the Southern Urals), Moscow: Nauka, 1993, pp. 48–67.
Pokarzhevskii, A.D. and Van Straalen, N.M., A Multielement View on Heavy Metal Biomagnification.Appl. Soil Ecol., 1996, vol. 3, pp. 95–98.
Pokarzhevskii, A.D., Panikov, N.S., Krivolutskii, D.A., and Zaboev, D.P., The Role of Microorganisms, Plants, and Animals in the Biological Cycle of Terrestrial Ecosystems,Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1992, vol. 322, no. 4, pp. 809–812.
Pokarzhevskii, A.D., Zaboyev, D.P., Ganin, G.N., and Gordienko, S.A., Amino Acids in Earthworms: Are Earthworms Ecosystemivorous?,Soil Biol. Biochem., 1997, vol. 29, pp. 559–567.
Pokarzhevskii, A.D., Van Straalen, N.M., Butovsky, R.O., Verhoef, S.C., and Filimonova, Z.V., The Use of Detritial Food-Webs to Predict Ecotoxicological Effects of Heavy Metals,Pollution-Induced Changes in Soil Invertebrate Food Webs, Amsterdam: Frije Universiteil Verl., 1988, pp. 9–30.
Root, R.F., The Niche Exploitation Pattern of the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher,Ecol. Monogr., 1967, vol. 37, pp. 317–350.
Römbke, J. and Moltmann, J.F.,Applied Ecotoxicology, Boca Raton: Lewis, 1995.
Santhos, P.F., Phillips, J., and Witford, W.G., The Role of Mites and Nematodes in Early Stages of Buried Litter Decomposition in a Desert.Ecology, 1981, vol. 62, pp. 664–669.
Simkiss, K. and Watkins, B. The Influence of Gut Microorganisms on Zinc Uptake inHelix aspersa, Environ. Pollut., 1990, vol. 66, no. 3, pp. 263–271.
Sukachev, V.N., Main Concepts of Forest Biocenology, inOsnovy lesnoi biogeotsenologii (Fundamentals of Forest Biocenology), Moscow: Nauka, 1964, pp. 5–49.
Tansley, A.G., The Use and Abuse of Vegetational Concepts and Terms,Ecology, 1935, vol. 16, pp. 284–307.
Trihaut, R., Ecotoxicology: A New Branch of Toxicology, inEcological Toxicological Research, New York: Plenum, 1975, pp. 3–24.
Tseitlin, V.B. and Byzova, Yu.B., Size Distribution of Soil Organisms in Different Natural Zones,Zh. Obshch. Biol., 1986, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 193–197.
Van Straalen, N.M. and Løkke, H., Ecological Approaches in Soil Ecotoxicology, inEcological Risk: Assessment of Contaminants in Soil, London: Chapman and Hall, 1997, pp. 3–21.
Vorobeichik, E.L., Sadykov, O.F., and Farafontov, M.G.,Ekologicheskoe normirovanie tekhnogennykh zagryaznenii nazemnykh ekosistem (Setting Ecological Norms for Technogenic Pollution of Terrestrial Ecosystems), Yekaterinburg: Nauka, 1994.
Vrednye khimicheskie veshchestva. Neorganicheskie soedineniya elementov I–IV grupp (Harmful Chemical Substances: Inorganic Compounds of Elements Belonging to Groups I–IV), Moscow: Khimiya, 1988.
Vrednye khimicheskie veshchestva. Neorganicheskie soedineniya elementov V–VIII grupp (Harmful Chemical Substances: Inorganic Compounds of Elements Belonging to Groups V–VIII), Moscow: Khimiya, 1989.
Walker, C.H., Hopkin, S.P., Sibly, R.M., and Peakall, D.B.,Principles of Ecotoxicology, London: Taylor and Francis, 1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pokarzhevskii, A.D., Van Straalen, N.M., Filimonova, Z.V. et al. Trophic structure of ecosystems and ecotoxicology of soil organisms. Russ J Ecol 31, 190–197 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02762820
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02762820