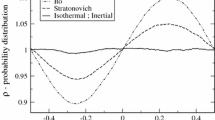
Abstract
The motion of a Brownian particle in the presence of a deformable interface is studied by considering the random distortions of interface shape due to spontaneous thermal impulses from the surrounding fluid. The fluctuation-dissipation theorem is derived for the spontaneous fluctuations of interface shape using the method of normal modes in conjunction with a Langevin type equation of motion for a Brownian particle, in which the fluctuating force arises from the continuum motions induced near the particle by the fluctuation of interface shape. The analysis results in the prediction of autocorrelation functions for the location of the dividing surface, for the random force acting on the particle, and for the particle velocity. The particle velocity correlation, in turn, yields the effective diffusion coefficient due to random fluctuations of the interface shape.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batchelor, G. K., “Developments in Microhydrodynamics”, In Theoretical and Applied Mechanics”, ed. W. Koiter, Amsterdam, Netherlands (1976).
Brenner, H. and Leal, L. G., “A Model of Surface Diffusion on Solids”,J Colloid Interface Sci.,62, 238 (1977).
Brenner, H. and Leal, L. G., “Conservation and Constitutive Equations for Adsorbed Species Undergoing Surface Diffusion and Convection at a Fluid-Fluid Interface”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,88, 136 (1982).
Buff, F. P., Lovett, R. A. and Stillinger, F. H., “Interfacial Density Profile for Fluids in the Critical Region”,Phys. Rev Lett,15, 621 (1965).
Chaplin, J. R., “Nonlinear Forces on a Horizontal Cylinder beneath Waves”,J Fluid Mech.,147, 449 (1984).
Evans, R., “The Role of Capillary Wave Fluctuations in Determining the Liquid-Vapor Interface”,Mol. Phys.,42, 1169 (1981).
Gotoh, T. and Kaneda, Y., “Effect of an Infinite Plane Wall on the Motion of a Spherical Brownian Particle”,J. Chem. Phys.,76, 3193 (1982).
Hauge, E. H. and Martin-Löf, A., “Fluctuating Hydrodynamics and Brownian Motion”,J Stat. Phys.,7, 259 (1973).
Hinch, E. J., “Application of the Langevin Equation to Fluid Suspensions”,J. Fluid Mech.,72, 499 (1975).
Jhon, M. S., Desai, R. C. and Dahler, J. S., “The Origin of Surface Wave”,J. Chem. Phys.,68, 5615 (1978).
Kreuzer, H. J., “Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics and its Statistical Foundations”, Oxford University Press, Oxford (1984).
Lamb, H., “Hydrodynamics”, Dover, New York, N.Y. (1932).
Landau, L. D. and Lifshitz, E. M., “Fluid Mechanics”, Pergamon Press, New York, N.Y. (1959).
Landau, L. D. and Lifshitz, E. M., “Statistical Physics. Part I”, Pergamon Press, New York, N.Y. (1980).
Lee, S. H., Chadwick, R. S. and Leal, L. G., “Motion of a Sphere in the Presence of a Plane Interface. Part 1. An Approximation Solution by Generalization of the Method of Lorentz”,J Fluid Mech.,93, 705(1979).
Lee, S. H. and Leal, L. G., “Motion of a Sphere in the Presence of a Plane Interface. Part 2. An Exact Solution in Bipolar Coordinates”,J. Fluid Mech.,98, 193 (1980).
Squire, H. B., “On the Stability for Three-Dimensional Disturbances of Viscous Fluid Flow between Parallel Walls”,Proc. Roy. Soc. London,A142, 621 (1933).
Teletzke, G. F., Scriven, L. E. and Davis, H. T., “Gradient Theory of Wetting Transitions”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,87, 550 (1982).
Whitham, G. B., “Linear and Nonlinear Waves”, Wiley-Interscience, New York, N.Y. (1974).
Yang, S.-M. and Leal, L. G., “Particle Motion in Stokes Flow near a Plane Fluid-Fluid Interface. Part 1. Slender Body in a Quiescent Fluid”,J.Fluid Mech.,136, 393 (1983).
Yang, S.-M. and Leal, L. G., “Particle Motion in Stokes Flow near a Plane Fluid-Fluid Interface. Part 2. Linear Shear and Axisymmetric Straining Flows”,J Fluid Mech.,149, 275 (1984).
Yang, S.-M., “Motions of a Sphere in a Time-Dependent Stokes Flow: A Generalization of Faxén’s Law”,KJChE,4(1), 15 (1987).
Yang, S.-M. and Hong, W.-H., “Brownian Diffusion near a Plane Fluid Interface”,KJChE,4, 187(1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, SM. Particle motions induced by capillary fluctuations of a fluid-fluid interface. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 12, 331–339 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705765
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705765