Abstract
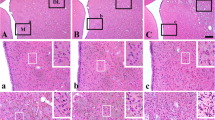
This study investigated the effect of intra-ischemic hypothermia on astroglial reactions in the hippocampus following cerebral ischemia. Mongolian gerbils were subjected to forebrain ischemia by bilateral carotid occlusion of 10 min at a) 30°C and b) 37°C followed by normothermic reperfusion ranging from 1 to 3 days (d). The astrocytes were visualized by immunostaining against glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and neuronal injury was evaluated by using hematoxylin-eosin staining. In normothermic brains, reactive astrocytosis was noted in 1 and 2 d postischemic animals, becoming prominent in the 3 d postischemic group. Intense GFAP-positive cells with thickened processes were noted in all regions of the hippocampus, especially the CA1 region. These cells were seen to have migrated toward the stratum pyramidale which was normally devoid of such staining. Hypothermia significantly inhibited the GFAP-upregulation seen 3 d after normothermic ischemia. There was no significant neuronal damage in the 3 d hypothermic ischemic group. Since glial cell activation, as evidenced by GFAP-upregulation, precedes as well as accompanies neuronal damage, and since hypothermia, known to be neuroprotective, inhibits glial cell activation in the 3 d postischemic brain, it appears that glial cells play critical roles in neuronal survival or death following ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araki, T., Kato, H., and Kogure, K. (1989). Selective neuronal vulnerability following transient cerebral ischemia in the gerbil: distribution and time course.Acta. Neurol. Scand. 80:548–553.
Baker, A.J., Zornow, M.H., Grafe, M.R., Scheller, M.S., Skilling, S.R., Smullin, D.H., and Larson, A.A. (1991). Hypothermia prevents ischemia-induced increases in hippocampal glycine concentrations in rabbits.Stroke 22:666–673.
Benveniste, H., Drejer, J., Schousboe, A., and Diemer, N.H. (1984). Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis.J. Neurochem.,43:1369–1374.
Busto, R., Globus, M.Y.-T., Dietrich, W.D., Martinez, E., Valdes, I., and Ginsberg, M.D. (1989). Effect of mild hypothermia on ischemia induced release of neurotransmitters and free fatty acids in rat brains.Stroke 20:904–910.
Choi, D.W. (1990). Cerebral hypoxia: some new approaches and unanswered questions.J. Neurosci. 10:2493–2501.
Colbourne, F. and Corbertt, D. (1994). Delayed and prolonged post-ischemic hypothermia is neuroprotective in the gerbil.Brain Res. 654:265–272.
Currie, D.N., and Kelly, J.S. (1981). Glial versus neuronal uptake of glutamate.J. Exp. Biol. 95: 181–193.
DeLeo, J., Toth, L., Schubert, P., Rudolphi, K., and Kreutzberg, G.W. (1987). Ischemia-induced neuronal cell death, calcium accumulation, and glial response in the hippocampus of the mongolian gerbil and protection by propentofylline (HWA 285),J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 7:745–751.
Dietrich, W.D., Busto, R., Alonso, O., Globus, M.Y.-T., and Ginsberg, M.D. (1993). Intraischemic but not postischemic brain hypothermia protects chronically following global forebrain ischemia in rats.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 13:541–549
Duffy, P.E. (1983).Astrocytes: Normal, Reactive, and Neoplastic. Raven Press, New York, pp. 39–44.
Gehrmann, J., Bonnekoh, P., Miyazawa, T., Hossmann, K.-A., and Kreutzberg, G.W. (1992) Immunocytochemical study of an early microglial activation in ischemia.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 12:257–269.
Ginsberg, M.D., Sternau, L.L., Globus, M.Y.-T., Dietrich, D.W., and Busto, R. (1992). Therapeutic modulation of brain temperature: Relevance to ischemic brain injury.Cerebravasc. Brain Metab. Rev. 4:189–225.
Giulian, D. (1993). Reactive glia as rivals in regulating neuronal survival.Glia 7:102–110.
Kato, H., Kogure, K., Araki, T. and Itoyama, Y. (1994). Astrological and microglial reactions in the gerbil hippocampus with induced ischemic tolerance.Brain Res. 664:69–76.
Kirino, T. (1982). Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia.Brain Res 239:57–69.
Kitamura, T., Nakanishi, K., Watanabe, S., Endo, Y., and Fujita, S. (1987). GFA-protein gene expression on the astroglia in cow and rat brains.Brain Res. 423:189–195.
Kumar, K., Wu, X.L., Evans, A.T., and Marcoux, F. (1995). Effect of hypothermia on induction of heat shockprotein-72 in ischemic brain.Metab. Brain Dis. 10:283–291.
Marty, S., Dusart, I., and Peschanski, M. (1991). Glial changes following an excitotoxic lesion in the CNS. I. Microglia/macrophages.Neuroscience 45:529–539.
Miyake, T., Hattori, T., Fukuda, M., and Kitamura, T. (1989). Reactions of S-100-positive glia after injury of mouse cerebral cortex.Brain Res. 489:31–40.
Nicholls, D., and Attwell, D. (1990). The release and uptake of excitatory amino acids.Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 11:462–468.
Ordy, J.M., Wengenack, T.M., Pialobok, P., Coleman, P.D., Rodier, P., Baggs, R.B., Dunlap, W.P., and Kates, B., (1993). Selective vulnerability, and early progression of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell degeneration and GFAP-positive astrocyte reactivity in the rat four-vessel occulsion model of transient global ischemia.Exp Neurol. 119:128–139.
Petito, C.K., and Babiak, T. (1982). Early proliferative changes in astrocytes in postischemic nonfareted rat brain.Ann Neurol 11:510–518.
Petito, C.K., and Chung, M., Halaby, I.A. and Cooper A.J.L. (1992). Influence of the neuronal environment on the pattern of reactive astrocytosis following cerebral ischemia.Prog. Brain Res. 94:381–387.
Petito, C.K., Morgello, S., Felix, J.C., and Lesser, M.L. (1990). The two patterns of reactive astrocytosis in postischemic rat brain.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 10:850–859.
Pulsinelli, W.A., Brierley, J.B., and Plum F. (1982). Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia.Ann. Neurol. 11:491–498.
Raichle, M.E. (1983). The pathophysiology of brain ischemia.Ann. Neurol. 13:2–10.
Rothman, S.M., and Olney, J.W. (1986). Glutamate and pathophysiology of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.Ann. Neurol. 19:105–111.
Schmidt-Kastner, R., and Freund, T.F. (1991). Selective vulnerability, of the hippocampus in brain ischemia.Neuroscience 40:599–636.
Schmidt-Kastner, R., Szymas, J., and Hossmann, K.-A. (1990). Immunohistochemical study of glial reaction and serum-protein extravasation in relation to neuronal damage in rat hippocampus after ischema.Neuroscience 38:527–540.
Tanaka, H., Masasuke, A., and Masuzawa, T. (1992). Reaction of astrocytes in the gerbil hippocampus following transient ischemia: immunohistochemical observations with antibodies against glial fibrillary acidic protein, glutamine synthetase, and S-1000 protein.Exp. Neurol. 116:264–274.
Walz, W. (1989). Role of glial cells in the regulation of the brain ion microenvironment.Prog Neurobiol. 33:306–333.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, K., Wu, X. & Evans, A.T. GFAP-Immunoreactivity following hypothermic forebrain ischemia. Metab Brain Dis 12, 21–27 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02676351
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02676351