Abstract
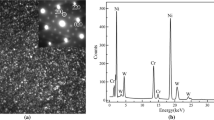
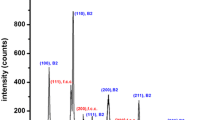
Ductile Ll2-type y′ compounds with rather high strengths and large elongations have been found in rapidly quenched Ni-Al-X (X = Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, or Si) ternary systems. The y′ compounds consist of a metastable phase which contains numerous APD with a size as small as about 50 to 75 nm. Further, the ductile y′ wires with circular cross section have been manufactured directly from the liquid state by an in-rotating-water spinning method. The wire diameter is in the range of 85 to 190 µm and the average grain size is about 2 to 5 µam. The Hv, σy, σf, and ερ of the y′ wires are about 240 to 400 DPN, 390 to 590 MPa, 580 to 910 MPa, and 4 to 10 pct, respectively, for Ni-Al- (Cr, Fe, Co, or Si) systems and about 220 DPN, 260 MPa, 440 MPa, and 27 pct, respectively, for the Ni-Al-Mn system. A cold drawing causes a significant increase in σy and σf and the attained values are about 2450 MPa and 2480 MPa, respectively, for Ni-20Al-10Cr wire drawn to about 90 pct reduction in area. Around the temperatures where the APB disappear on annealing, the Hv, σy, σf, and εgr of the y′ wires decrease significantly accompanied with a drastic change in fracture surface morphology from a transgranular type to an intergranular type. It has been therefore inferred that the high strengths and good ductility of the melt-quenched y′ compounds are due to the structural changes to a low degree of ordered state containing a high density of APB and the suppression of grain boundary segregation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. W. Guard and J. H. Westbrook:Trans. AIME, 1956, vol. 215, p. 807.
I. Ohnaka, T. Fukusako, and T. Daido:J. Japan Inst. Metals, 1981, vol. 45, p. 751.
T. Masumoto, I. Ohnaka, A. Inoue, and M. Hagiwara:Scripta Met., 1981, vol. 15, p. 293.
I. G. Butler, W. Jurz, and B. Lux:Fibre Sci. Tech., 1972, vol. 5, p. 243.
N. S. Stoloff:Strengthening Methods in Crystals, A. Kelly and R. B.Nicholson, eds., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1971, p. 193.
Metals Databook, Japan Inst. Metals, Maruzen, Tokyo, 1974, p. 156.
P.A. Flinn:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1960, vol. 218, p. 145.
A. Inoue, H. Tomioka, and T. Masumoto: unpublished research, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, 1982.
A. Inoue, H. Tomioka, T. Naohara, and T. Masumoto: unpublished research, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, 1982.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, A., Tomioka, H. & Masumoto, T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of rapidly quenched L11 alloys in Ni-Al-X systems. Metall Trans A 14, 1367–1377 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02664820
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02664820