Summary
The residual effects of lormetazepam 1 mg and 2 mg in soft gelatine capsules on driving performance were assessed and compared to those of flurazepam 30 mg, which is also a powerful hypnotic, but possesses a far less favourable pharmacokinetic profile with a longacting sedative metabolite.
Driving performance was tested 10 to 11 h and 16 to 17 h post administration, after 2 days on placebo (baseline), and 2,4 and 7 days of drug treatment (active), and after 1 and 3 days following the resumption of placebo (washout).
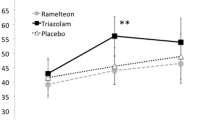
The driving test consisted of operating an instrumented motor-vehicle over a 72 km highway circuit in light traffic. Flurazepam 30 mg significantly impaired the ability to control the lateral position of the vehicle compared to placebo baseline measurements. The degree of impairment was substantial in the female subjects and was greater in the morning than in the afternoon. Lormetazepam 1 mg showed no residual effect on driving performance. Lormetazepam 2 mg impaired driving performance to some extent on the following morning, 10 to 11 h post administration, but no residual effect was found in the afternoon.
All drugs improved sleep quality and prolonged sleep duration to more or less the same extent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brookhuis KA, Borgman AE (1988) The effects of some anxiolytics on driving performance. J Drug Ther Res 13:227–231
Clayton AB (1976) The effects of psychotropic drugs upon driving- related skills. Hum Factors 18:241–252
Griffith AN, Jones DM, Richens A (1986) Zopiclone produces ef- fects on human performance similar to flurazepam, lormetaze- pare and triazolam. Br J Clin Pharmaco1 21:647–53
Hindmarch I (1976) A sub-chronic study of the subjective quality of sleep and psychological measures of performance in the morning following night-time medication with temazepam. Arzneim Forsch 26:2113–2116
Kales A, Bixler EO, Soldatos CR, Mitsky DJ, Kales JD (1982) Dose- response studies of lormetazepam: Efficacy, side-effects, and re- bound insomnia. J Clin Pharmaco1 22: 520–530
Kales A, Soldatos CR, Bixler EO, Kales JD (1983) Rebound insom- nia and rebound anxiety: a review. Pharmacology 26:121–137
Lader MH, Makin EJB, Nicholson AN (1978) Temazepam and re- lated 1,4-benzodiazepines: effects on sleep and performance. Br J Clin Pharmacol [Suppl] 8:62–68
Louwerens JW, Brookhuis KA, O’Hanlon JF (1986) Several antide- pressants’ acute effects upon actual driving performance and sub- jective mental activation. In: O’Hanlon JF, de Gier JJ (eds) Drugs and driving. Taylor and Francis, London, pp 203–213
Nicholson AN, Stone BM (1982) Hypnotic activity and effects on performance of lormetazepam and camazepam — analogues of te- mazepam. Br J Clin Pharmacol 13:433–439
Nicholson AN (1986) Hypnotics: Their place in therapeutics. Drugs 31:164–176
O’Hanlon JF, Haak TW, Blaauw GJ, Riemersma JBJ (1982) Diaze- pam impairs lateral position control in highway driving. Science 217:79–80
O’Hanlon JF (1984) Driving performance under the influence of drugs: rationale for, and application of, a new test. Br J Clin Phar- maco1 18:121S-129S
Oswald I, Adam K, Burrow S, Zdzikowski C (1979) The effects of two hypnotics on sleep subjective feelings and skilled perfor- mance. In: Passount P, Oswald I (eds) Pharmacology of the States of Alertness. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 51–63
Pierce DM, Franklin RA, Harry TVA, Nicholson AN (1984) Phar- macodynamic correlates of modified absorption: studies with lor- metazepam. Br J Clin Pharmaco1 18:31–35
Silverstone T (1974) Drugs and driving. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1: 451–454
Subhan Z, Hindmarch I (1983) The effects of lormetazepam on as- pects of sleep and early morning performance. Eur J Clin Pharma- col 25:47–51
Volkerts ER, O’Hanlon JF (1986) Hypnotics’ residual effects on driving performance. In: O’Hanlon JF, de Gier JJ (eds) Drugs and Driving. Taylor and Francis, London, Philadelphia, pp 123–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brookhuis, K.A., Volkerts, E.R. & O’Hanlon, J.F. Repeated dose effects of lormetazepam and flurazepam upon driving performance . Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39, 83–87 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02657065
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02657065